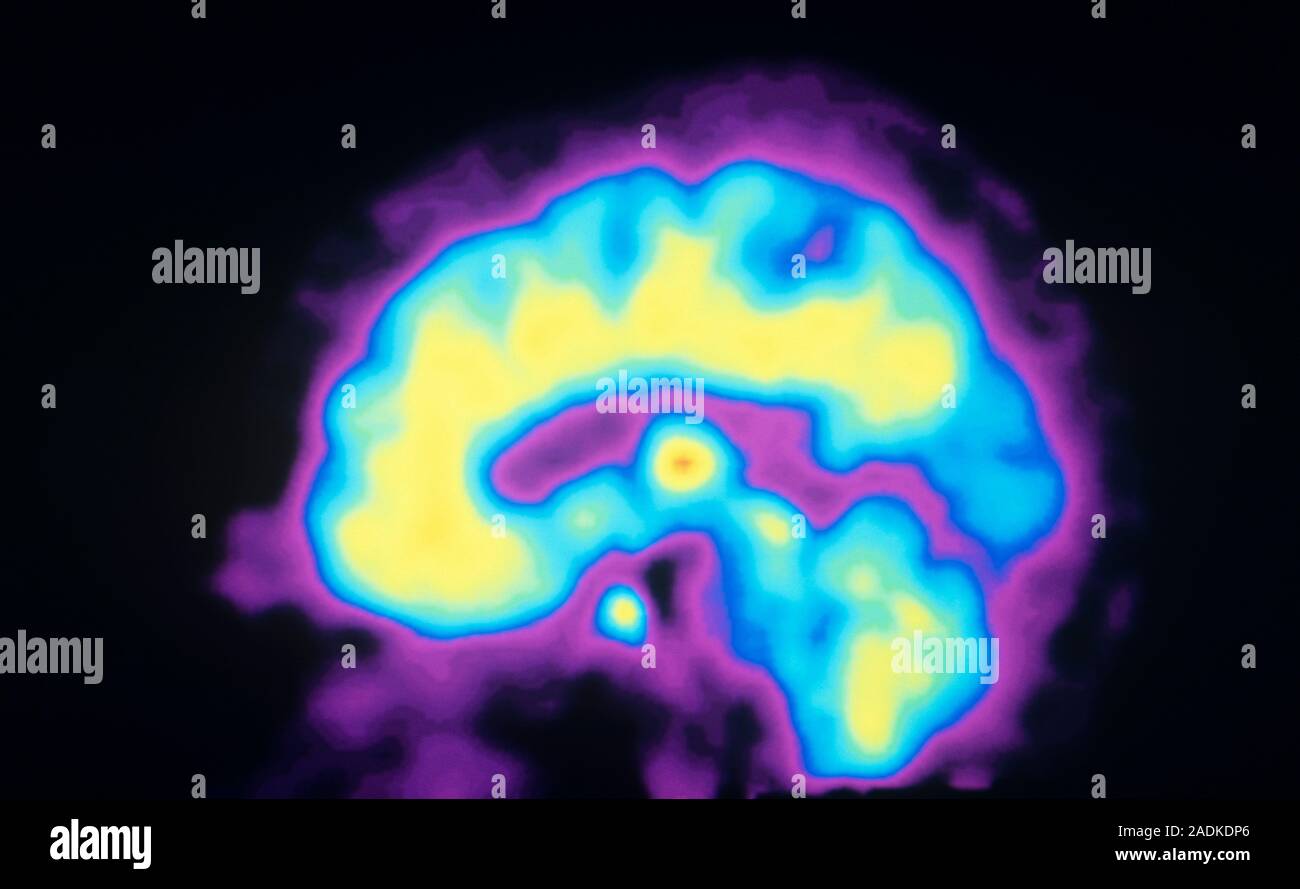
Opioid receptors. Coloured sagittal Positron Emission Tomography (PET) scan showing the normal distribution of opioid receptors in the human brain. Op
RMID:Image ID:2ADKDP6
Image details
Contributor:
Science Photo Library / Alamy Stock PhotoImage ID:
2ADKDP6File size:
50.3 MB (853.9 KB Compressed download)Releases:
Model - no | Property - noDo I need a release?Dimensions:
5349 x 3289 px | 45.3 x 27.8 cm | 17.8 x 11 inches | 300dpiDate taken:
13 July 2005Photographer:
PHILIPPE PSAILA/SCIENCE PHOTO LIBRARYMore information:
Opioid receptors. Coloured sagittal Positron Emission Tomography (PET) scan showing the normal distribution of opioid receptors in the human brain. Opiod receptors are located on the exterior of nerve cells (neurons). When pain is detected by the body, endorphins are released and attach to the receptors. They temporarily prevent the nerve cells from firing and therefore provide pain relief. Opioid drugs mimic endorphins. By injecting a patient with an opioid tagged with carbon-11 (radioactive tracer), a colour-coded scan is produced, showing the concentration of opioid receptors from red (highest) through yellow and green to blue (lowest).