. Human physiology. these papillae ? 4. From what sources does the tongue receive its nerve supply ? 5. What is the organ of taste ? What are the conditions necessary for the ?production of the sensation called taste ? 6. How do the different portions of the mucous membrane of the tongue differ with regard to the sensations they produce ? 202 ELEMENTARY PHYSIOLOGY 7. How would you prove that the sense of smell is intimately associated with that of taste ? 8. Describe the general structure of the walls of the nasal cavities. How are these cavities separated from the mouth, the brain, and from e
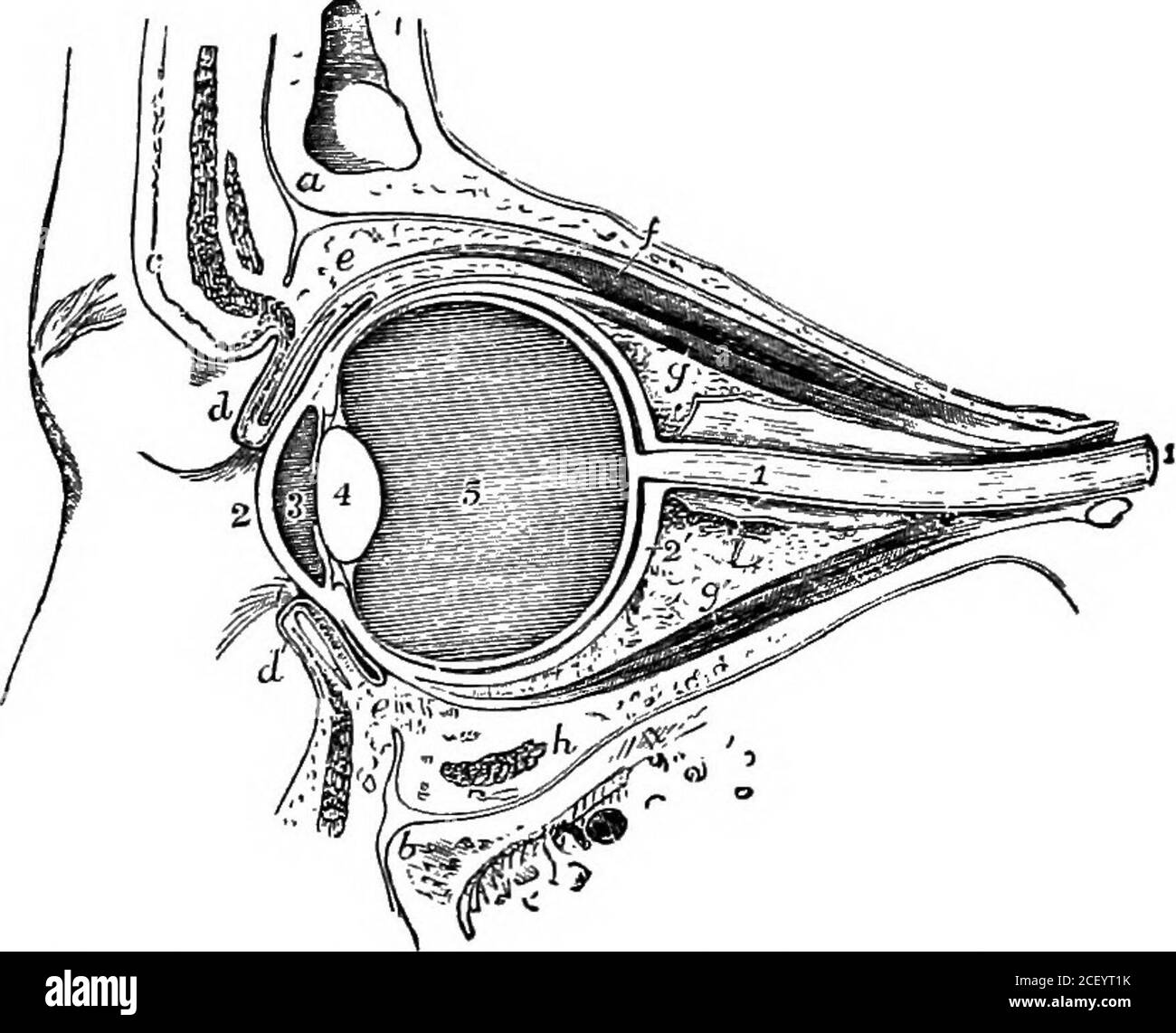
Image details
Contributor:
Reading Room 2020 / Alamy Stock PhotoImage ID:
2CEYT1KFile size:
7.1 MB (312.6 KB Compressed download)Releases:
Model - no | Property - noDo I need a release?Dimensions:
1757 x 1422 px | 29.8 x 24.1 cm | 11.7 x 9.5 inches | 150dpiMore information:
This image is a public domain image, which means either that copyright has expired in the image or the copyright holder has waived their copyright. Alamy charges you a fee for access to the high resolution copy of the image.
This image could have imperfections as it’s either historical or reportage.
. Human physiology. these papillae ? 4. From what sources does the tongue receive its nerve supply ? 5. What is the organ of taste ? What are the conditions necessary for the ?production of the sensation called taste ? 6. How do the different portions of the mucous membrane of the tongue differ with regard to the sensations they produce ? 202 ELEMENTARY PHYSIOLOGY 7. How would you prove that the sense of smell is intimately associated with that of taste ? 8. Describe the general structure of the walls of the nasal cavities. How are these cavities separated from the mouth, the brain, and from eachother ? 9. What is the course taken by the air when we breathe (1) with the mouth open and (2) with the mouth shut ?10. By what part of the nose do we smell ? How does sniffing assist the senseof smell ? LESSON XXXV.THE EYE AND VISION. The organ of vision consists of the eyeball, which, with itsmuscles, blood-vessels, nerves, fatty tissue and other protectingstructures, completely fill the orbit or eye-socket.. Fig. 185.—Section through the Orbit and its Contents. 1, frontal bone ; i, superior maxillary bone ; c, eyebrow; d, eyelids ; e, conjunctiva ; f, themuscle which raises the upper lid ; g and g1, recti muscles ; h, inferior oblique muscle cutacross; 1, optic nerve; 2, cornea ; 2, sclerotic ; 3, aqueous chamber; 4, crystalline lens ;5, vitreous chamber. In front the ball of the eye is protected by movable folds ofthe skin or integument called the eyelids. The inner surfaces ofthe lids are lined by a mucous membrane called the conjunctiva, which is also reflected over the front of the ball. The uppereyelid is larger and more movable than the lower one, and it is THE EYE AND VISION 203 chiefly by the elevation and depression of this lid that the eye isopened and closed. The eyelids are closed by the contraction ofmuscular fibres which are arranged in the form of a ring aroundthe eye. This circular muscle is called the orbicularis (Lat. orbi-culus, a little circle). The l