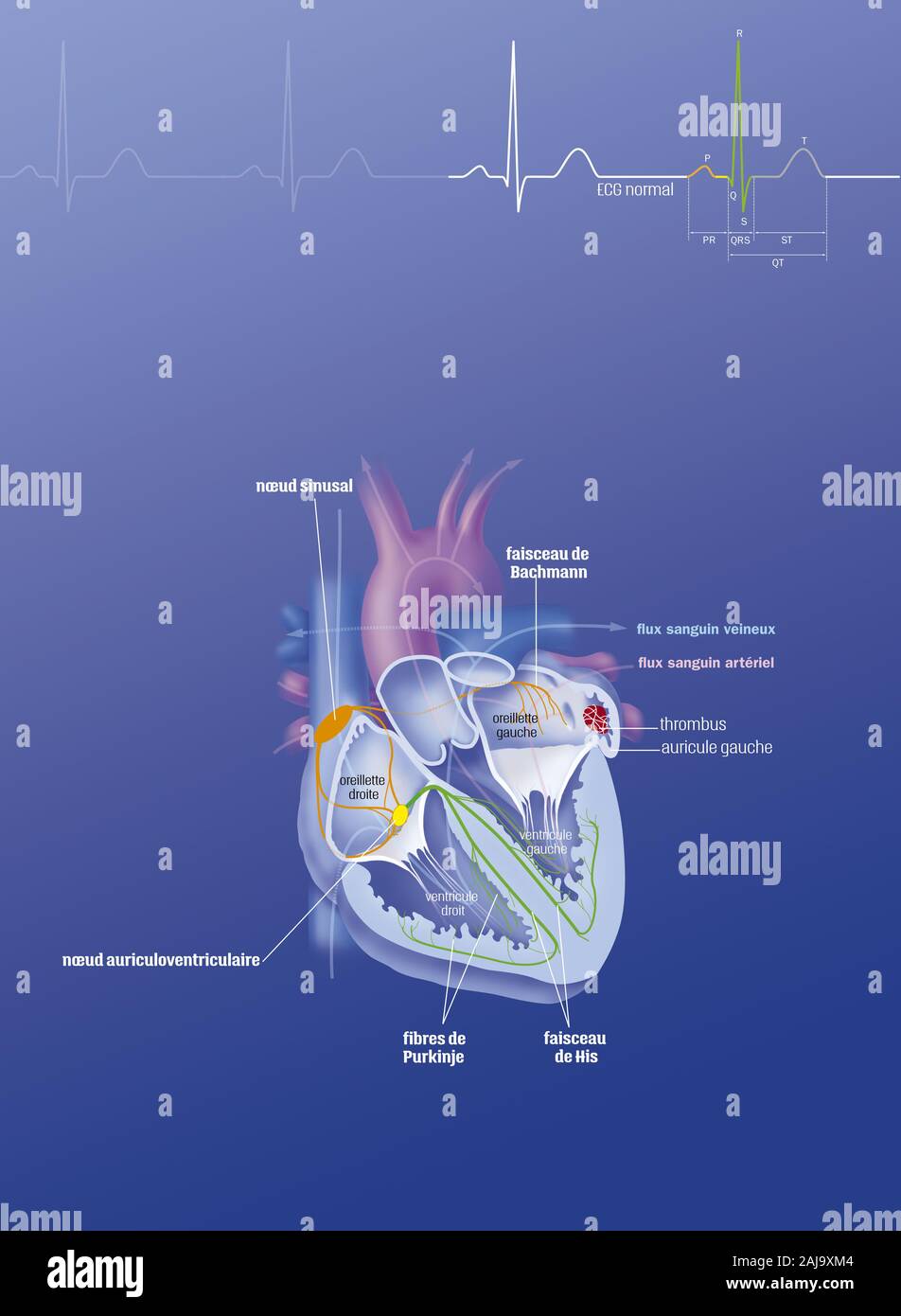
Quick filters:
Purkinje fibers Stock Photos and Images
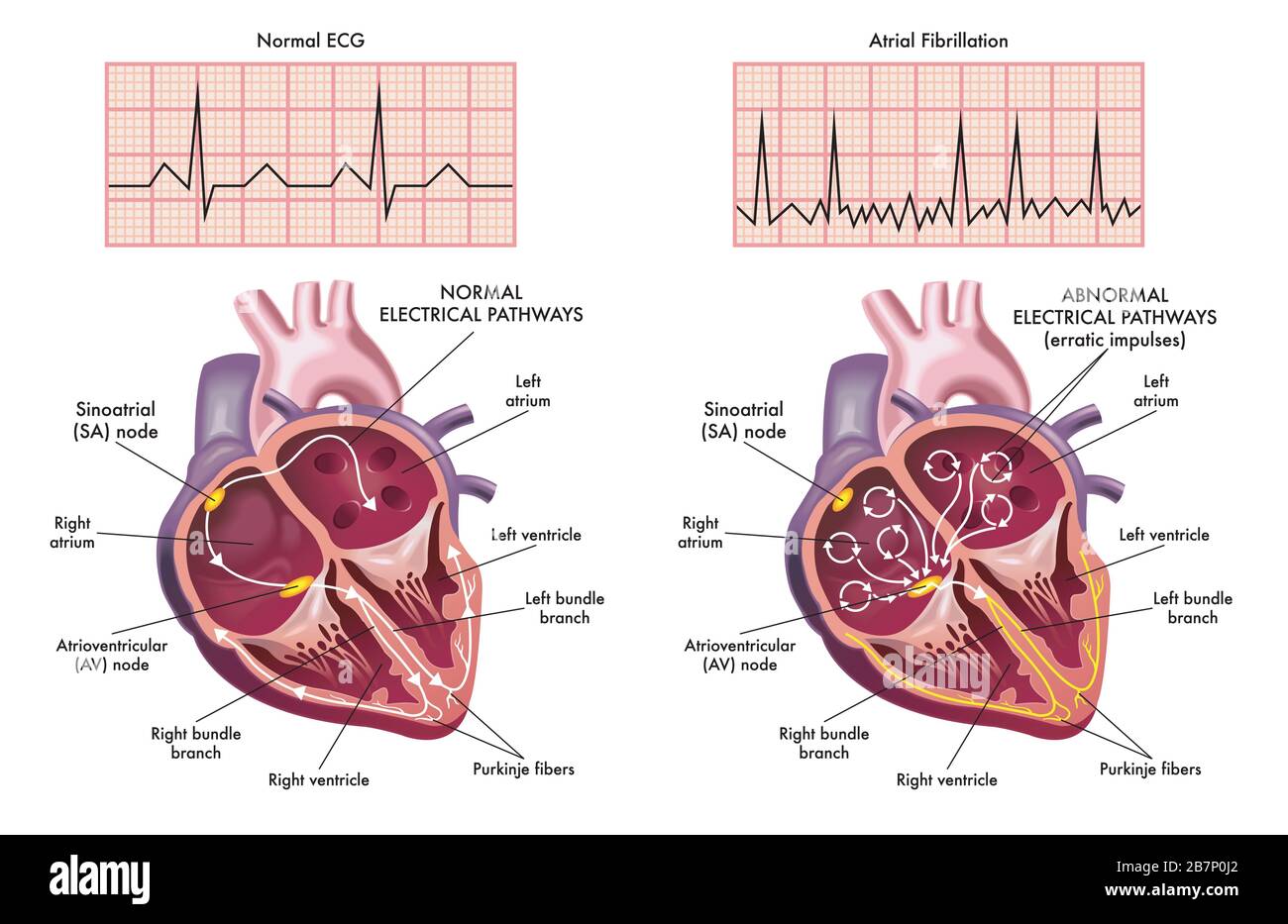 Medical illustration showing the symptoms of a heart with atrial fibrillation compared to normal one. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/medical-illustration-showing-the-symptoms-of-a-heart-with-atrial-fibrillation-compared-to-normal-one-image348993402.html
Medical illustration showing the symptoms of a heart with atrial fibrillation compared to normal one. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/medical-illustration-showing-the-symptoms-of-a-heart-with-atrial-fibrillation-compared-to-normal-one-image348993402.htmlRF2B7P0J2–Medical illustration showing the symptoms of a heart with atrial fibrillation compared to normal one.
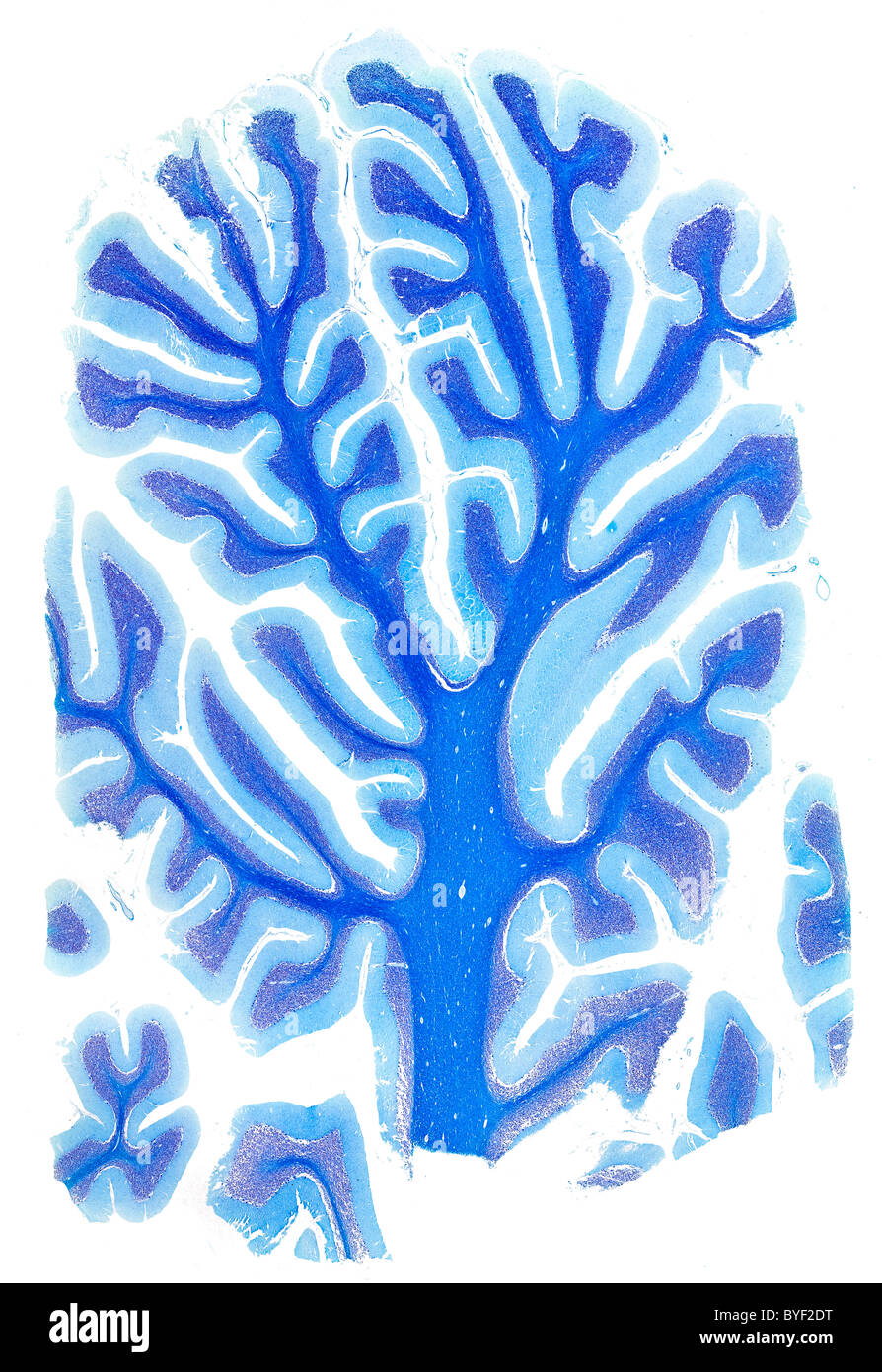 Brightfield photomicrograph human brain cerebellum section Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-brightfield-photomicrograph-human-brain-cerebellum-section-34137316.html
Brightfield photomicrograph human brain cerebellum section Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-brightfield-photomicrograph-human-brain-cerebellum-section-34137316.htmlRMBYF2DT–Brightfield photomicrograph human brain cerebellum section
 Medical illustration showing the symptoms of a heart with atrial fibrillation compared to normal one. Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/medical-illustration-showing-the-symptoms-of-a-heart-with-atrial-fibrillation-compared-to-normal-one-image341394492.html
Medical illustration showing the symptoms of a heart with atrial fibrillation compared to normal one. Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/medical-illustration-showing-the-symptoms-of-a-heart-with-atrial-fibrillation-compared-to-normal-one-image341394492.htmlRF2ARBT4C–Medical illustration showing the symptoms of a heart with atrial fibrillation compared to normal one.
