. Comparative embryology of the vertebrates; with 2057 drawings and photos. grouped as 380 illus. Vertebrates -- Embryology; Comparative embryology. DEVELOPMENT OF THE DIGESTIVE TUBE 615. Fig. 289. Palatal conditions in frog, chick, and mammal. (A) Frog, adult. (B) Chick, 16-day embryo. (C) Human adult. (Redrawn and modified from Morris, 1942, Human Anatomy, Blakiston, Phila.) Only the anterior or hard palate is supported by bone, the soft palate being a fleshy continuation of the palate caudally toward the pharyngeal area. (D-F) Stages in development of the palate in the pig. (D) 20.5 mm. (E)
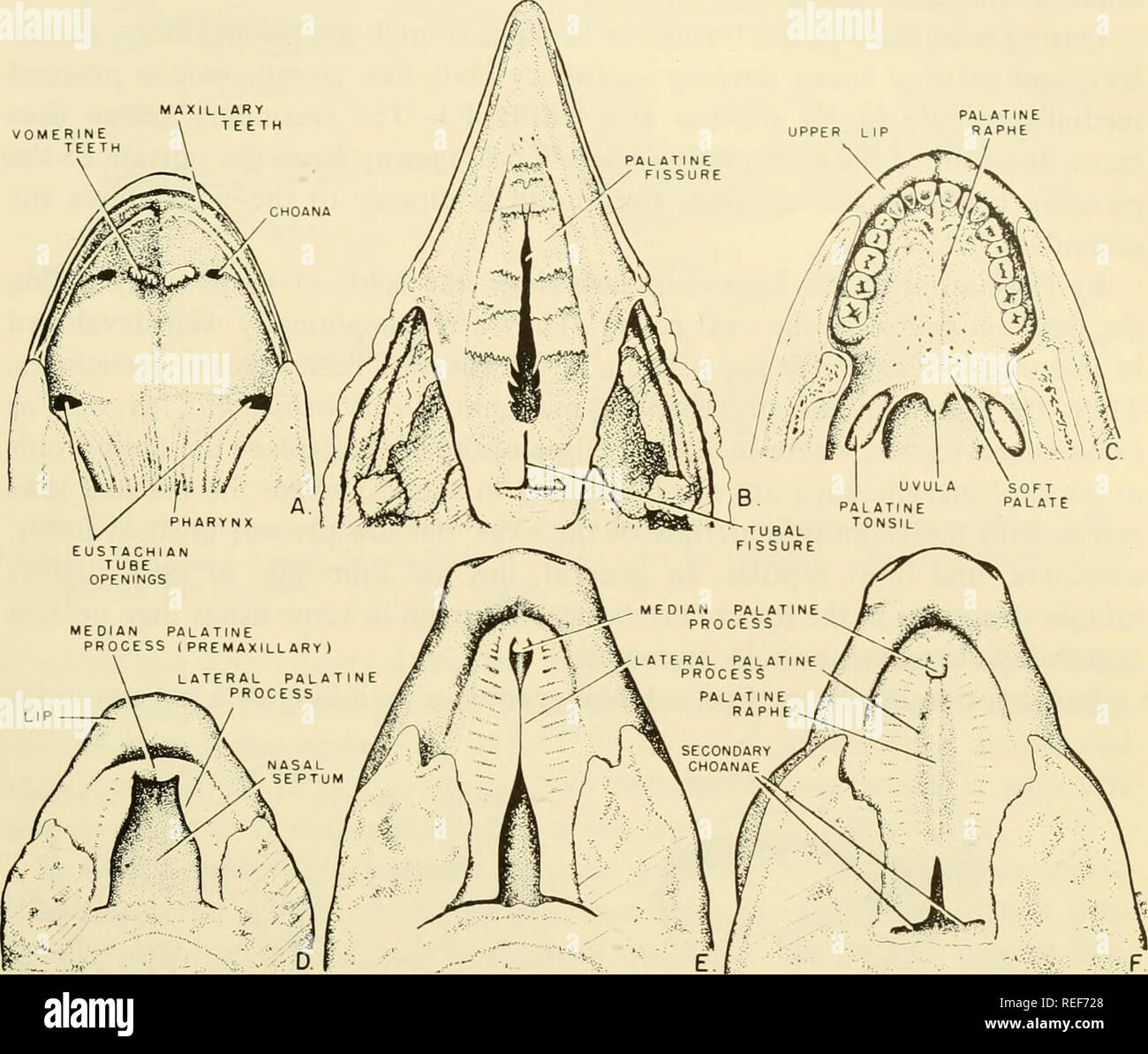
Image details
Contributor:
The Book Worm / Alamy Stock PhotoImage ID:
REF728File size:
7.1 MB (342 KB Compressed download)Releases:
Model - no | Property - noDo I need a release?Dimensions:
1716 x 1456 px | 29.1 x 24.7 cm | 11.4 x 9.7 inches | 150dpiMore information:
This image is a public domain image, which means either that copyright has expired in the image or the copyright holder has waived their copyright. Alamy charges you a fee for access to the high resolution copy of the image.
This image could have imperfections as it’s either historical or reportage.
. Comparative embryology of the vertebrates; with 2057 drawings and photos. grouped as 380 illus. Vertebrates -- Embryology; Comparative embryology. DEVELOPMENT OF THE DIGESTIVE TUBE 615. Fig. 289. Palatal conditions in frog, chick, and mammal. (A) Frog, adult. (B) Chick, 16-day embryo. (C) Human adult. (Redrawn and modified from Morris, 1942, Human Anatomy, Blakiston, Phila.) Only the anterior or hard palate is supported by bone, the soft palate being a fleshy continuation of the palate caudally toward the pharyngeal area. (D-F) Stages in development of the palate in the pig. (D) 20.5 mm. (E) 26.5 mm. (F) 29.5 mm. is formed between the root of the tooth and the walls of the alveolar socket, is called a gomphosis (fig. 286E). The permanent teeth, which supplant the deciduous teeth, develop in much the same manner as the deciduous teeth. Man, Uke the majority of mammals, develops two sets of teeth and, consequently, is diphyodont. Some mammals, such as the mole, Scalopus, never cut the permanent teeth, while the guinea pig sheds its deciduous teeth in utero. 5) Formation of the Secondary Palate. In the fishes and the amphibia, a secondary palate, separating the oral cavity from an upper respiratory passage- way, is not formed. The formation of a secondary palate begins in the turtle group and is well developed in the crocodilians and mammals. The bird also. Please note that these images are extracted from scanned page images that may have been digitally enhanced for readability - coloration and appearance of these illustrations may not perfectly resemble the original work.. Nelsen, Olin E. (Olin Everett), b. 1898. New York, Blakiston