. The Cambridge natural history. Zoology. taining processes from the more important organs of the parent- body, which give rise to an endodermal tube, two peribranchial tubes, a neural tube, two blood-sinuses and mesoblast cells, a genital cord, and over all the ectodermal covering (see Fig. 64). This stolon becomes segmented (Fig. 63) into a series of buds or. Fig. 64.—Transverse section through endostyle and young stolon of Halpaipinnata. ec, Ectoderm of parent reiiected at ec' to cover base of stolon ; ec", ecto- derm of stolon ; end, endoderm of stolon ; g, ovary ; mes, mesoderm cells
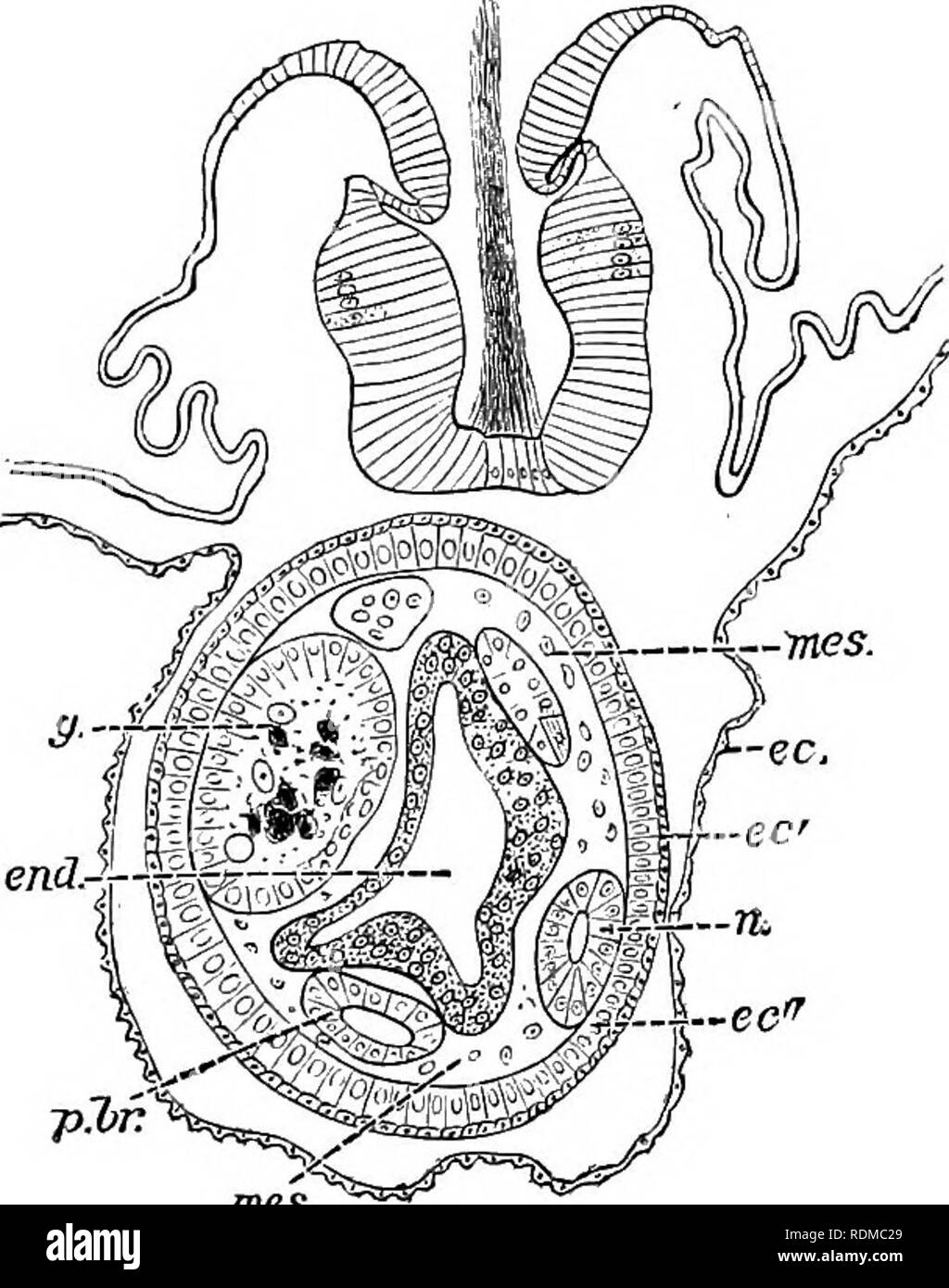
Image details
Contributor:
The Book Worm / Alamy Stock PhotoImage ID:
RDMC29File size:
7.1 MB (350.4 KB Compressed download)Releases:
Model - no | Property - noDo I need a release?Dimensions:
1403 x 1781 px | 23.8 x 30.2 cm | 9.4 x 11.9 inches | 150dpiMore information:
This image is a public domain image, which means either that copyright has expired in the image or the copyright holder has waived their copyright. Alamy charges you a fee for access to the high resolution copy of the image.
This image could have imperfections as it’s either historical or reportage.
. The Cambridge natural history. Zoology. taining processes from the more important organs of the parent- body, which give rise to an endodermal tube, two peribranchial tubes, a neural tube, two blood-sinuses and mesoblast cells, a genital cord, and over all the ectodermal covering (see Fig. 64). This stolon becomes segmented (Fig. 63) into a series of buds or. Fig. 64.—Transverse section through endostyle and young stolon of Halpaipinnata. ec, Ectoderm of parent reiiected at ec' to cover base of stolon ; ec", ecto- derm of stolon ; end, endoderm of stolon ; g, ovary ; mes, mesoderm cells ; n, nerve- tube of stolon ; p, hr, peribranchial tubes of stolon. (After Brooks.) mes. young " chain" individuals, of which there may be several hundreds. As the stolon elongates (Fig. 61, B, st"), the buds. Please note that these images are extracted from scanned page images that may have been digitally enhanced for readability - coloration and appearance of these illustrations may not perfectly resemble the original work.. Harmer, S. F. (Sidney Frederic), Sir, 1862- ed; Shipley, A. E. (Arthur Everett), Sir, 1861-1927. ed. [London, Macmillan and Co. , Limited; New York, The Macmillan Company