Fungi, Ascomycetes, Ustilaginales, Uredinales . Fig- >79- • Phragmidium Rubi Pers.; uredosorus, x6oo; after Sappin-Trouffy; b. Phragmidiumviolaceum Wint.; uredosorus, X480; after Blackman. by paraphyses, or in certain genera (Pucciniastrum, UrcJinopsis) by a pseudo-peridium. In the young sorus a regular layer of somewhat rectangular basalcells is formed, from which the uredospore mother-cells arise. In Colco-sporitim, in Chrysomyxa, and in the secondary caeomata of Phragmidiumsubcorlicium, they are produced in vertical rows like the typical aecidiosporemother-cells and divide to form uredos
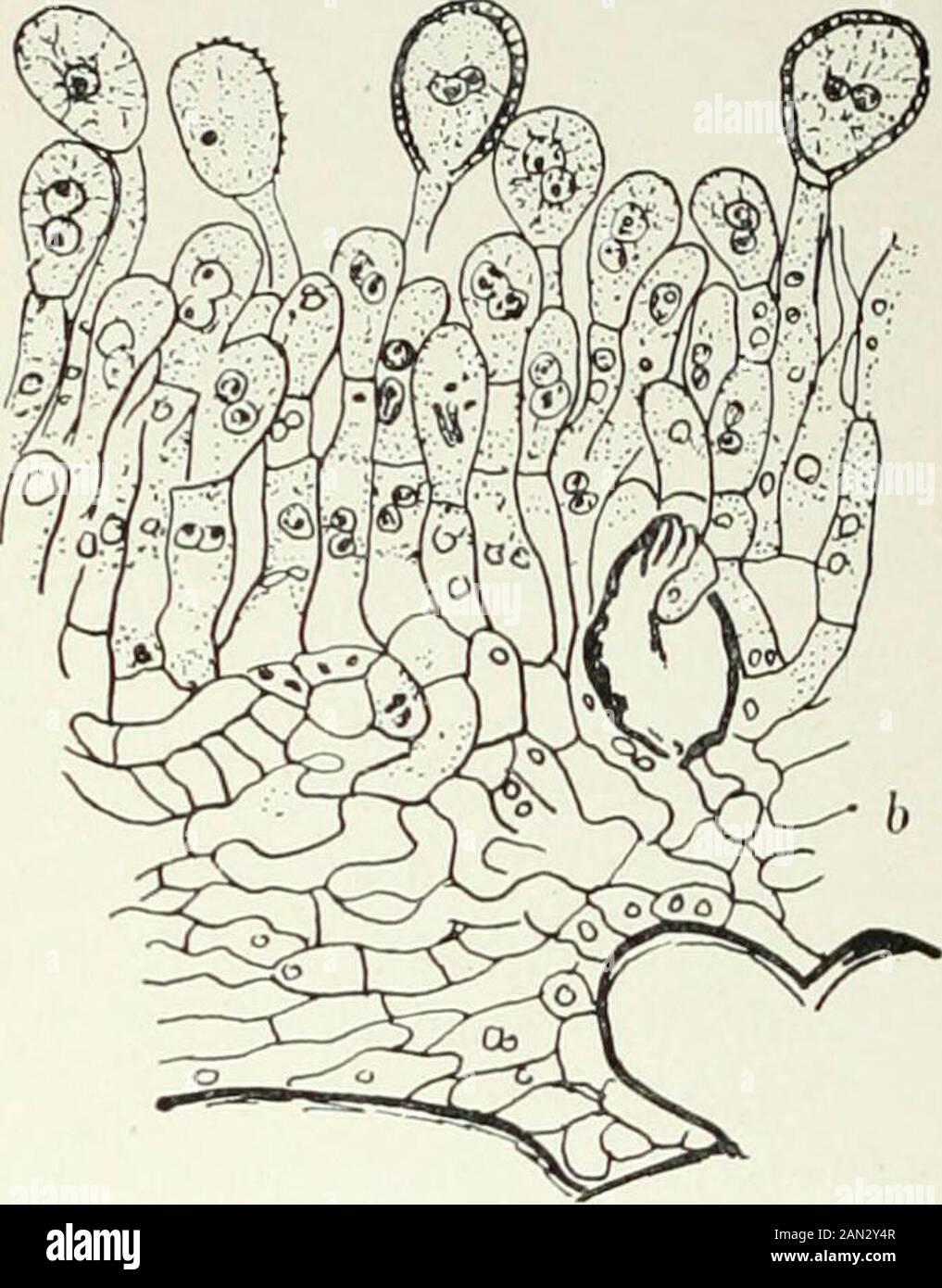
Image details
Contributor:
The Reading Room / Alamy Stock PhotoImage ID:
2AN2Y4RFile size:
7.1 MB (323 KB Compressed download)Releases:
Model - no | Property - noDo I need a release?Dimensions:
1398 x 1787 px | 23.7 x 30.3 cm | 9.3 x 11.9 inches | 150dpiMore information:
This image is a public domain image, which means either that copyright has expired in the image or the copyright holder has waived their copyright. Alamy charges you a fee for access to the high resolution copy of the image.
This image could have imperfections as it’s either historical or reportage.
Fungi, Ascomycetes, Ustilaginales, Uredinales . Fig- >79- • Phragmidium Rubi Pers.; uredosorus, x6oo; after Sappin-Trouffy; b. Phragmidiumviolaceum Wint.; uredosorus, X480; after Blackman. by paraphyses, or in certain genera (Pucciniastrum, UrcJinopsis) by a pseudo-peridium. In the young sorus a regular layer of somewhat rectangular basalcells is formed, from which the uredospore mother-cells arise. In Colco-sporitim, in Chrysomyxa, and in the secondary caeomata of Phragmidiumsubcorlicium, they are produced in vertical rows like the typical aecidiosporemother-cells and divide to form uredospores and intercalary cells, but, in the large majority of cases, they appear as a succession of buds fromdifferent parts of the basal cell. Each bud elongates, its nuclei undergoconjugate division, a stalk is cut off which grows in length but remainsnarrow, while the uredospore enlarges considerably, its contents acquire anorange or yellow colour, and its wall is variously roughened in most speciesby minute projections on the surface. Two or