A system of surgery . rrence of this dislocation in those with lax ligaments. Re-markable difficulty has sometimes been experienced in the reductionof the rotatory vertical dislocation. This is usually declared by authorsto be due to the wedging of the bone into the inter-condyloid notch.Considering the size of the latter as compared with the edge of thepatella, this explanation seems to me hardly satisfactory. It is farmore likely that the bone lacerates the capsule, and is tightly girtin its new position by the tough ligamentous fibres of this structure.In the cases I have seen, no difficult
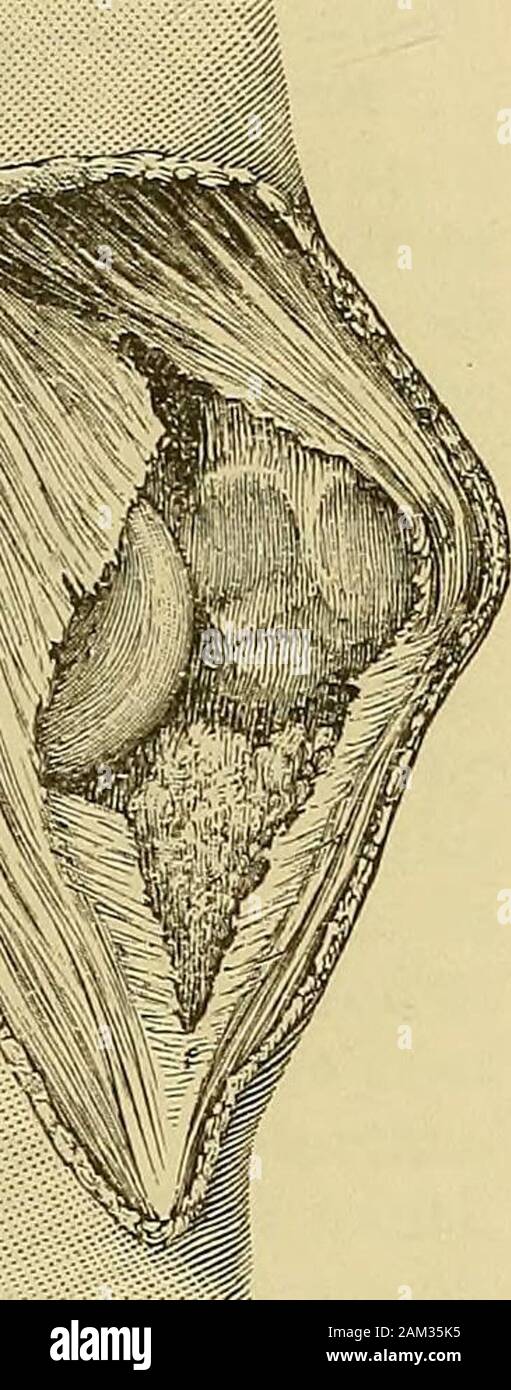
Image details
Contributor:
The Reading Room / Alamy Stock PhotoImage ID:
2AM35K5File size:
7.2 MB (407.5 KB Compressed download)Releases:
Model - no | Property - noDo I need a release?Dimensions:
992 x 2520 px | 8.4 x 21.3 cm | 3.3 x 8.4 inches | 300dpiMore information:
This image is a public domain image, which means either that copyright has expired in the image or the copyright holder has waived their copyright. Alamy charges you a fee for access to the high resolution copy of the image.
This image could have imperfections as it’s either historical or reportage.
A system of surgery . rrence of this dislocation in those with lax ligaments. Re-markable difficulty has sometimes been experienced in the reductionof the rotatory vertical dislocation. This is usually declared by authorsto be due to the wedging of the bone into the inter-condyloid notch.Considering the size of the latter as compared with the edge of thepatella, this explanation seems to me hardly satisfactory. It is farmore likely that the bone lacerates the capsule, and is tightly girtin its new position by the tough ligamentous fibres of this structure.In the cases I have seen, no difficulty was experienced in reduction, by very complete extension of the leg, and forcible pressure uponthe prominent edge of the bone, under deep ether anaesthesia. Supposing, however, the displacement remains irreducible, whatcourse is to be adopted ? Subcutaneous division of the ligamentumpatellae has not proved very satisfactory ? the bone has remainedobstinately fixed after this, and more extensive subcutaneous cutting. M Fig. 416.—Vertical Displacement of thePatella. 1012 DISLOCATIONS. measures have been vainly adopted. A fairly useful joint results ifthe case be left to nature. Bearing this in mind, the surgeon willdo well to leave such a case alone, unless he has complete confi-dence in his practical knowledge of perfect aseptic surgery. Withelaborate care and precaution, it would be justifiable freely to openthe joint in such a case, and divide those structures which couldthus be certainly felt and seen, preventing reduction. The woundin the capsule and soft parts over the joint should be accuratelyunited with scrupulous attention to every detail that may directlyor indirectly promote rapid and perfect union.