. Cytology. Cytology. OH (2-6) OH H 2-Deoxy-D-ribose the purines are adenine and guanine (Formula (2-7)). In so far as the bases are concerned, the only difference between the two kinds of nucleic acids is that thymine is found as a component only in DNA. Uracil ap- pears to be confined exclusively to RNA. As to distribution in the cell, DNA appears to be specifically associated with the chromosomes while RNA is found in the nucleolus, chromosomes, and cytoplasm. Although OH NH. C .^6- N 1 se- ll CH HO- -C2 N CH Thymine c N I HO—C2 CH II CH N Cytosine. CH II CH NH, C N HC ^^ N N N H Adenine
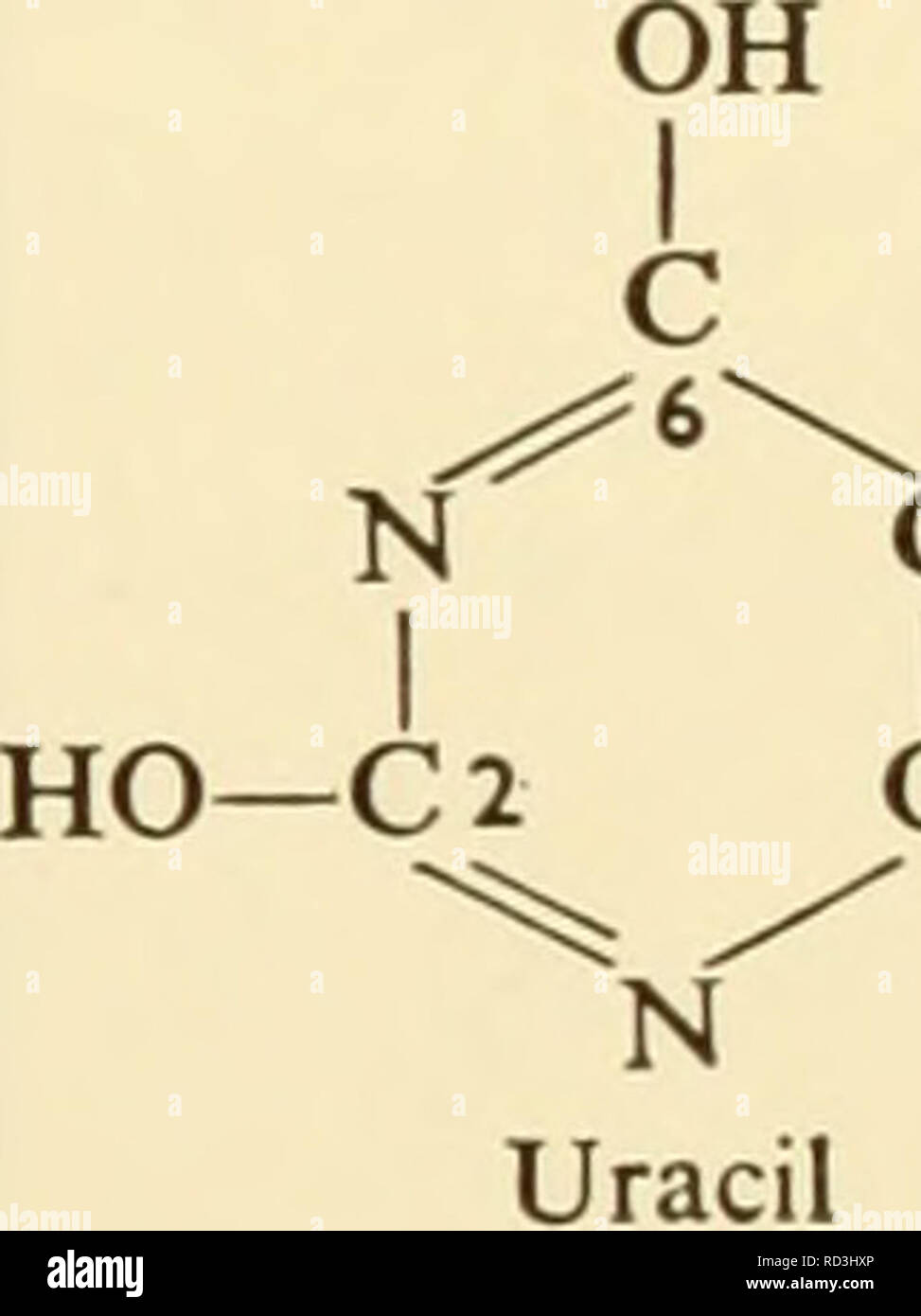
Image details
Contributor:
The Book Worm / Alamy Stock PhotoImage ID:
RD3HXPFile size:
7.2 MB (103.8 KB Compressed download)Releases:
Model - no | Property - noDo I need a release?Dimensions:
1368 x 1827 px | 23.2 x 30.9 cm | 9.1 x 12.2 inches | 150dpiMore information:
This image is a public domain image, which means either that copyright has expired in the image or the copyright holder has waived their copyright. Alamy charges you a fee for access to the high resolution copy of the image.
This image could have imperfections as it’s either historical or reportage.
. Cytology. Cytology. OH (2-6) OH H 2-Deoxy-D-ribose the purines are adenine and guanine (Formula (2-7)). In so far as the bases are concerned, the only difference between the two kinds of nucleic acids is that thymine is found as a component only in DNA. Uracil ap- pears to be confined exclusively to RNA. As to distribution in the cell, DNA appears to be specifically associated with the chromosomes while RNA is found in the nucleolus, chromosomes, and cytoplasm. Although OH NH. C .^6- N 1 se- ll CH HO- -C2 N CH Thymine c N I HO—C2 CH II CH N Cytosine. CH II CH NH, C N HC ^^ N N N H Adenine OH CH C N I HaN—C 2 N C II c N N H Guanine (2-7) CH the role of nucleic acid in cell metabolism is not completely known, there are some general relationships which are now accepted rather widely. There apparently is a relatively clear-cut relationship between DNA and sites of "genetic information." The strongest direct evidence for this is the fact that in some strains of bacteria it has been clearly shown that highly purified DNA can transmit genetic material. RNA appears to be intimately associated with protein synthesis but exactly what this relationship is has yet to be determined (see Chapter 4 for GENERAL MORPHOLOGY AND CHEMISTRY OF THE CELL / 17. Please note that these images are extracted from scanned page images that may have been digitally enhanced for readability - coloration and appearance of these illustrations may not perfectly resemble the original work.. Wilson, G. B. (George Bernard), 1914-; Morrison, John H. (John Herbert), 1927-. New York, Reinhold