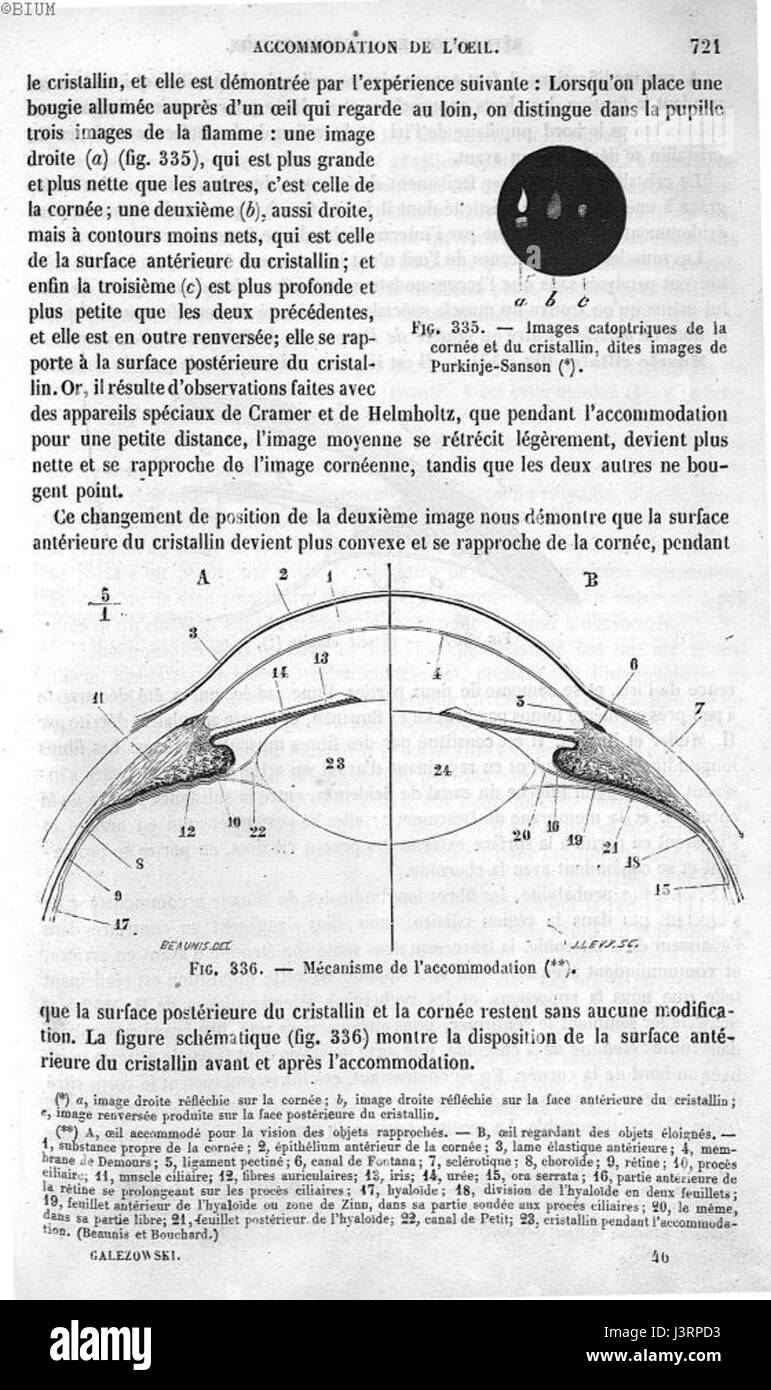 Images de Purkinje Sanson Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-images-de-purkinje-sanson-140049423.html
Images de Purkinje Sanson Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-images-de-purkinje-sanson-140049423.htmlRMJ3RPD3–Images de Purkinje Sanson
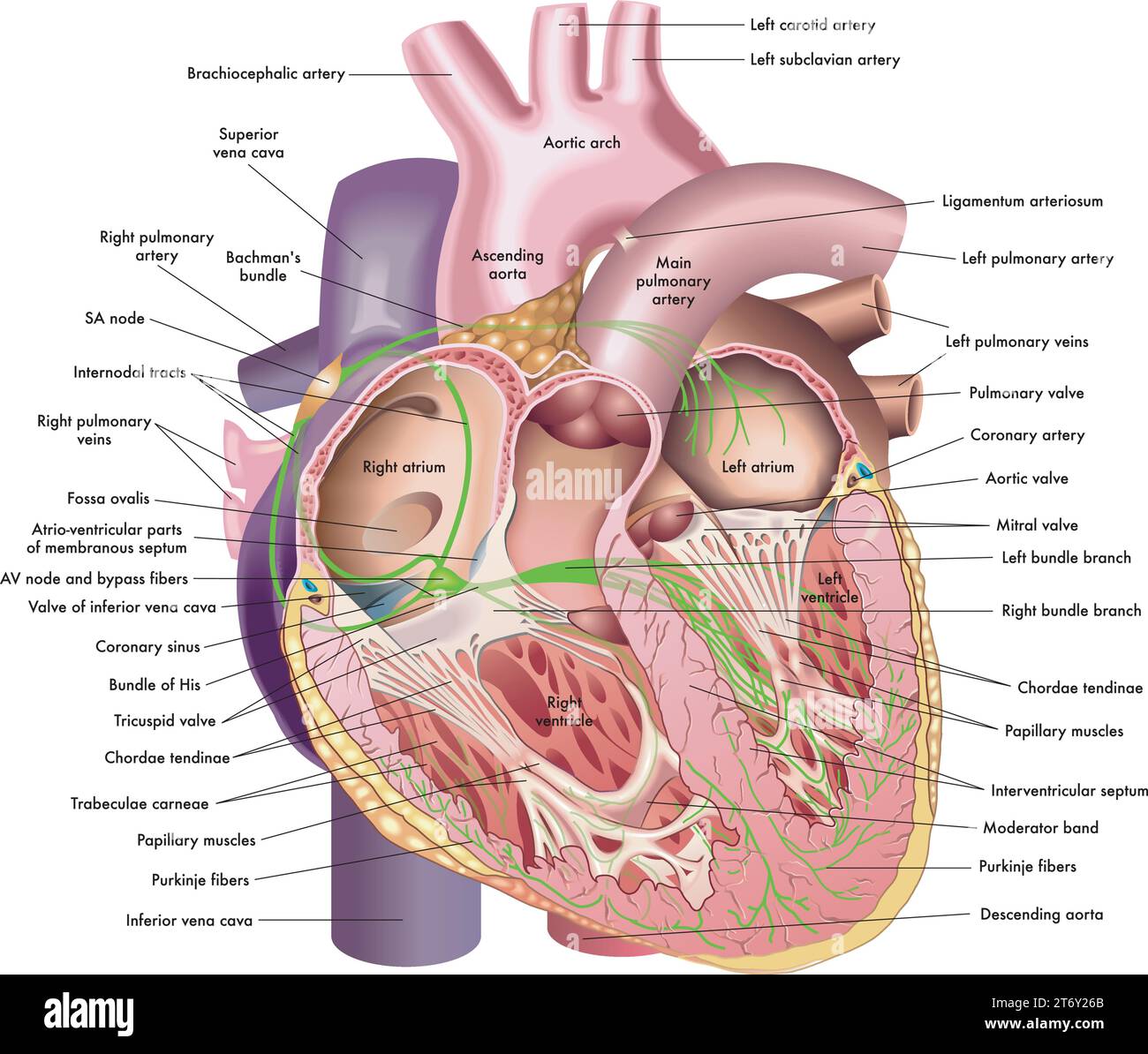 Medical illustration of internal anatomy of the heart, with annotations. Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/medical-illustration-of-internal-anatomy-of-the-heart-with-annotations-image572224531.html
Medical illustration of internal anatomy of the heart, with annotations. Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/medical-illustration-of-internal-anatomy-of-the-heart-with-annotations-image572224531.htmlRF2T6Y26B–Medical illustration of internal anatomy of the heart, with annotations.
