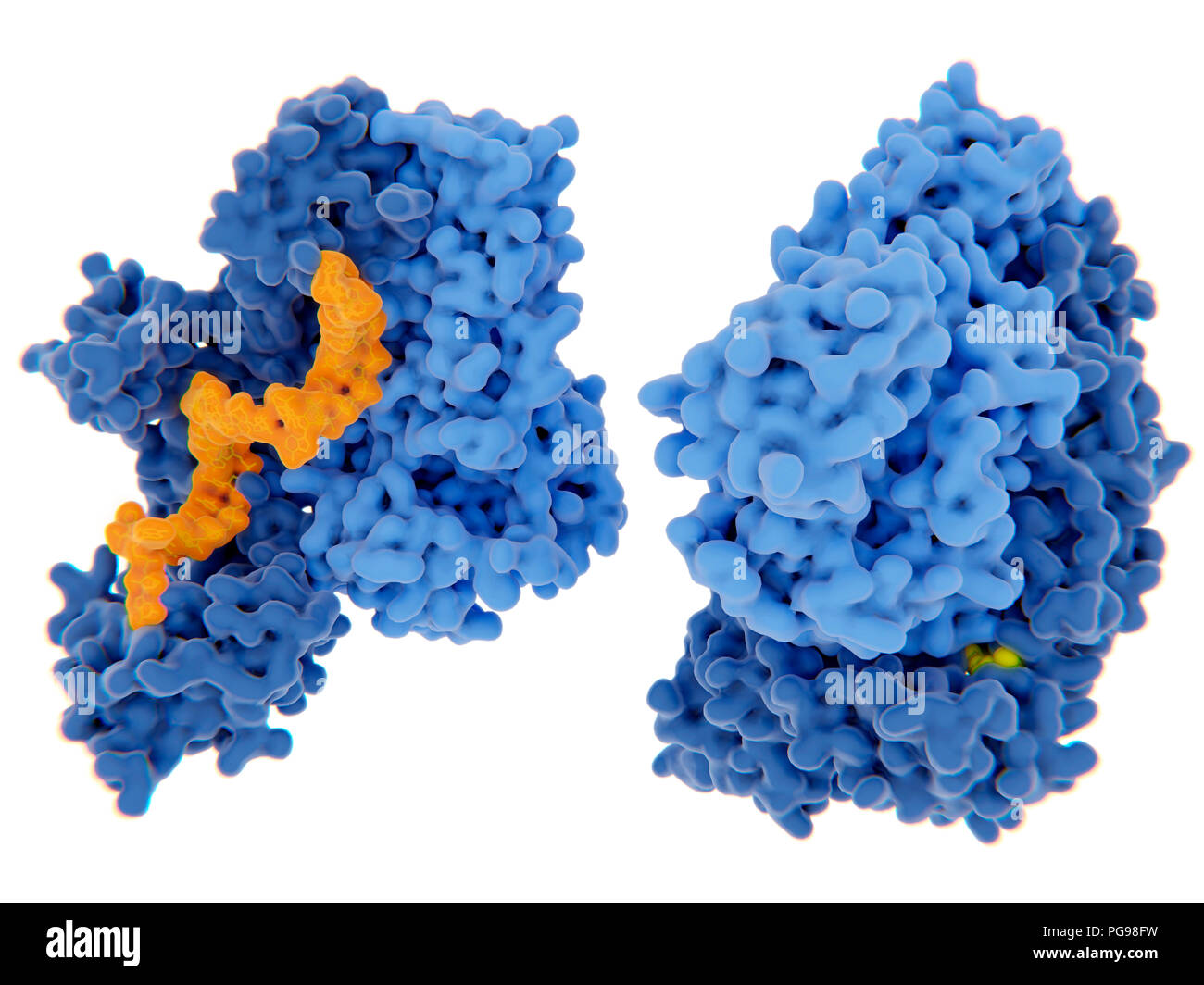
HIV-1 reverse transcriptase inhibition, illustration. The human immunodeficiency virus single-stranded RNA genome is converted into double-stranded DNA by the viral reverse transcriptase (blue) and then the DNA is integrated in the DNA of an infected human cell. The reverse transcriptase is one of the main targets to disrupt the virus multiplication through an inhibitor. There are nucleoside and nucleotide inhibitors and non-nucleoside analogue inhibitors. Two examples of these inhibitors (yellow) are shown binding to the reverse transcriptase.
RFID:Image ID:PG98FW
Image details
Contributor:
Science Photo Library / Alamy Stock PhotoImage ID:
PG98FWFile size:
100 MB (1.7 MB Compressed download)Releases:
Model - no | Property - noDo I need a release?Dimensions:
6827 x 5120 px | 57.8 x 43.3 cm | 22.8 x 17.1 inches | 300dpiDate taken:
17 August 2018Photographer:
JUAN GAERTNER/SCIENCE PHOTO LIBRARY