. Nature and development of plants. Botany. 432 THE FAGALES phylls are usually developed upon the same plant. Several bracts are usually associated with sporophylls (Figs. 298, B-F; 299, B-E) so that the flowers are of a higher type than the willows. The innermost of these bracts is often of a delicate structure and has been referred to as a primitive form of the calyx (Fig. 298, B, pr) and when present in the pistillate flowers it adheres to. Fig. 298. Flowers and fruits of the birch family, order Fagales: A, in- florescence of hornbeam (Carpinus)—s, staminate ament; p, pistillate ament. B, s
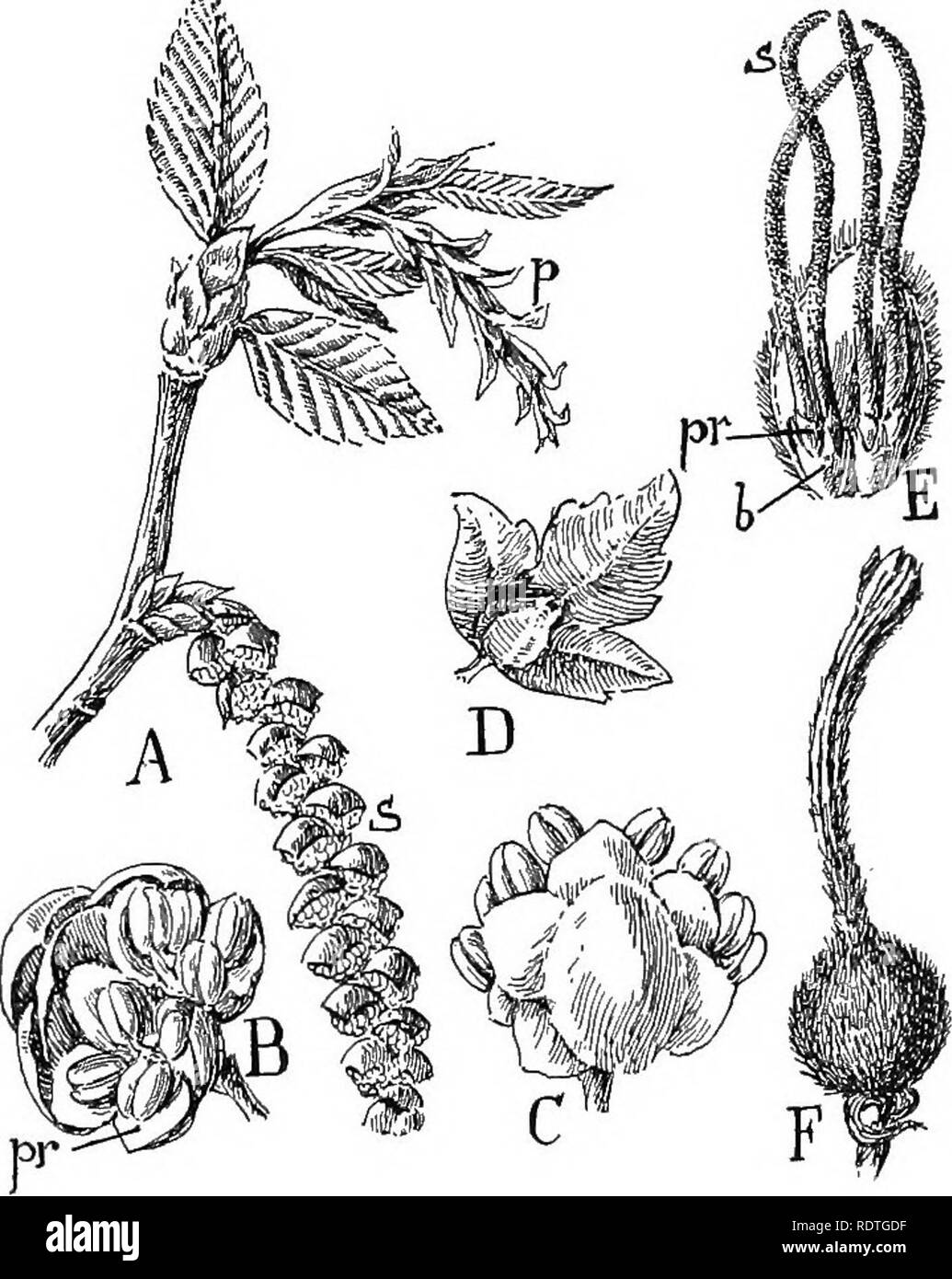
Image details
Contributor:
The Book Worm / Alamy Stock PhotoImage ID:
RDTGDFFile size:
7.1 MB (382.5 KB Compressed download)Releases:
Model - no | Property - noDo I need a release?Dimensions:
1411 x 1771 px | 23.9 x 30 cm | 9.4 x 11.8 inches | 150dpiMore information:
This image is a public domain image, which means either that copyright has expired in the image or the copyright holder has waived their copyright. Alamy charges you a fee for access to the high resolution copy of the image.
This image could have imperfections as it’s either historical or reportage.
. Nature and development of plants. Botany. 432 THE FAGALES phylls are usually developed upon the same plant. Several bracts are usually associated with sporophylls (Figs. 298, B-F; 299, B-E) so that the flowers are of a higher type than the willows. The innermost of these bracts is often of a delicate structure and has been referred to as a primitive form of the calyx (Fig. 298, B, pr) and when present in the pistillate flowers it adheres to. Fig. 298. Flowers and fruits of the birch family, order Fagales: A, in- florescence of hornbeam (Carpinus)—s, staminate ament; p, pistillate ament. B, staminate clusters from ament of alder (Alnus), each flower consisting of four stamens attached to a four-parted perianth, pr. C, upper view of the same cluster, showing the numerous bracts associated with the flowers. D, fruit of Carpinus attached to the greatly enlarged three-lobed bract. D, fruit cluster of hazel (Corylus)—b, bract encircling the ovary and within a more delicate bract, pr, adnate to the ovary; i, stigma. 7^, fruit of Corylus, the bract, b, in E has grown out into a tubular beaked structure that com- pletely envelops the nut. the ovary (Figs. 298, E, pr; 300, B, pr). The pistils are pro- vided with long delicate stigmas and are compound, containing several ovules but only one usually matures. The wall of the ovary develops into a tough coat about the seed, forming a fruit. Please note that these images are extracted from scanned page images that may have been digitally enhanced for readability - coloration and appearance of these illustrations may not perfectly resemble the original work.. Curtis, Carlton Clarence, 1864-1945. New York, H. Holt