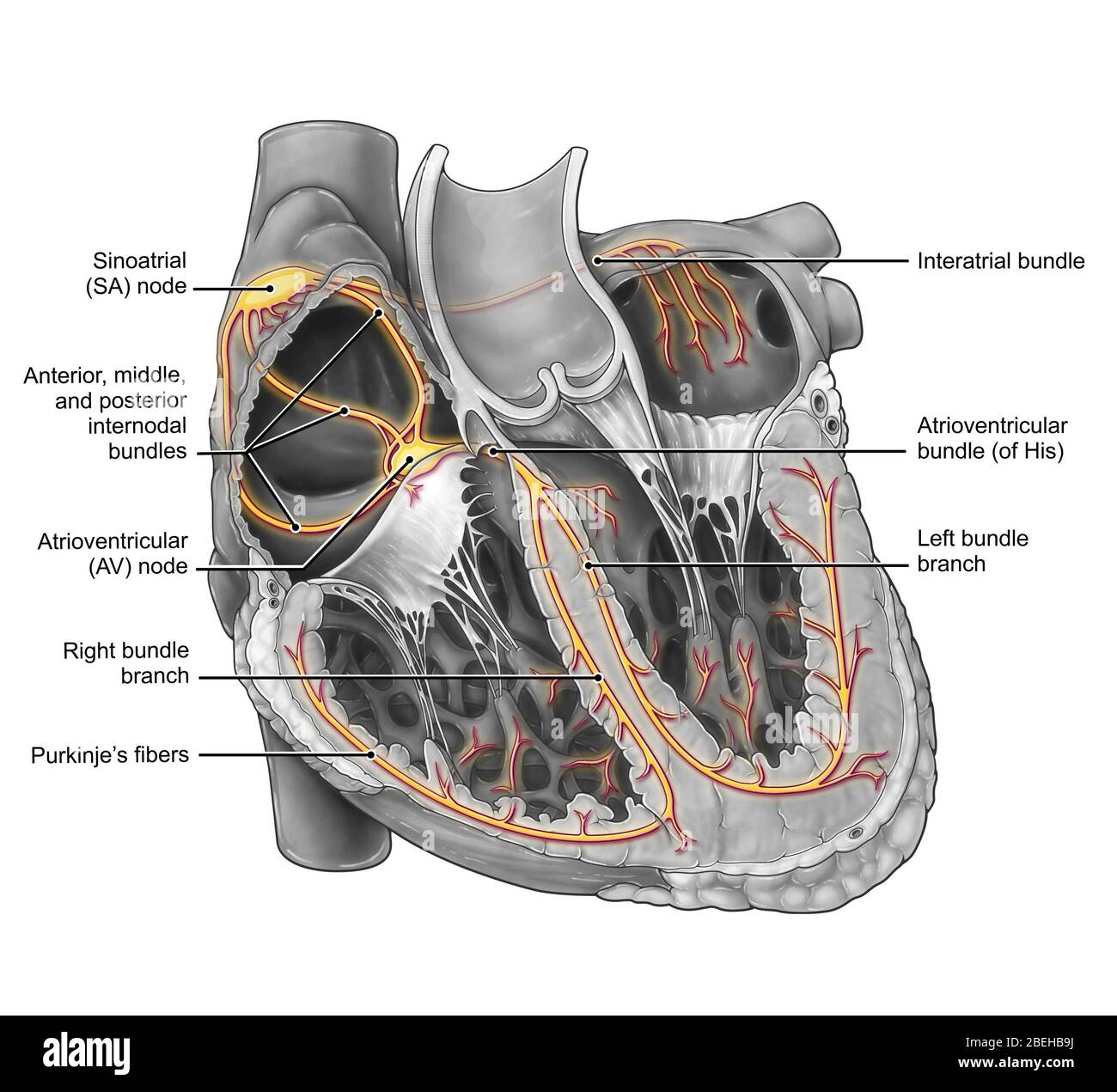
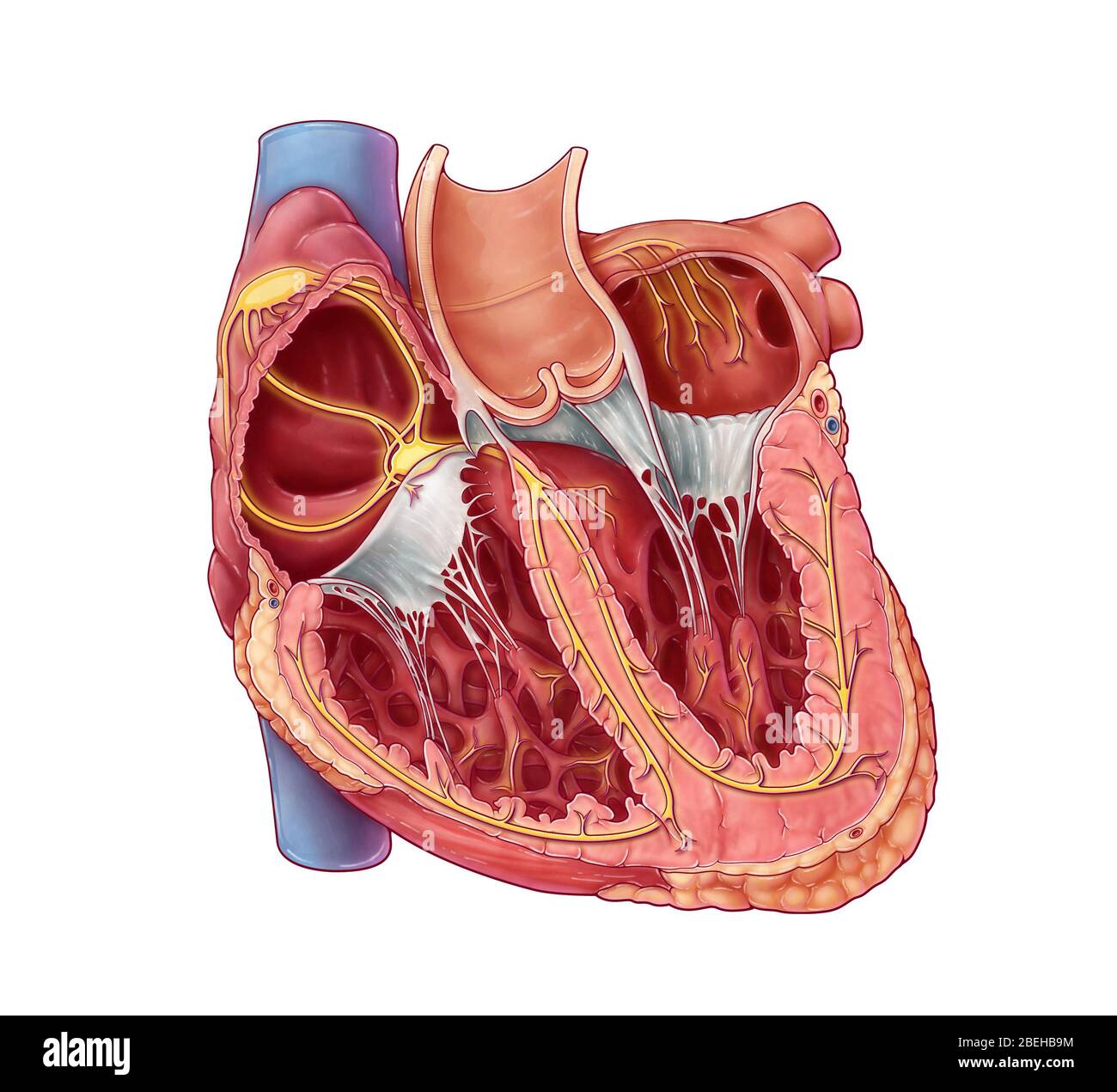 Cardiac Conduction System Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/cardiac-conduction-system-image353194624.html
Cardiac Conduction System Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/cardiac-conduction-system-image353194624.htmlRM2BEHB9M–Cardiac Conduction System
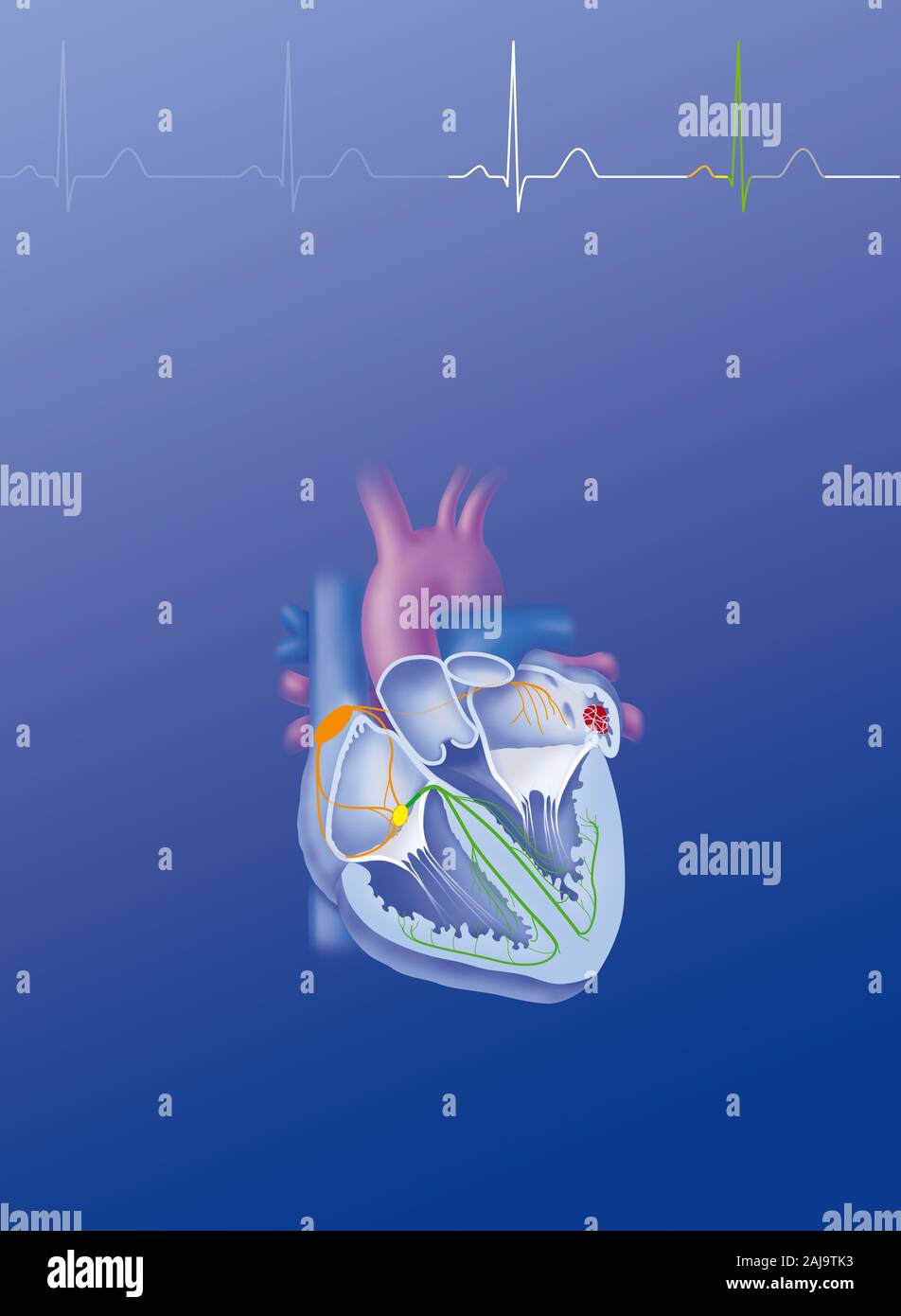 Atriale fibrillation Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/atriale-fibrillation-image338277719.html
Atriale fibrillation Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/atriale-fibrillation-image338277719.htmlRM2AJ9TK3–Atriale fibrillation
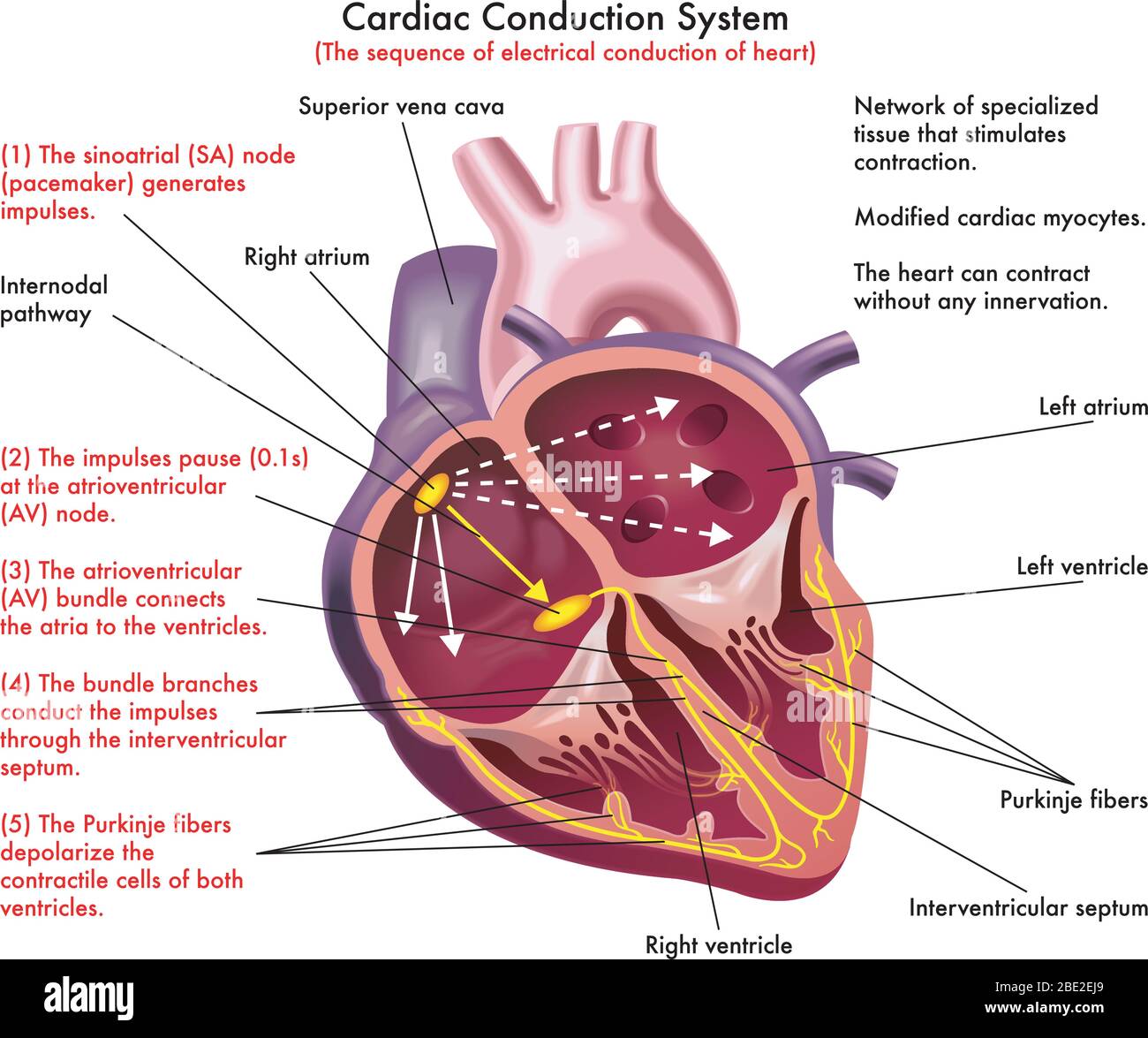 Diagram of Cardiac Conduction System (the sequence of electrical conduction of heart) with annotations Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/diagram-of-cardiac-conduction-system-the-sequence-of-electrical-conduction-of-heart-with-annotations-image352867937.html
Diagram of Cardiac Conduction System (the sequence of electrical conduction of heart) with annotations Stock Vectorhttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/diagram-of-cardiac-conduction-system-the-sequence-of-electrical-conduction-of-heart-with-annotations-image352867937.htmlRF2BE2EJ9–Diagram of Cardiac Conduction System (the sequence of electrical conduction of heart) with annotations
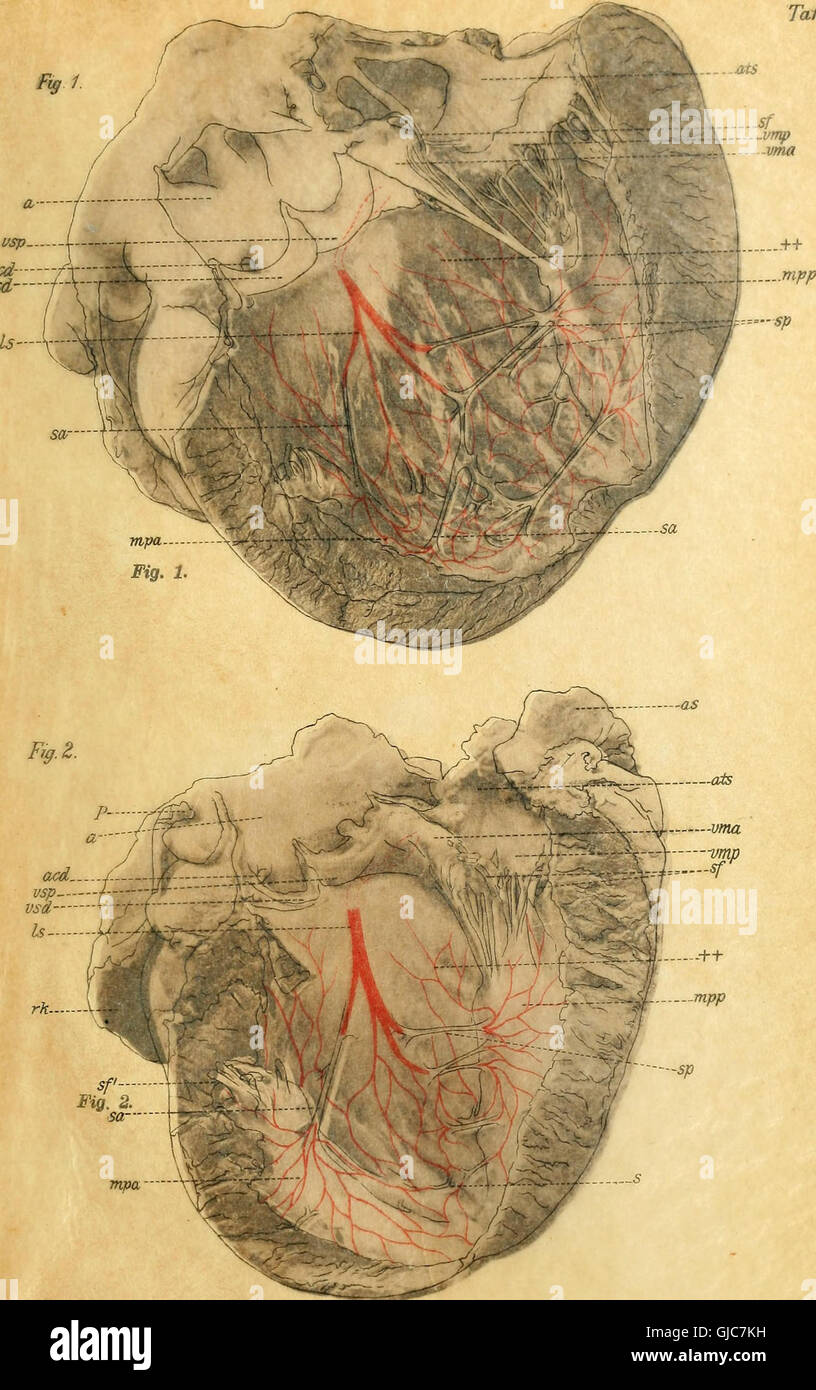 A 1906 anatomical and histological study on the conduction system of the mammalian heart, focusing on the atrioventricular bundle and Purkinje fibers. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-a-1906-anatomical-and-histological-study-on-the-conduction-system-114595477.html
A 1906 anatomical and histological study on the conduction system of the mammalian heart, focusing on the atrioventricular bundle and Purkinje fibers. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-a-1906-anatomical-and-histological-study-on-the-conduction-system-114595477.htmlRMGJC7KH–A 1906 anatomical and histological study on the conduction system of the mammalian heart, focusing on the atrioventricular bundle and Purkinje fibers.
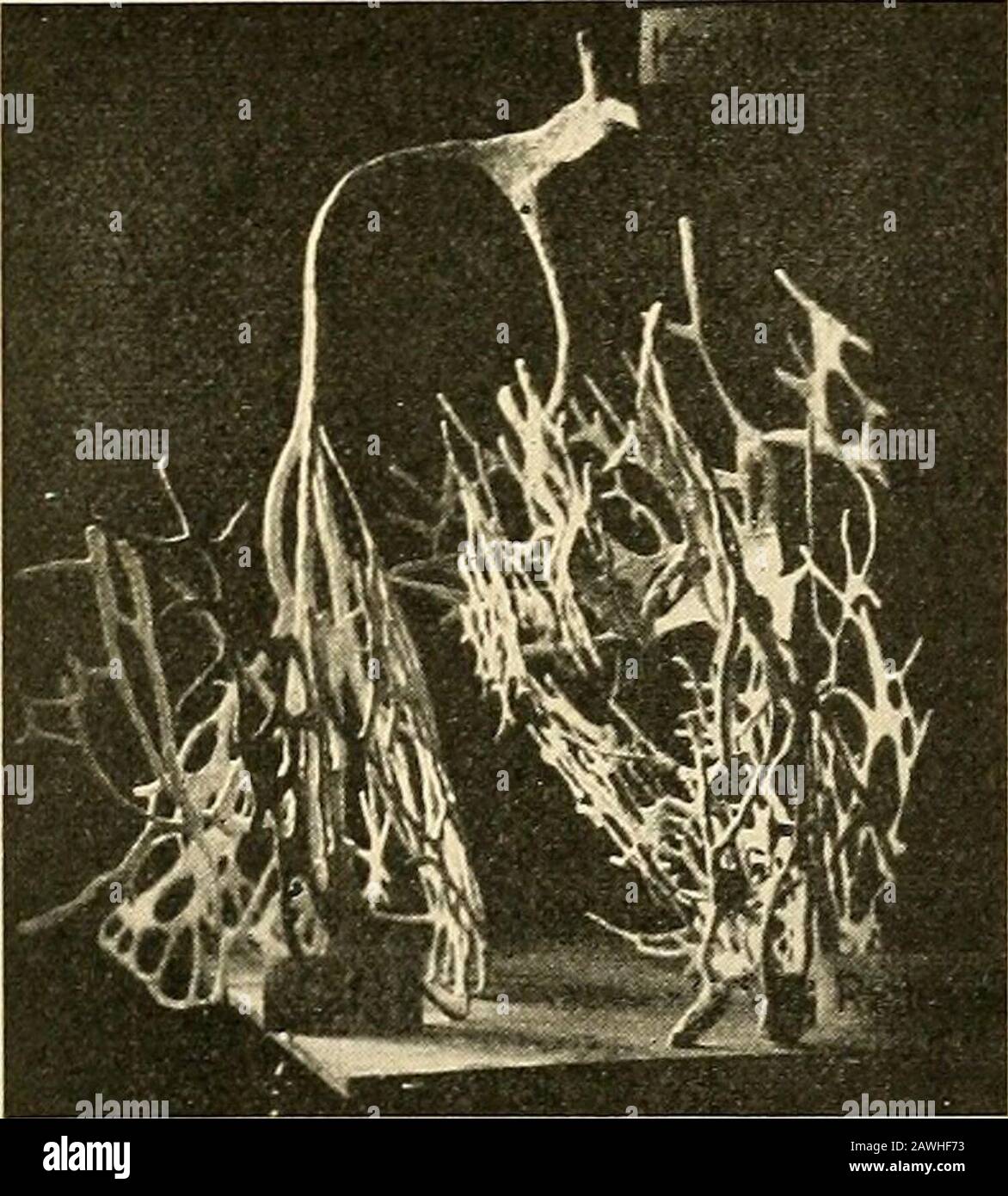 A text-book of physiology for medical students and physicians . as repre-sented in Fig. 226, to form a system of strands that can be traced * See Retzer, Archiv f. Anatomie, 1904, p. 1, and Anatomical Record,2, 149, 1908; Braeunig, Archiv f. Physiologie, 1904, suppl. volume, p. 1;Tawara, Das Reizleitungssystem des Saugethierherzens, Jena, 1906. t DeWitt, Anatomical Record, 3, 475, 1909. THE HEART BEAT. 531 over the inner surface of the ventricles, constituting what wereformerly designated as Purkinje fibers. The auriculoventricularnode in the interauricular septum is connected with the