A text-book of mycology and plant pathology . spores are small, egg-shaped orelongated, unseptate and in color pale green, or hyaline, produced inpycnidia. The most important species of this genus are Phyllostictaampelopsidis on the Virginia creeper {Ampelopsis); catalpa on catalpaleaves; labrusccB on the leaves of the grape; pavice on horse chest-nut leaves (Fig. 102); Phyllosticta solitaria E. and E. (Figs. 103 and104) is the cause of apple blotch, and vtolce on violets. The conidio- 262 MYCOL(3GY spores in Phoma are colorless and unicellular. The pycnidia areblack with a terminal pore and d
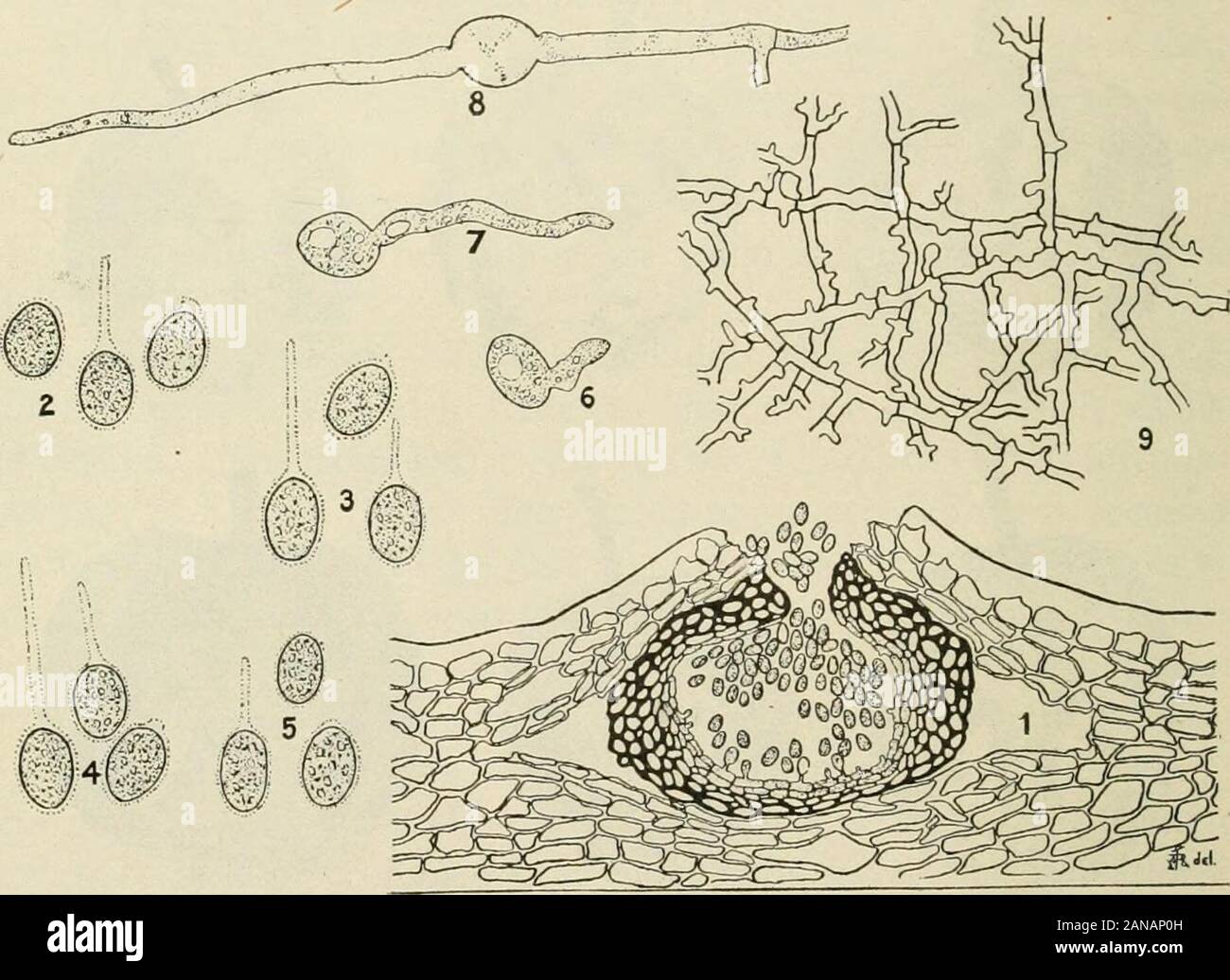
Image details
Contributor:
The Reading Room / Alamy Stock PhotoImage ID:
2ANAP0HFile size:
7.2 MB (348.7 KB Compressed download)Releases:
Model - no | Property - noDo I need a release?Dimensions:
1853 x 1349 px | 31.4 x 22.8 cm | 12.4 x 9 inches | 150dpiMore information:
This image is a public domain image, which means either that copyright has expired in the image or the copyright holder has waived their copyright. Alamy charges you a fee for access to the high resolution copy of the image.
This image could have imperfections as it’s either historical or reportage.
A text-book of mycology and plant pathology . spores are small, egg-shaped orelongated, unseptate and in color pale green, or hyaline, produced inpycnidia. The most important species of this genus are Phyllostictaampelopsidis on the Virginia creeper {Ampelopsis); catalpa on catalpaleaves; labrusccB on the leaves of the grape; pavice on horse chest-nut leaves (Fig. 102); Phyllosticta solitaria E. and E. (Figs. 103 and104) is the cause of apple blotch, and vtolce on violets. The conidio- 262 MYCOL(3GY spores in Phoma are colorless and unicellular. The pycnidia areblack with a terminal pore and depressed in the tissues of the host.The genus is arbitrarily limited to those species in which the sporesare less than 15//, for the larger spored forms have been placed in thegenus Macrophoma. The most important species from the pathologicviewpoint are out of the iioo species recognized the following: PhomabetcB is the cause of the heart rot and blight of beets. Phoma batataproduces a dry rot of sweet potato; while Phoma solani behaves much. Fig. 104.— Microscopic characters of apple blotch fungus {Phylloslicla solitaria).I, vertical section of pycnidium showing pycnospores; 2, 3, 4, 5, mature pycnospores;6, 7, 8, germinating spores; 9, mycelium. {After Scott, W M.. and Rarer, J. B., Bull.144, U. S. Bureau of Plant Industry, pi. in, March 16, 1909.) like the damping-off fungus, attacking seedling egg plants near the sur-face of the ground. The most destructive fungus of the genus Sphmrop-sis is S. malorum which causes the decay of apples, quinces and pearsand attacks the stem of the apple tree producing characteristic cankers.The genus includes about 180 species. The 150 species of the genusConiothyrium are widely spread geographically. The blight of rasp-berry canes is due to Coniothyrium Fuckelii, which has only recentlycome into prominence in the United States. The genus Septoria in- FUNGI IMPERrECTI (dEUTEROMYCETES) 263