. Elements of the comparative anatomy of vertebrates. Anatomy, Comparative. 00 COMPARATIVE ANATOMY of ossification, which gives the skull a very firm and solid appear- ance ; only amongst Lizards (Fig. 71), and especially in Hatteria is the cartilage retained to any considerable extent, and owing to the conformation of the bones in the posterior region, the skull in these forms presents a number of distinct spaces or fossae in the dry state. In Snakes and Amphisbsenians the cranial cavity extends forwards between the orbits as far as the ethmoidal region, while in the Lacertilia, Chelonia, and
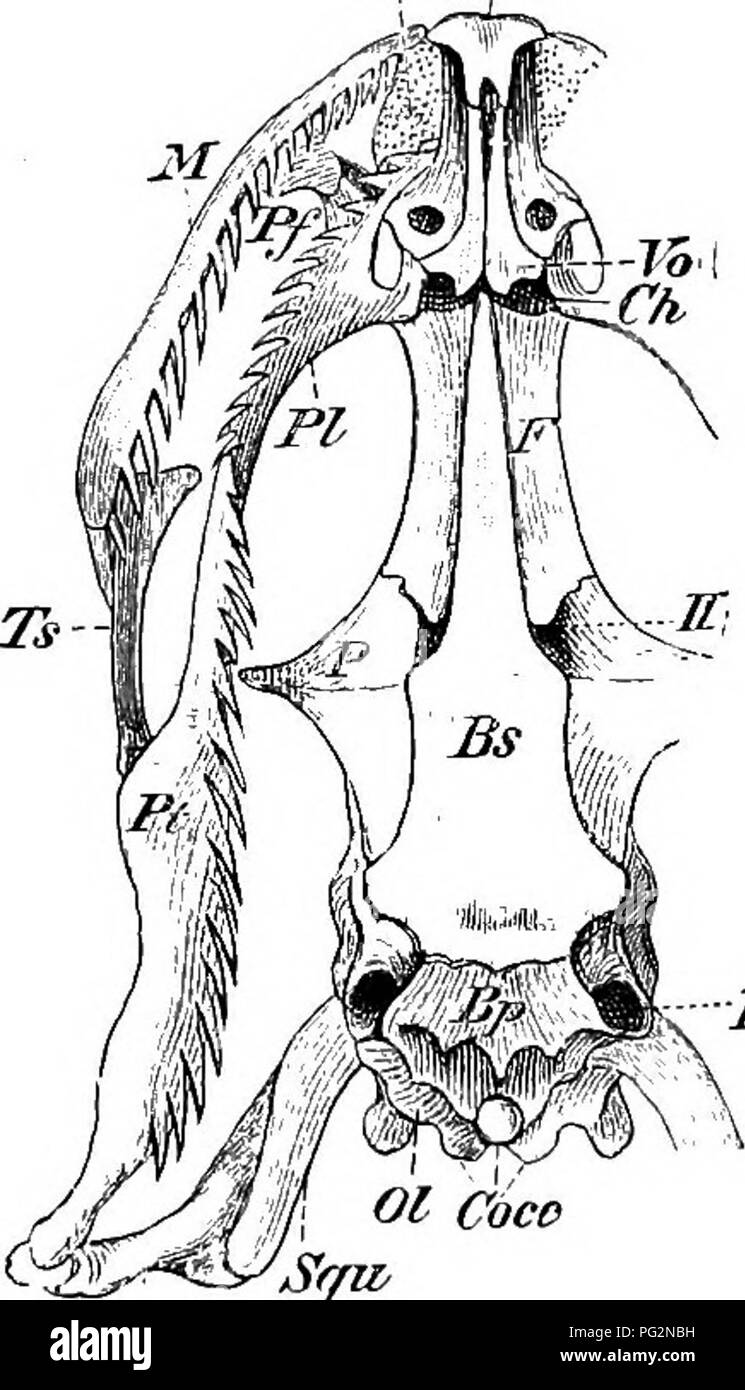
Image details
Contributor:
Central Historic Books / Alamy Stock PhotoImage ID:
PG2NBHFile size:
7.1 MB (309.5 KB Compressed download)Releases:
Model - no | Property - noDo I need a release?Dimensions:
1197 x 2087 px | 20.3 x 35.3 cm | 8 x 13.9 inches | 150dpiMore information:
This image is a public domain image, which means either that copyright has expired in the image or the copyright holder has waived their copyright. Alamy charges you a fee for access to the high resolution copy of the image.
This image could have imperfections as it’s either historical or reportage.
. Elements of the comparative anatomy of vertebrates. Anatomy, Comparative. 00 COMPARATIVE ANATOMY of ossification, which gives the skull a very firm and solid appear- ance ; only amongst Lizards (Fig. 71), and especially in Hatteria is the cartilage retained to any considerable extent, and owing to the conformation of the bones in the posterior region, the skull in these forms presents a number of distinct spaces or fossae in the dry state. In Snakes and Amphisbsenians the cranial cavity extends forwards between the orbits as far as the ethmoidal region, while in the Lacertilia, Chelonia, and Crocodiliaâin which a fibro-carti- laginous interorbital septum perforated by the olfactory nerve is presentâits anterior boundary is much further back. The parasphenoid, which plays so important a part as an investing bone of the roof of the mouth in Fishes and Amphibians, J^thFm.^. Pmx â Foi/ Ol COCD (fa. Please note that these images are extracted from scanned page images that may have been digitally enhanced for readability - coloration and appearance of these illustrations may not perfectly resemble the original work.. Wiedersheim, Robert, 1848-1923; Parker, William Newton, 1857-1923. London, Macmillan