muscula Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-text-book-of-physiology-for-medical-students-and-physicians-as-repre-sented-in-fig-226-to-form-a-system-of-strands-that-can-be-traced-see-retzer-archiv-f-anatomie-1904-p-1-and-anatomical-record2-149-1908-braeunig-archiv-f-physiologie-1904-suppl-volume-p-1tawara-das-reizleitungssystem-des-saugethierherzens-jena-1906-t-dewitt-anatomical-record-3-475-1909-the-heart-beat-531-over-the-inner-surface-of-the-ventricles-constituting-what-wereformerly-designated-as-purkinje-fibers-the-auriculoventricularnode-in-the-interauricular-septum-is-connected-with-the-muscula-image342748535.html
A text-book of physiology for medical students and physicians . as repre-sented in Fig. 226, to form a system of strands that can be traced * See Retzer, Archiv f. Anatomie, 1904, p. 1, and Anatomical Record,2, 149, 1908; Braeunig, Archiv f. Physiologie, 1904, suppl. volume, p. 1;Tawara, Das Reizleitungssystem des Saugethierherzens, Jena, 1906. t DeWitt, Anatomical Record, 3, 475, 1909. THE HEART BEAT. 531 over the inner surface of the ventricles, constituting what wereformerly designated as Purkinje fibers. The auriculoventricularnode in the interauricular septum is connected with the muscula Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-text-book-of-physiology-for-medical-students-and-physicians-as-repre-sented-in-fig-226-to-form-a-system-of-strands-that-can-be-traced-see-retzer-archiv-f-anatomie-1904-p-1-and-anatomical-record2-149-1908-braeunig-archiv-f-physiologie-1904-suppl-volume-p-1tawara-das-reizleitungssystem-des-saugethierherzens-jena-1906-t-dewitt-anatomical-record-3-475-1909-the-heart-beat-531-over-the-inner-surface-of-the-ventricles-constituting-what-wereformerly-designated-as-purkinje-fibers-the-auriculoventricularnode-in-the-interauricular-septum-is-connected-with-the-muscula-image342748535.htmlRM2AWHF73–A text-book of physiology for medical students and physicians . as repre-sented in Fig. 226, to form a system of strands that can be traced * See Retzer, Archiv f. Anatomie, 1904, p. 1, and Anatomical Record,2, 149, 1908; Braeunig, Archiv f. Physiologie, 1904, suppl. volume, p. 1;Tawara, Das Reizleitungssystem des Saugethierherzens, Jena, 1906. t DeWitt, Anatomical Record, 3, 475, 1909. THE HEART BEAT. 531 over the inner surface of the ventricles, constituting what wereformerly designated as Purkinje fibers. The auriculoventricularnode in the interauricular septum is connected with the muscula
 Twoo smooth muscle fibres. Vintage illustration. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/twoo-smooth-muscle-fibres-vintage-illustration-image483154039.html
Twoo smooth muscle fibres. Vintage illustration. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/twoo-smooth-muscle-fibres-vintage-illustration-image483154039.htmlRF2K21FWB–Twoo smooth muscle fibres. Vintage illustration.
