. The fungi which cause plant disease . Plant diseases; Fungi. 366 THE FUNGI WHICH CAUSE PLANT DISEASE III. Telia caulicolous, appearing on long fusiform swellings of various sized branches, numerous, scattered, or sometimes aggre- gated, cylindric, or slightly compressed, 5-10 mm. long by 0.8-1.5 mm. in diameter, acutish, or sometimes forked at the apex, brownish-yellow; teliospores 2-celled, lanceolate, 13-20 x 40-80 /x, occasionally longer, rounded or narrowed above, usually narrowed below, very slightly or not at all constricted at the septum, wall golden-yellow, thin, about 1 ju; pores 2
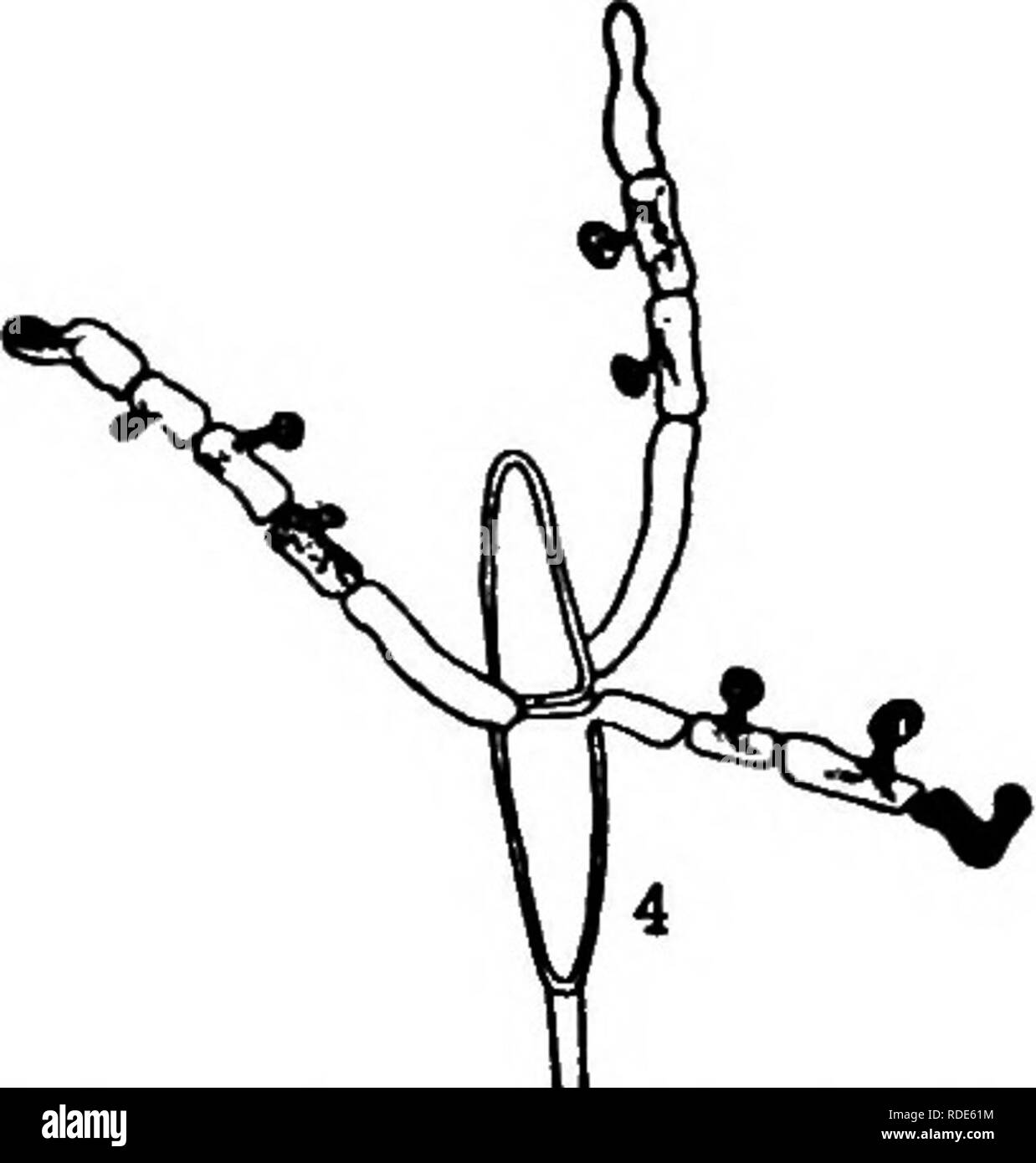
Image details
Contributor:
The Book Worm / Alamy Stock PhotoImage ID:
RDE61MFile size:
7.1 MB (116.7 KB Compressed download)Releases:
Model - no | Property - noDo I need a release?Dimensions:
1543 x 1619 px | 26.1 x 27.4 cm | 10.3 x 10.8 inches | 150dpiMore information:
This image is a public domain image, which means either that copyright has expired in the image or the copyright holder has waived their copyright. Alamy charges you a fee for access to the high resolution copy of the image.
This image could have imperfections as it’s either historical or reportage.
. The fungi which cause plant disease . Plant diseases; Fungi. 366 THE FUNGI WHICH CAUSE PLANT DISEASE III. Telia caulicolous, appearing on long fusiform swellings of various sized branches, numerous, scattered, or sometimes aggre- gated, cylindric, or slightly compressed, 5-10 mm. long by 0.8-1.5 mm. in diameter, acutish, or sometimes forked at the apex, brownish-yellow; teliospores 2-celled, lanceolate, 13-20 x 40-80 /x, occasionally longer, rounded or narrowed above, usually narrowed below, very slightly or not at all constricted at the septum, wall golden-yellow, thin, about 1 ju; pores 2 in each cell, near the sep- tum. I. ^cia on Crataegus spp., Amelanchier, Aronia, Cotoneaster, Cydonia, and Pyrus. III. Telia on Jimiperus communis, J. Fio. 266. — Gymnosporan- oxycedrus, and J. sibirica. Spindle-shaped &mtSS™'Af^ swelUngs occur on Juniper branches. Richards. Cylindric spore-masses ooze through rifts in the bark. iEciospores shed in June germinate at once on Juniper twigs and result in the following year in swellings which often later cause death. In spring the spore-masses emerge and the teliospores germinate in situ. Upon the Rosaceous hosts spots appear eight to fourteen days after infection. Kienitz-Gerloff reports the occasional formation of a germ tube instead of a promycelium. This is, however, to be regarded as an abnormal condition. G. globosum Fari. ^ "3.216.216 O. and I. .^cia chiefly hypophyllous and crowded irr^ularly or rarely in approximately annular groups 2-7 mm. across, cylin- dric, 1.5-3 mm. high by 0.1-0.2 mm. in diameter; peridium soon splitting in the upper part, becoming reticulate half way to base; peridial cells seen in both face and side views, broadly lanceolate in face view, 15-23 x 60-90 /i, linear rhomboid in side view, 13-19 m thick, outer wall about 1.5 /x thick, smooth, inner and side walls 3-5 fi, thick, rather densely rugose with ridge-like papillae of varying length; seciospores globoid or broadly ellipsoid, 15-19