. Cunningham's Text-book of anatomy. Anatomy. THE IXTEENAL CAEOTID AETEEY. 901 carotid artery for a short distance below, and afterwards the wall of the pharynx, the areolar tissue posterior to the wall of the pharynx, the ascending pharyngeal artery, the pharyngeal plexus of veins, and the external and internal laryngeal nerves. Just before it enters the temporal bone the levator palati muscle is to its medial side. Lateral or superficial to it are the sterno-mastoid, skin, and fascia?, and it is crossed under cover of the sterno-mastoid, from below upwards, by the hypoglossal nerve, the occi
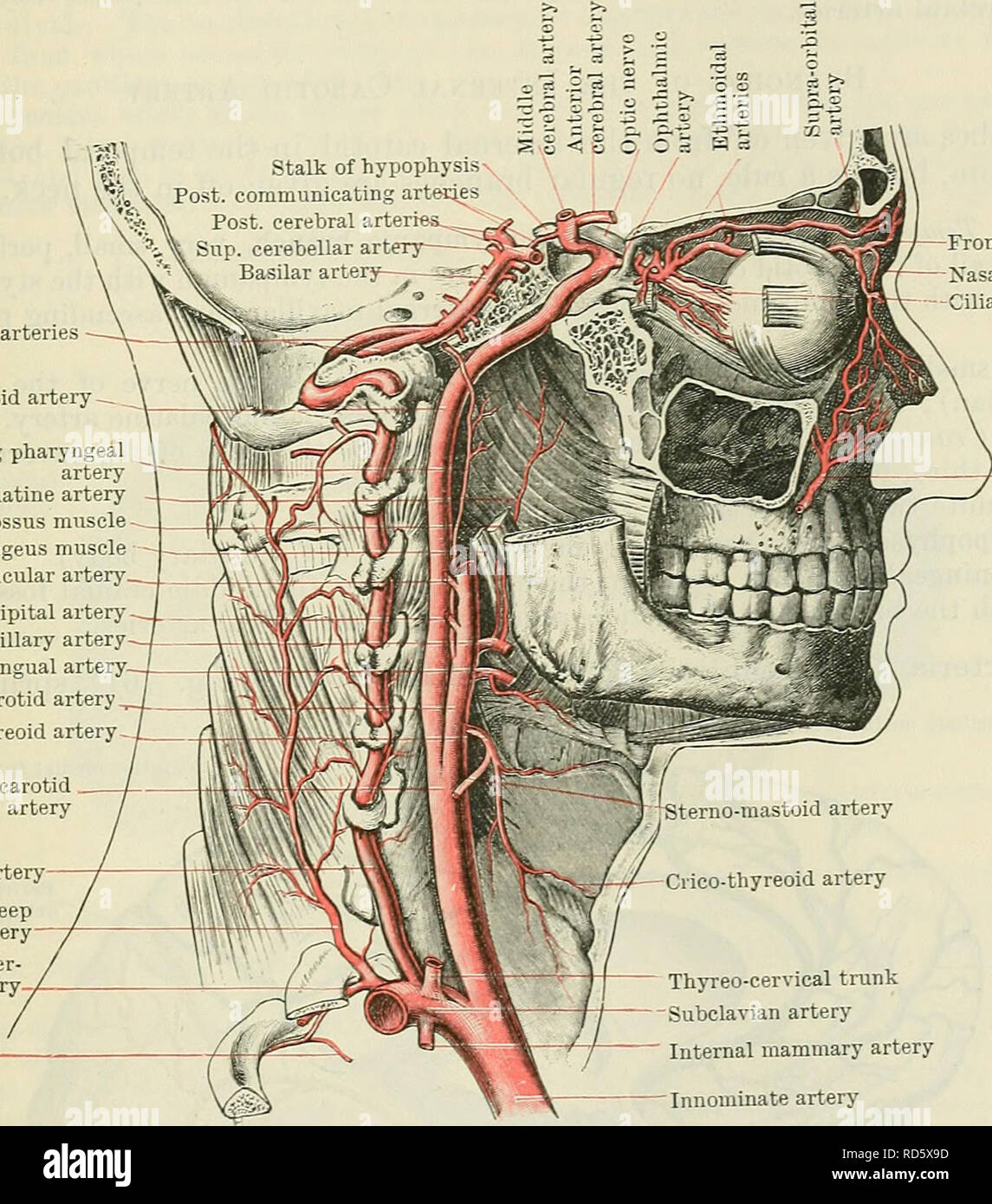
Image details
Contributor:
The Book Worm / Alamy Stock PhotoImage ID:
RD5X9DFile size:
7.1 MB (468.4 KB Compressed download)Releases:
Model - no | Property - noDo I need a release?Dimensions:
1484 x 1684 px | 25.1 x 28.5 cm | 9.9 x 11.2 inches | 150dpiMore information:
This image is a public domain image, which means either that copyright has expired in the image or the copyright holder has waived their copyright. Alamy charges you a fee for access to the high resolution copy of the image.
This image could have imperfections as it’s either historical or reportage.
. Cunningham's Text-book of anatomy. Anatomy. THE IXTEENAL CAEOTID AETEEY. 901 carotid artery for a short distance below, and afterwards the wall of the pharynx, the areolar tissue posterior to the wall of the pharynx, the ascending pharyngeal artery, the pharyngeal plexus of veins, and the external and internal laryngeal nerves. Just before it enters the temporal bone the levator palati muscle is to its medial side. Lateral or superficial to it are the sterno-mastoid, skin, and fascia?, and it is crossed under cover of the sterno-mastoid, from below upwards, by the hypoglossal nerve, the occipital artery, and the posterior auricular artery. It is also crossed superficially, between the last- mentioned arteries, by the digastric and stylo-hyoid muscles, which separate it from the parotid gland, and below the digastric it is covered by the lower part of the postero-medial surface of the gland. Passing obliquely across its anterior lateral surface, and separating Vertebral arteries Internal carotid artery -_. Ascending pharyngeal artery Ascending palatine artery Styloglossus muscle Stylopharyngeus muscle Posterior auricular artery Occipital artery External maxillary artery Lingual artery. External carotid artery Superior thyreoid artery Common carotid artery Vertebral artery- Deep cervical artery Superior inter- costal artery Anastomosis with first aortic inter- costal artery. Frontal artery Nasal artery Ciliary arteries External max- illary artery Thyreo-cervical trunk Subclavian artery "" Internal mammary artery Innominate artery Fig. 7 61.âThe Carotid, Subclavian, and Vertebral Arteries and their Main Branches. it from the external carotid artery, are the following structures viz. the stylo-pharyngeus the styloid process, or the styloglossus muscle, and the glossopharyngeal nerve, the pharyngeal branch of the vagus, and some sympathetic twigs. P In !he Carotid CW.-The artery, as it passes upwards is anteroinferior to the cochlea and the tympanum: postero