![. Figur 26. Sarkosporidicn in den Purkinje'schen Fäden des Herzmuskels vum Schaf. 100 fache Vergrösserang. ^ / beim Kalb, Rind, Schwein, Ziege, Marder, Igel, Hund, Huhn, Taube und Gans vorhanden. Man findet die Sarkosporidien in und unter den Purkinje'schen Fäden als meist gleich grosse ovale Gebilde, in welchen man bei starker Vergrösserung sowohl die sichelförmigen Körperchen, wie auch die gestreifte Umhül- lungsmembran erkennen kann. Ebenso findet man die Sarko- sporidien in dem ]Iyokardium, wo ich dieselben als kurze Schläuche vorwiegend in den peripheren Ab- schnitten des Herzmuskels be- Stock Photo . Figur 26. Sarkosporidicn in den Purkinje'schen Fäden des Herzmuskels vum Schaf. 100 fache Vergrösserang. ^ / beim Kalb, Rind, Schwein, Ziege, Marder, Igel, Hund, Huhn, Taube und Gans vorhanden. Man findet die Sarkosporidien in und unter den Purkinje'schen Fäden als meist gleich grosse ovale Gebilde, in welchen man bei starker Vergrösserung sowohl die sichelförmigen Körperchen, wie auch die gestreifte Umhül- lungsmembran erkennen kann. Ebenso findet man die Sarko- sporidien in dem ]Iyokardium, wo ich dieselben als kurze Schläuche vorwiegend in den peripheren Ab- schnitten des Herzmuskels be- Stock Photo](https://c8.alamy.com/comp/MCR6RK/figur-26-sarkosporidicn-in-den-purkinjeschen-fden-des-herzmuskels-vum-schaf-100-fache-vergrsserang-beim-kalb-rind-schwein-ziege-marder-igel-hund-huhn-taube-und-gans-vorhanden-man-findet-die-sarkosporidien-in-und-unter-den-purkinjeschen-fden-als-meist-gleich-grosse-ovale-gebilde-in-welchen-man-bei-starker-vergrsserung-sowohl-die-sichelfrmigen-krperchen-wie-auch-die-gestreifte-umhl-lungsmembran-erkennen-kann-ebenso-findet-man-die-sarko-sporidien-in-dem-iyokardium-wo-ich-dieselben-als-kurze-schluche-vorwiegend-in-den-peripheren-ab-schnitten-des-herzmuskels-be-MCR6RK.jpg) . Figur 26. Sarkosporidicn in den Purkinje'schen Fäden des Herzmuskels vum Schaf. 100 fache Vergrösserang. ^ / beim Kalb, Rind, Schwein, Ziege, Marder, Igel, Hund, Huhn, Taube und Gans vorhanden. Man findet die Sarkosporidien in und unter den Purkinje'schen Fäden als meist gleich grosse ovale Gebilde, in welchen man bei starker Vergrösserung sowohl die sichelförmigen Körperchen, wie auch die gestreifte Umhül- lungsmembran erkennen kann. Ebenso findet man die Sarko- sporidien in dem ]Iyokardium, wo ich dieselben als kurze Schläuche vorwiegend in den peripheren Ab- schnitten des Herzmuskels be- Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/figur-26-sarkosporidicn-in-den-purkinjeschen-fden-des-herzmuskels-vum-schaf-100-fache-vergrsserang-beim-kalb-rind-schwein-ziege-marder-igel-hund-huhn-taube-und-gans-vorhanden-man-findet-die-sarkosporidien-in-und-unter-den-purkinjeschen-fden-als-meist-gleich-grosse-ovale-gebilde-in-welchen-man-bei-starker-vergrsserung-sowohl-die-sichelfrmigen-krperchen-wie-auch-die-gestreifte-umhl-lungsmembran-erkennen-kann-ebenso-findet-man-die-sarko-sporidien-in-dem-iyokardium-wo-ich-dieselben-als-kurze-schluche-vorwiegend-in-den-peripheren-ab-schnitten-des-herzmuskels-be-image179989815.html
. Figur 26. Sarkosporidicn in den Purkinje'schen Fäden des Herzmuskels vum Schaf. 100 fache Vergrösserang. ^ / beim Kalb, Rind, Schwein, Ziege, Marder, Igel, Hund, Huhn, Taube und Gans vorhanden. Man findet die Sarkosporidien in und unter den Purkinje'schen Fäden als meist gleich grosse ovale Gebilde, in welchen man bei starker Vergrösserung sowohl die sichelförmigen Körperchen, wie auch die gestreifte Umhül- lungsmembran erkennen kann. Ebenso findet man die Sarko- sporidien in dem ]Iyokardium, wo ich dieselben als kurze Schläuche vorwiegend in den peripheren Ab- schnitten des Herzmuskels be- Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/figur-26-sarkosporidicn-in-den-purkinjeschen-fden-des-herzmuskels-vum-schaf-100-fache-vergrsserang-beim-kalb-rind-schwein-ziege-marder-igel-hund-huhn-taube-und-gans-vorhanden-man-findet-die-sarkosporidien-in-und-unter-den-purkinjeschen-fden-als-meist-gleich-grosse-ovale-gebilde-in-welchen-man-bei-starker-vergrsserung-sowohl-die-sichelfrmigen-krperchen-wie-auch-die-gestreifte-umhl-lungsmembran-erkennen-kann-ebenso-findet-man-die-sarko-sporidien-in-dem-iyokardium-wo-ich-dieselben-als-kurze-schluche-vorwiegend-in-den-peripheren-ab-schnitten-des-herzmuskels-be-image179989815.htmlRMMCR6RK–. Figur 26. Sarkosporidicn in den Purkinje'schen Fäden des Herzmuskels vum Schaf. 100 fache Vergrösserang. ^ / beim Kalb, Rind, Schwein, Ziege, Marder, Igel, Hund, Huhn, Taube und Gans vorhanden. Man findet die Sarkosporidien in und unter den Purkinje'schen Fäden als meist gleich grosse ovale Gebilde, in welchen man bei starker Vergrösserung sowohl die sichelförmigen Körperchen, wie auch die gestreifte Umhül- lungsmembran erkennen kann. Ebenso findet man die Sarko- sporidien in dem ]Iyokardium, wo ich dieselben als kurze Schläuche vorwiegend in den peripheren Ab- schnitten des Herzmuskels be-
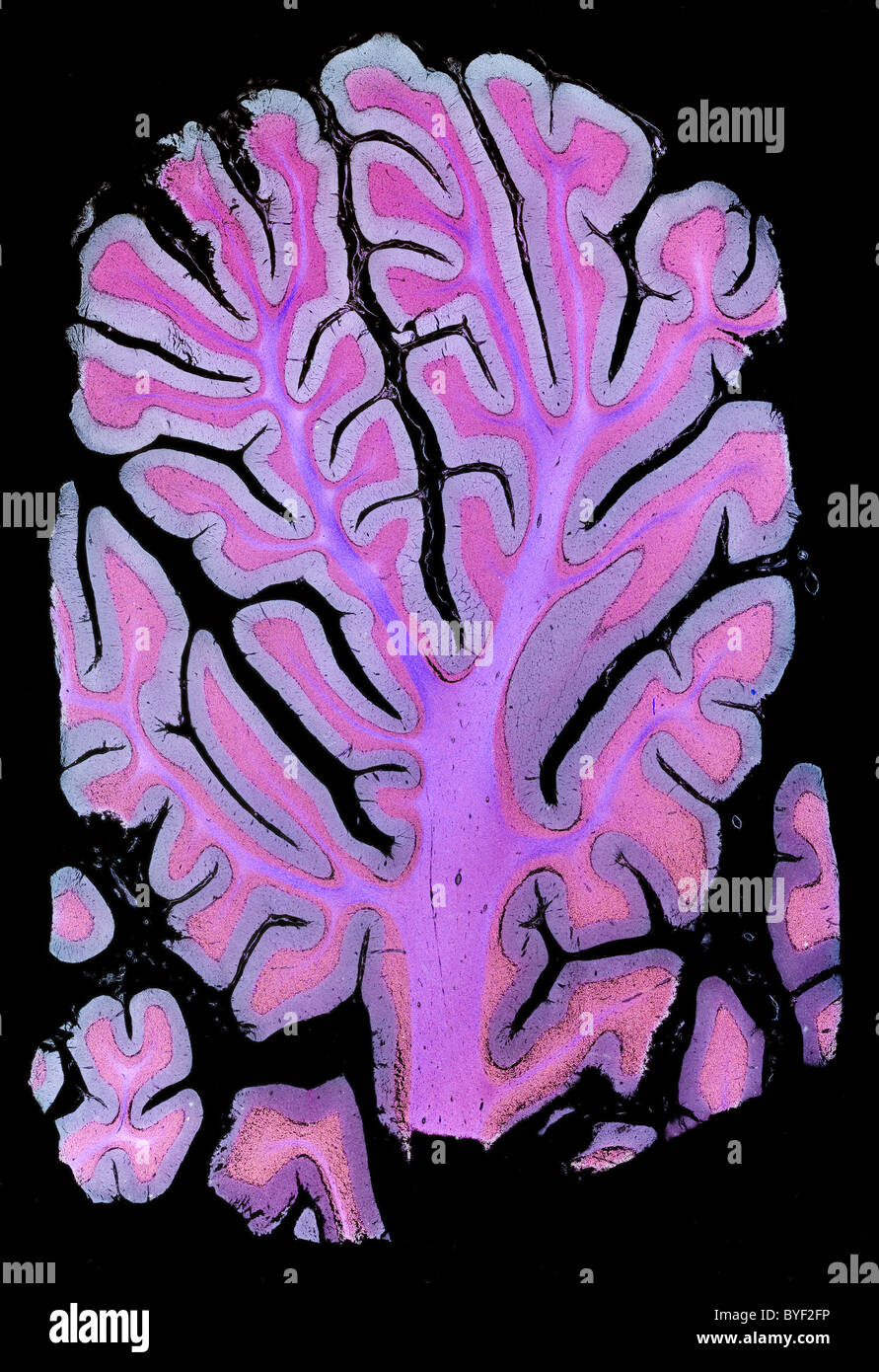 Darkfield photomicrograph human brain cerebellum section Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-darkfield-photomicrograph-human-brain-cerebellum-section-34137370.html
Darkfield photomicrograph human brain cerebellum section Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-darkfield-photomicrograph-human-brain-cerebellum-section-34137370.htmlRMBYF2FP–Darkfield photomicrograph human brain cerebellum section
