The hydropathic encyclopedia: a system of hydropathy and hygiene .. . substance. The medul-lary structure is fibrous, the fibresbeing looped at their termina-tions, and containing a centralstripe, called the cylinder axis ofPurkinje. The cineiilious ismore vascular, and composed ofkidney-shaped globules, contain-ing a vesicular nucleus with anucleolus. These globules aresoft, and of a yellow or browDishcolor. The ganglions and nervouscentres consist of a mixture ofwhite fibres and gray globules.The sheath of the nerves is call-ed neurilemma, and the enclosedmatter neurine. The trunks of nerves
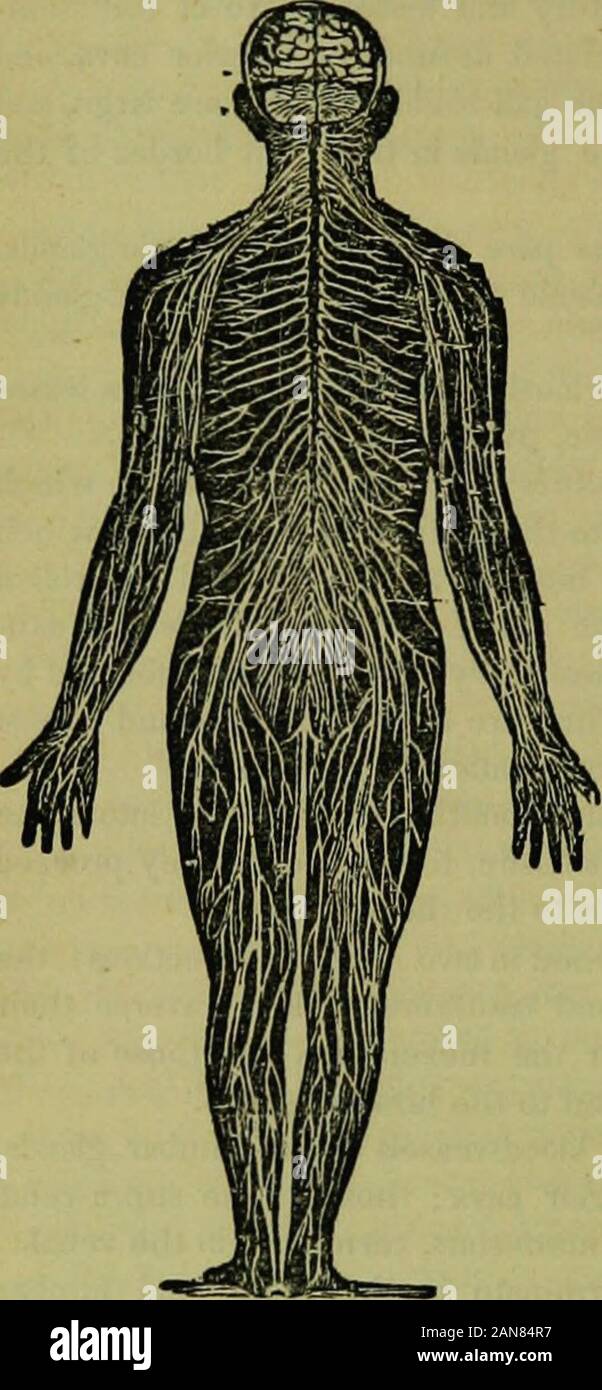
Image details
Contributor:
The Reading Room / Alamy Stock PhotoImage ID:
2AN84R7File size:
7.2 MB (310.6 KB Compressed download)Releases:
Model - no | Property - noDo I need a release?Dimensions:
1076 x 2323 px | 18.2 x 39.3 cm | 7.2 x 15.5 inches | 150dpiMore information:
This image is a public domain image, which means either that copyright has expired in the image or the copyright holder has waived their copyright. Alamy charges you a fee for access to the high resolution copy of the image.
This image could have imperfections as it’s either historical or reportage.
The hydropathic encyclopedia: a system of hydropathy and hygiene .. . substance. The medul-lary structure is fibrous, the fibresbeing looped at their termina-tions, and containing a centralstripe, called the cylinder axis ofPurkinje. The cineiilious ismore vascular, and composed ofkidney-shaped globules, contain-ing a vesicular nucleus with anucleolus. These globules aresoft, and of a yellow or browDishcolor. The ganglions and nervouscentres consist of a mixture ofwhite fibres and gray globules.The sheath of the nerves is call-ed neurilemma, and the enclosedmatter neurine. The trunks of nerves frequently interchange trunks*r fasciculi, forming anastomoses ; and a combination of these anasto-moses into a network forms a plexus. N-jmerous small elliptical bodies, attached to the ulnar and digitalaerves, are called Pacinian corpuscles; these have no terminal loops, being the only exception to the general ruie. JMicroscopic observation makes c t the elements of the nervous sys-tem to be, white nerve-Sbres, gray tervo-fibios, nerce-cells, and nerve-p anules.. NERVOUS SYSTEM. NEUROLOGY 1HJ Fig. S5 represents the mict jscopic elements of thenervous structure. 1. Mode of termination of whitenej vn-fibres in loops ; three ji these loops are simple, the fourth s convoluted. The latter is found in situ-fctiuns who -o a high degree of sensation exists. 2. Awhit/? nerve-fibre from the brain, showing the vari-cose 01 knotty appearance produced by traction orpressure. 3. A white nerve-fibre enlarged to showIts structure, a tubular envelope and a contah.-od sub-stance—neurilemma and aeurine. 4. A nerve-cell, •hawing its composition of a granular-looking cap-tule and granular contents. 5. Its nucleus containinga nucleolus. 6. A nerve-cell, Irom which severalprocesses are given off; it coutains also a nucleatednucleus. 7. Nerve-granules. Fig. 65,