. Biological structure and function; proceedings. Biochemistry; Cytology. NUCLEOTIDES AND MITOCHONDRIAL FUNCTION 237 by a slow reduction; whereas the ATP-induced reduction of DPN or flavoprotein is comparatively slow. Also the respiration is inhibited immediately after the addition of ATP. Thus the rapid inhibition of the overall electron transport by ATP appears to be reflected in the cyto- chromes. This was to be expected since cytochromes c and a are thought to be in the direct electron transport of succinate or glycerolphosphate oxidation. On the other hand, the assumed reversal of electro
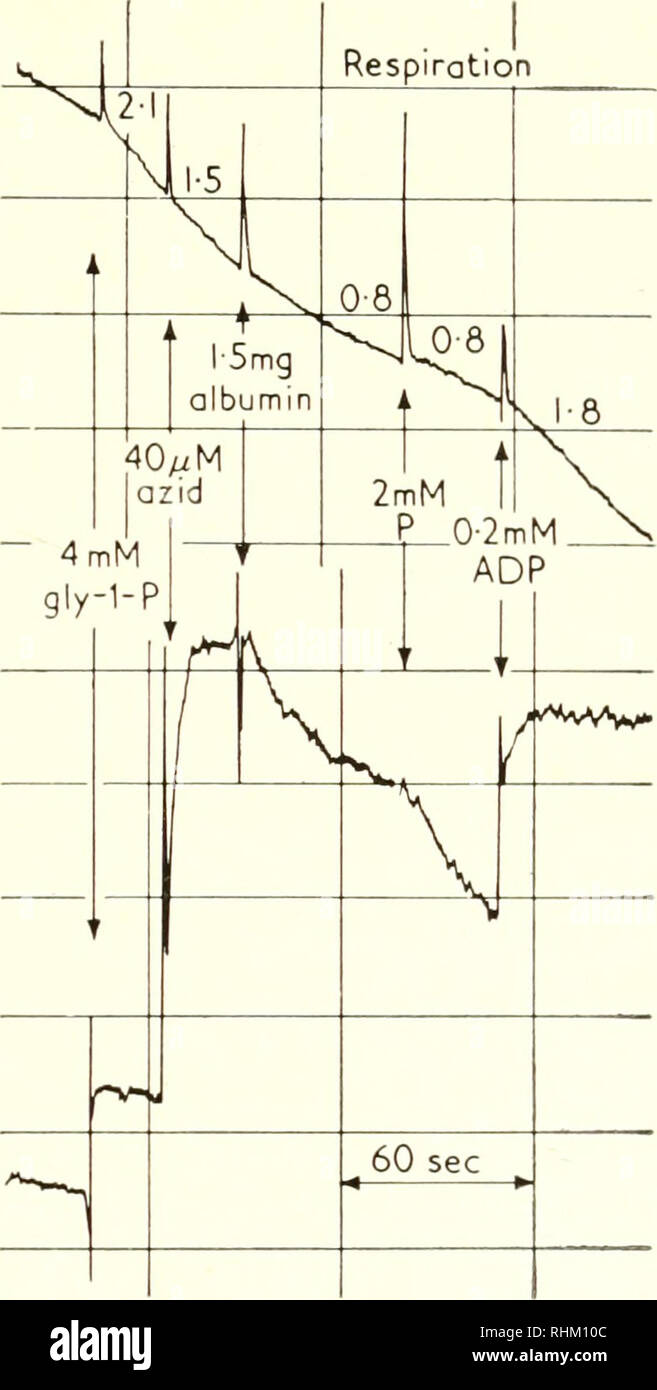
Image details
Contributor:
Library Book Collection / Alamy Stock PhotoImage ID:
RHM10CFile size:
7.1 MB (173.4 KB Compressed download)Releases:
Model - no | Property - noDo I need a release?Dimensions:
1124 x 2223 px | 19 x 37.6 cm | 7.5 x 14.8 inches | 150dpiMore information:
This image is a public domain image, which means either that copyright has expired in the image or the copyright holder has waived their copyright. Alamy charges you a fee for access to the high resolution copy of the image.
This image could have imperfections as it’s either historical or reportage.
. Biological structure and function; proceedings. Biochemistry; Cytology. NUCLEOTIDES AND MITOCHONDRIAL FUNCTION 237 by a slow reduction; whereas the ATP-induced reduction of DPN or flavoprotein is comparatively slow. Also the respiration is inhibited immediately after the addition of ATP. Thus the rapid inhibition of the overall electron transport by ATP appears to be reflected in the cyto- chromes. This was to be expected since cytochromes c and a are thought to be in the direct electron transport of succinate or glycerolphosphate oxidation. On the other hand, the assumed reversal of electron transport 400 //-atom O liter 300 200- 605- 630 m/x. /1E = 00025 Cyt a reduction Fig. 9. The effect of albumin on respiration and on the redox state of cyto- chrome a in the presence of glycerol-1-phosphate. can account for the lower velocity of the ATP-induced reduction of DPN and of flavoprotein. These components receive reducing equivalents in a reverse reaction from succinate of glycerolphosphate at a speed which may depend on the velocity of the energy supply. The parallel behaviour between cytochrome oxidation and the inhibition of respiration extends also to the effect of albumin (Fig. 9). Both the inhibition of respiration and initiation of cytochrome oxidation increase slowly after the addition of albumin. This kinetic behaviour is understandable on the grounds of the proposed mechanism of albumin action.. Please note that these images are extracted from scanned page images that may have been digitally enhanced for readability - coloration and appearance of these illustrations may not perfectly resemble the original work.. IUB/IUBS International Symposium (1st : 1960 : Stockholm); International Union of Biochemistry; International Union of Biological Sciences; Goodwin, T. W. (Trevor Walworth); Lindberg, Olov, 1914-. London, New York, Academic Press