 Cardiac Conduction System Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/cardiac-conduction-system-image353194622.html
Cardiac Conduction System Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/cardiac-conduction-system-image353194622.htmlRM2BEHB9J–Cardiac Conduction System
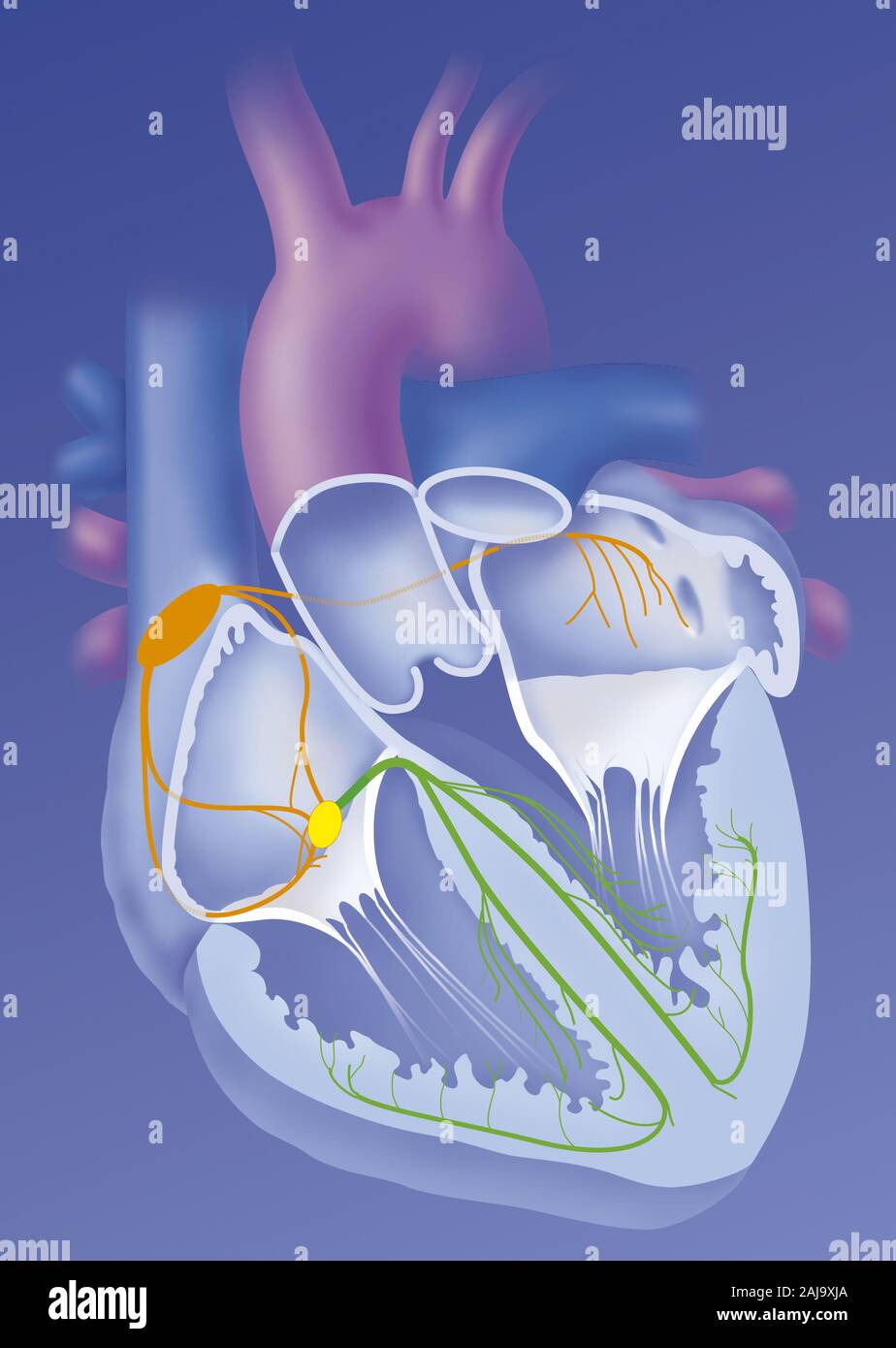 Heart and cardionector system Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/heart-and-cardionector-system-image338279266.html
Heart and cardionector system Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/heart-and-cardionector-system-image338279266.htmlRM2AJ9XJA–Heart and cardionector system
 'Das Reizleitungensystem des Säugetierherzens' (1906) is a detailed anatomical and histological study on the conduction system of the mammalian heart, specifically focusing on the atrioventricular bundle and Purkinje fibers. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-das-reizleitungensystem-des-sugetierherzens-1906-is-a-detailed-anatomical-114595705.html
'Das Reizleitungensystem des Säugetierherzens' (1906) is a detailed anatomical and histological study on the conduction system of the mammalian heart, specifically focusing on the atrioventricular bundle and Purkinje fibers. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-das-reizleitungensystem-des-sugetierherzens-1906-is-a-detailed-anatomical-114595705.htmlRMGJC7YN–'Das Reizleitungensystem des Säugetierherzens' (1906) is a detailed anatomical and histological study on the conduction system of the mammalian heart, specifically focusing on the atrioventricular bundle and Purkinje fibers.
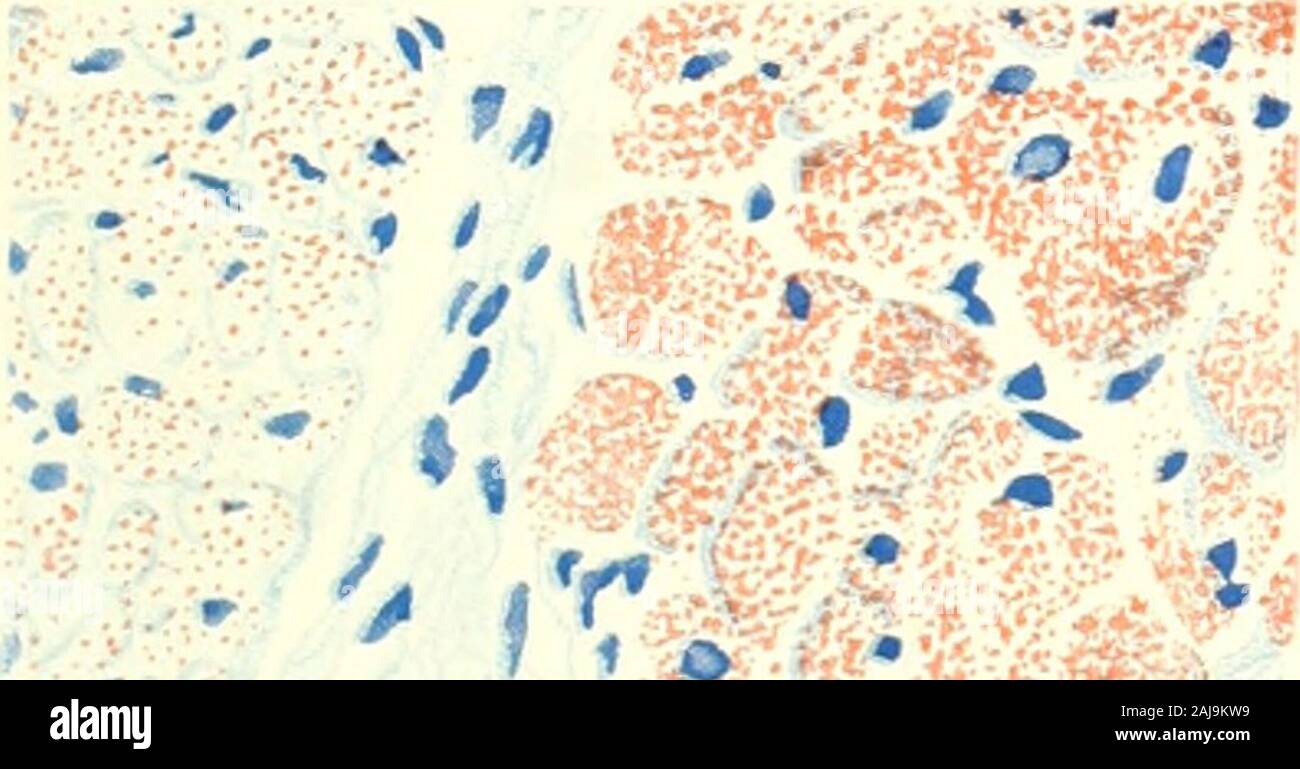 The American journal of anatomy . bers is large; L, light fiber; D, dark fiber. X 500. 5 Longitudinal section from same preparation as in figure 4; L, light fibers;D, dark fibers (animal 46, table 3). X 500. 6 From the interventricular septum of a cat killed 17 hours after receivinga large meal of pork fat (animal 84, table 5). Very large amount of fat in cardiacfibers, C; moderate or large amount in Purkinje fibers of the left limb of bundle ofHis, P. X500. 7 From the interventricular septum of an eight months human fetus (animal141, table 8). There is a moderate amount of fat in the cardiac Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-american-journal-of-anatomy-bers-is-large-l-light-fiber-d-dark-fiber-x-500-5-longitudinal-section-from-same-preparation-as-in-figure-4-l-light-fibersd-dark-fibers-animal-46-table-3-x-500-6-from-the-interventricular-septum-of-a-cat-killed-17-hours-after-receivinga-large-meal-of-pork-fat-animal-84-table-5-very-large-amount-of-fat-in-cardiacfibers-c-moderate-or-large-amount-in-purkinje-fibers-of-the-left-limb-of-bundle-ofhis-p-x500-7-from-the-interventricular-septum-of-an-eight-months-human-fetus-animal141-table-8-there-is-a-moderate-amount-of-fat-in-the-cardiac-image338273973.html
The American journal of anatomy . bers is large; L, light fiber; D, dark fiber. X 500. 5 Longitudinal section from same preparation as in figure 4; L, light fibers;D, dark fibers (animal 46, table 3). X 500. 6 From the interventricular septum of a cat killed 17 hours after receivinga large meal of pork fat (animal 84, table 5). Very large amount of fat in cardiacfibers, C; moderate or large amount in Purkinje fibers of the left limb of bundle ofHis, P. X500. 7 From the interventricular septum of an eight months human fetus (animal141, table 8). There is a moderate amount of fat in the cardiac Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-american-journal-of-anatomy-bers-is-large-l-light-fiber-d-dark-fiber-x-500-5-longitudinal-section-from-same-preparation-as-in-figure-4-l-light-fibersd-dark-fibers-animal-46-table-3-x-500-6-from-the-interventricular-septum-of-a-cat-killed-17-hours-after-receivinga-large-meal-of-pork-fat-animal-84-table-5-very-large-amount-of-fat-in-cardiacfibers-c-moderate-or-large-amount-in-purkinje-fibers-of-the-left-limb-of-bundle-ofhis-p-x500-7-from-the-interventricular-septum-of-an-eight-months-human-fetus-animal141-table-8-there-is-a-moderate-amount-of-fat-in-the-cardiac-image338273973.htmlRM2AJ9KW9–The American journal of anatomy . bers is large; L, light fiber; D, dark fiber. X 500. 5 Longitudinal section from same preparation as in figure 4; L, light fibers;D, dark fibers (animal 46, table 3). X 500. 6 From the interventricular septum of a cat killed 17 hours after receivinga large meal of pork fat (animal 84, table 5). Very large amount of fat in cardiacfibers, C; moderate or large amount in Purkinje fibers of the left limb of bundle ofHis, P. X500. 7 From the interventricular septum of an eight months human fetus (animal141, table 8). There is a moderate amount of fat in the cardiac
 . Figur 27. Sarkosporidicn in den Purkinje'schen Fäden des Herzmuskels vom Schaf. 500 fache Vergrösserung. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/figur-27-sarkosporidicn-in-den-purkinjeschen-fden-des-herzmuskels-vom-schaf-500-fache-vergrsserung-image179989799.html
. Figur 27. Sarkosporidicn in den Purkinje'schen Fäden des Herzmuskels vom Schaf. 500 fache Vergrösserung. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/figur-27-sarkosporidicn-in-den-purkinjeschen-fden-des-herzmuskels-vom-schaf-500-fache-vergrsserung-image179989799.htmlRMMCR6R3–. Figur 27. Sarkosporidicn in den Purkinje'schen Fäden des Herzmuskels vom Schaf. 500 fache Vergrösserung.
