Elementary botany . Fig. 247.Hydnum rcpandum, spines hanging down from under side of cap. 212 MORPHOLOGY.. Fig. 248.Clavaria botrytes. CHAPTER XXII. CLASSIFICATION OF THE FUNGI. 429. Classification of the fungi.—Those who believe that the fungi repre-sent a natural group of plants arrange them in three large series related toeach other somewhat as follows •. The Basidium Type or Series.The number of gonidia on a ba-sidium is limited and definite,and the basidium is a characteris-tic structure; examples: uredineae(rusts), mushrooms, etc. The Ascus Type or Series. Thenumber of spores in an ascus
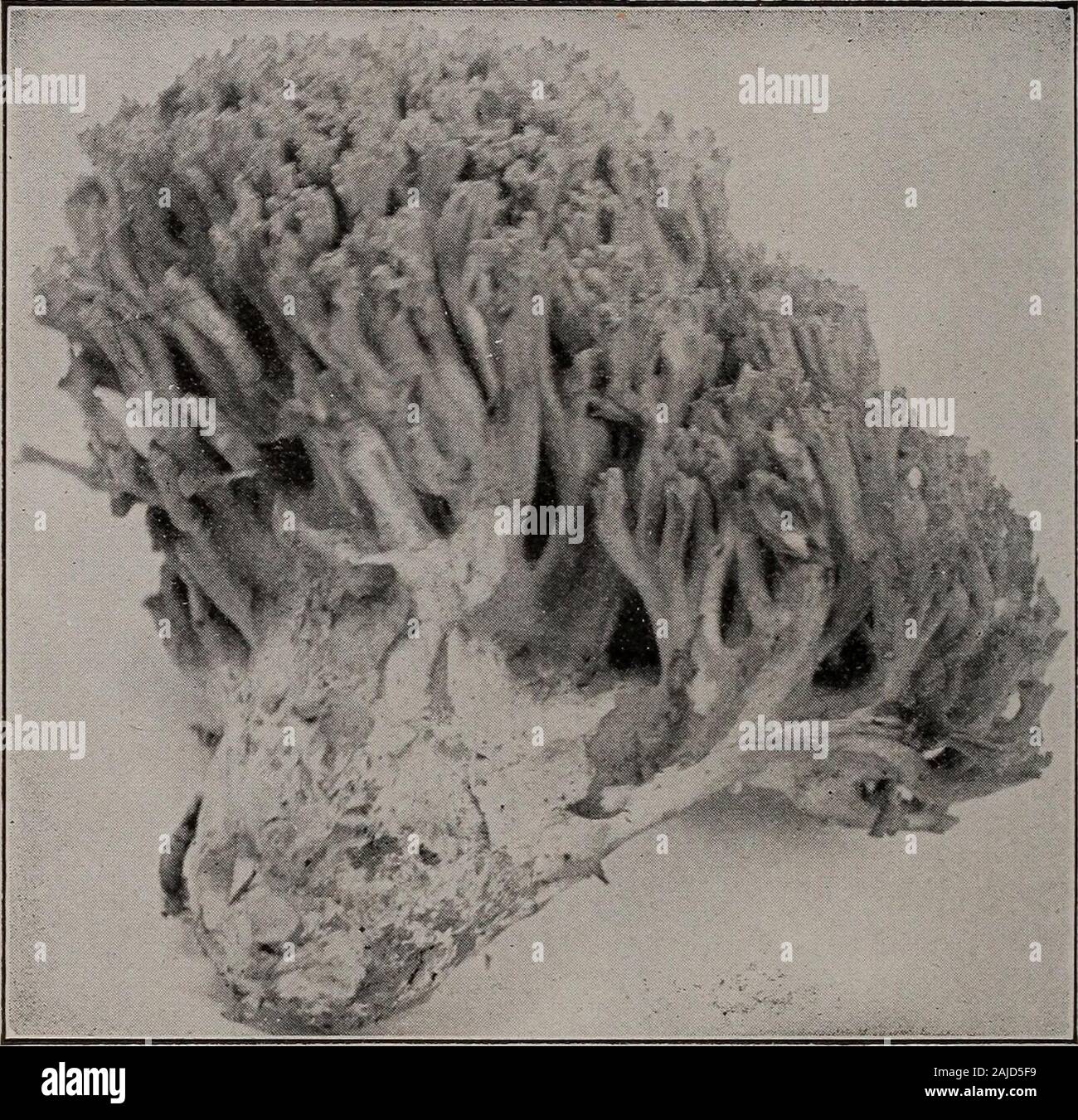
Image details
Contributor:
The Reading Room / Alamy Stock PhotoImage ID:
2AJD5F9File size:
7.1 MB (713.9 KB Compressed download)Releases:
Model - no | Property - noDo I need a release?Dimensions:
1604 x 1557 px | 27.2 x 26.4 cm | 10.7 x 10.4 inches | 150dpiMore information:
This image is a public domain image, which means either that copyright has expired in the image or the copyright holder has waived their copyright. Alamy charges you a fee for access to the high resolution copy of the image.
This image could have imperfections as it’s either historical or reportage.
Elementary botany . Fig. 247.Hydnum rcpandum, spines hanging down from under side of cap. 212 MORPHOLOGY.. Fig. 248.Clavaria botrytes. CHAPTER XXII. CLASSIFICATION OF THE FUNGI. 429. Classification of the fungi.—Those who believe that the fungi repre-sent a natural group of plants arrange them in three large series related toeach other somewhat as follows •. The Basidium Type or Series.The number of gonidia on a ba-sidium is limited and definite, and the basidium is a characteris-tic structure; examples: uredineae(rusts), mushrooms, etc. The Ascus Type or Series. Thenumber of spores in an ascus islimited and definite, and the ascus isa characteristic structure; examples:leaf curl of peach (exoascus), pow-dery mildews, black knot of plum, black rot of grapes, etc. 430. Others believe that the fungi do not represent a natural group, butthat they have developed off from different groups of the algae by becomingparasitic. As parasites they no longer needed chlorophyll, and conse-quently lost it. According to this view the lower fungi have developed off from the loweralgae (saprolegnias, muco