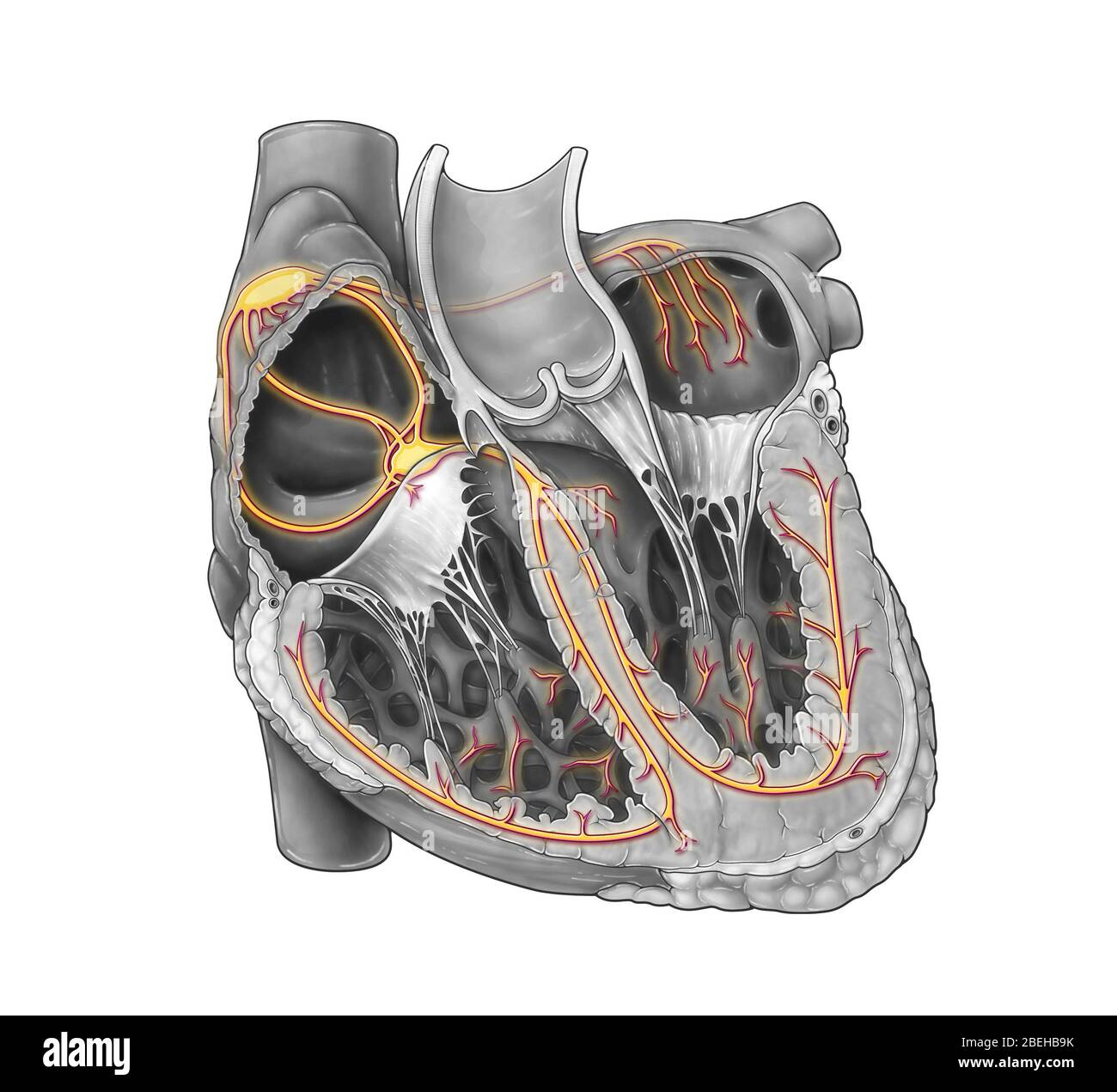 Cardiac Conduction System Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/cardiac-conduction-system-image353194623.html
Cardiac Conduction System Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/cardiac-conduction-system-image353194623.htmlRM2BEHB9K–Cardiac Conduction System
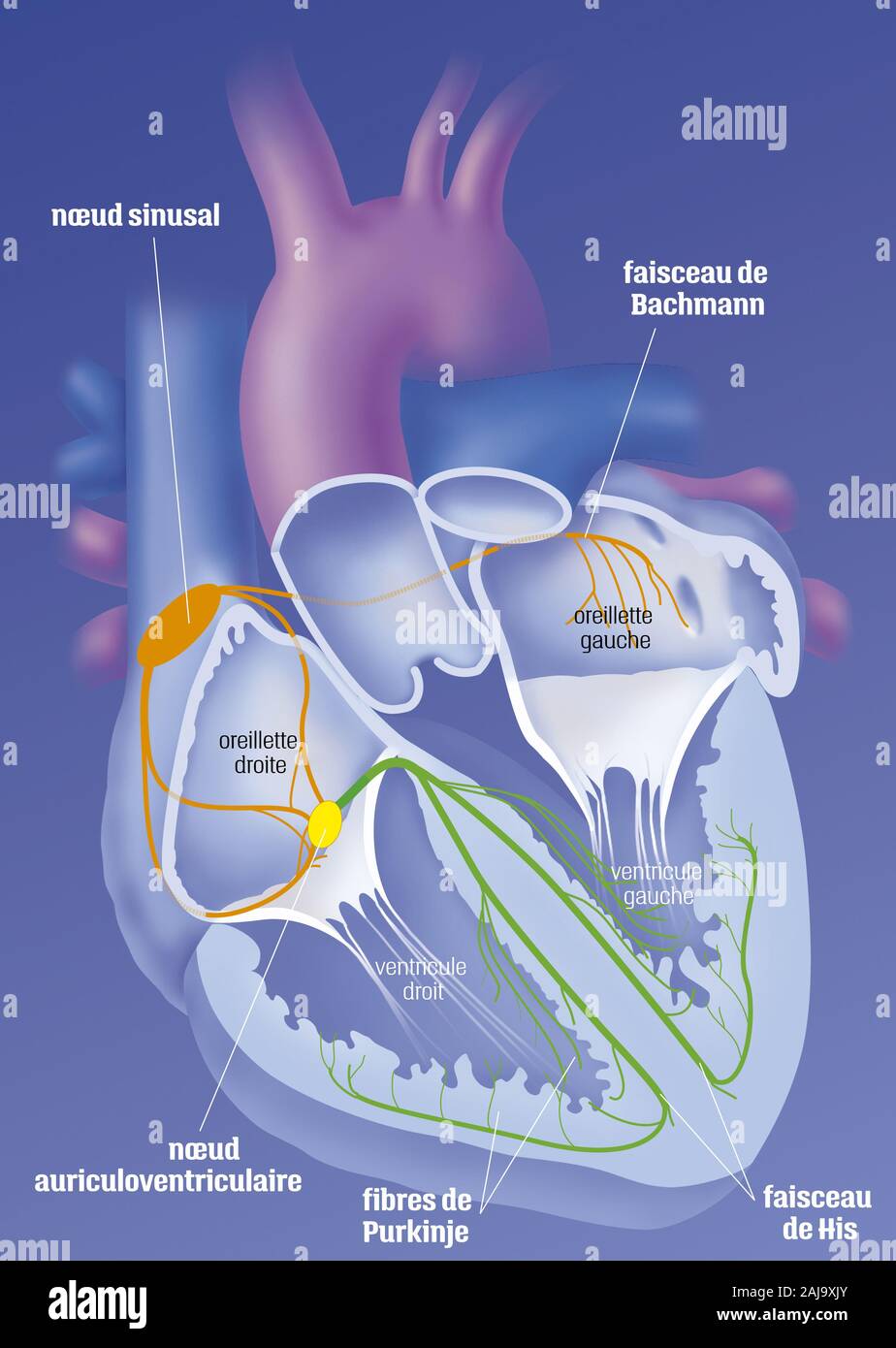 Heart and cardionector system Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/heart-and-cardionector-system-image338279283.html
Heart and cardionector system Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/heart-and-cardionector-system-image338279283.htmlRM2AJ9XJY–Heart and cardionector system
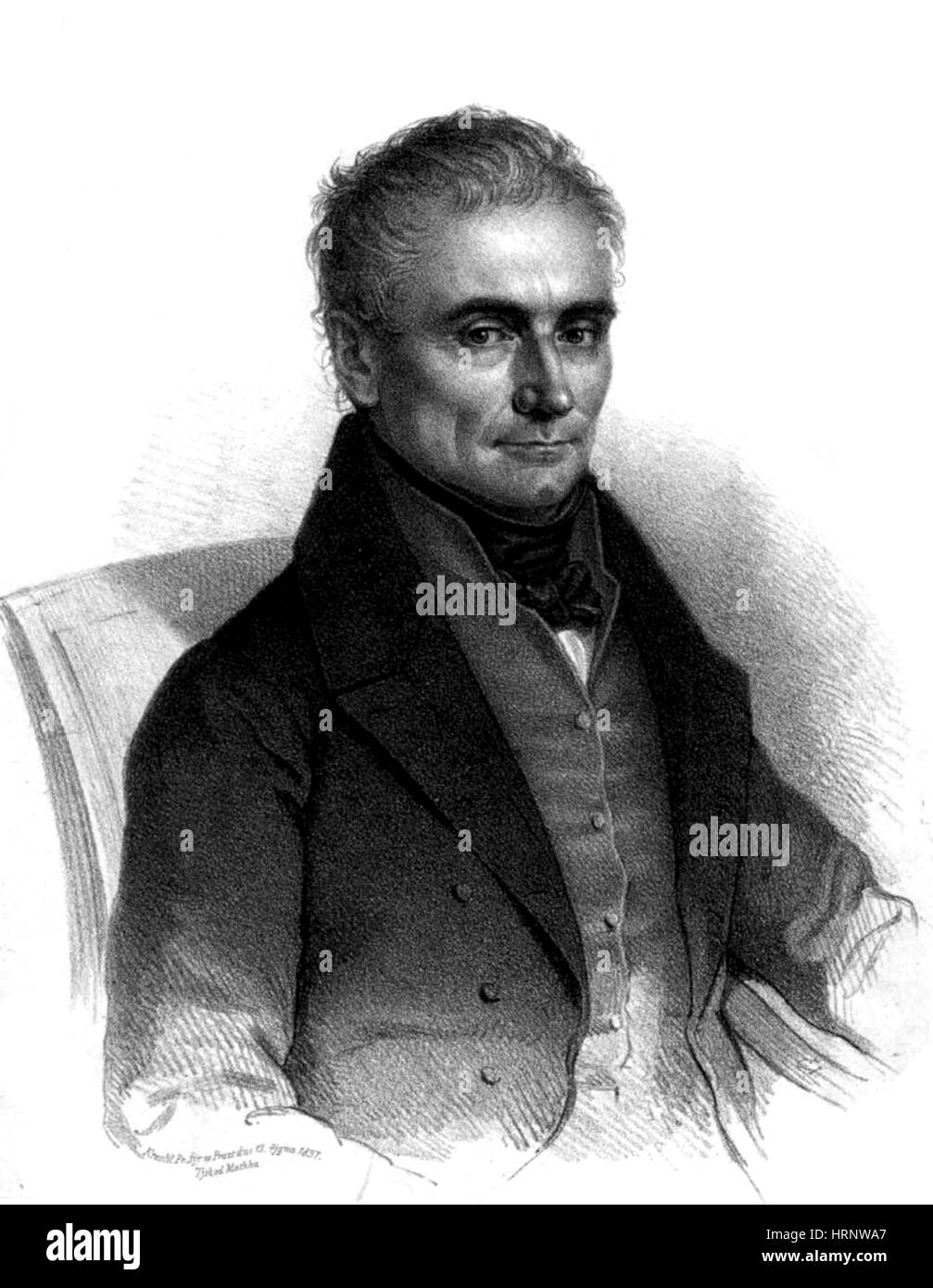 Johannes Purkinje, Czech Physiologist Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-johannes-purkinje-czech-physiologist-135090543.html
Johannes Purkinje, Czech Physiologist Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-johannes-purkinje-czech-physiologist-135090543.htmlRMHRNWA7–Johannes Purkinje, Czech Physiologist
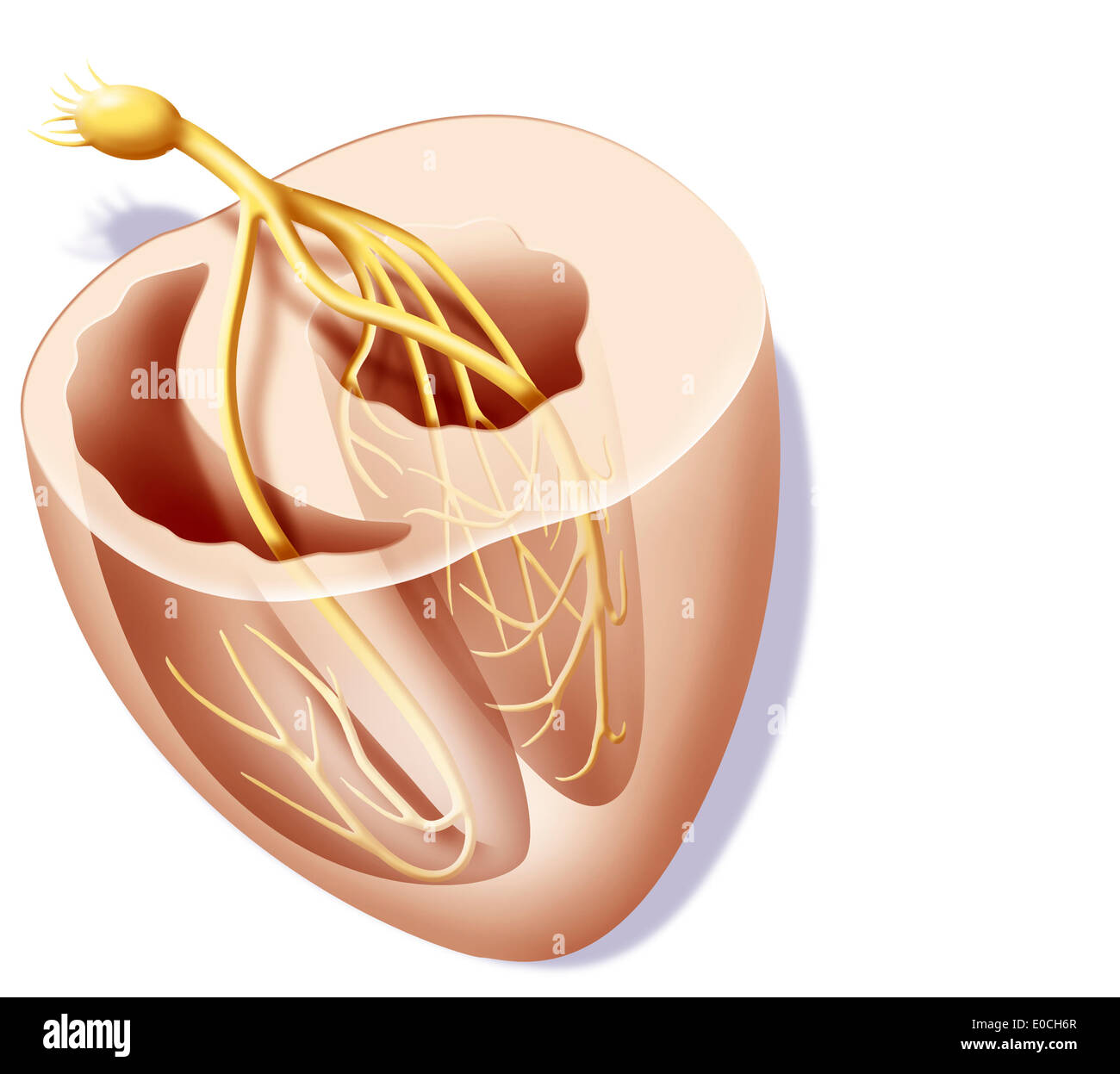 Heart rate, illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/heart-rate-illustration-image69118415.html
Heart rate, illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/heart-rate-illustration-image69118415.htmlRME0CH6R–Heart rate, illustration
 *Das Reizleitungensystem des Säugetierherzens* (1906) is an anatomical and histological study focusing on the conduction system of the mammalian heart, including the atrioventricular bundle and Purkinje fibers. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-das-reizleitungensystem-des-sugetierherzens-1906-is-an-anatomical-114595698.html
*Das Reizleitungensystem des Säugetierherzens* (1906) is an anatomical and histological study focusing on the conduction system of the mammalian heart, including the atrioventricular bundle and Purkinje fibers. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-das-reizleitungensystem-des-sugetierherzens-1906-is-an-anatomical-114595698.htmlRMGJC7YE–*Das Reizleitungensystem des Säugetierherzens* (1906) is an anatomical and histological study focusing on the conduction system of the mammalian heart, including the atrioventricular bundle and Purkinje fibers.
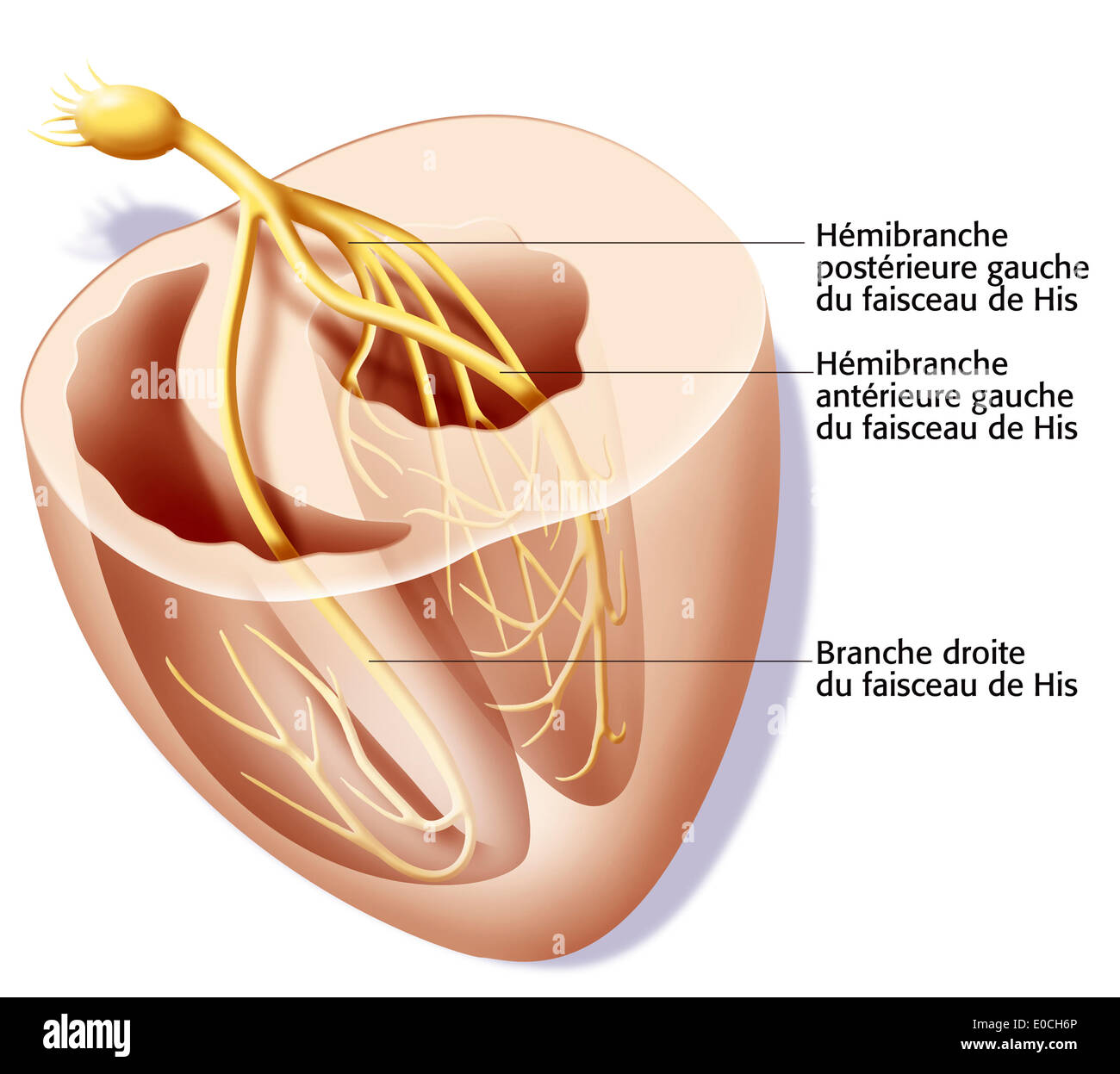
 . A text-book of physiology : for medical students and physicians . as repre-sented in Fig. 226, to form a system of strands that can be traced * See Retzer, Archiv f. Anatomie, 1904, p. 1, and Anatomical Record,2, 149, 1908; Braeunig, Archiv f. Physiologie, 1904, suppl. volume, p. 1;Tawara, Das Reizleitungssystem des Saugethierherzens, Jena, 1906. t DeWitt, Anatomical Record, 3, 475, 1909. THE HEART BEAT. 539 over the inner surface of the ventricles, constituting what wereformerly designated as Purkinje fibers. The auriculoventricularnode in the interauricular septum is connected with the mus Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-text-book-of-physiology-for-medical-students-and-physicians-as-repre-sented-in-fig-226-to-form-a-system-of-strands-that-can-be-traced-see-retzer-archiv-f-anatomie-1904-p-1-and-anatomical-record2-149-1908-braeunig-archiv-f-physiologie-1904-suppl-volume-p-1tawara-das-reizleitungssystem-des-saugethierherzens-jena-1906-t-dewitt-anatomical-record-3-475-1909-the-heart-beat-539-over-the-inner-surface-of-the-ventricles-constituting-what-wereformerly-designated-as-purkinje-fibers-the-auriculoventricularnode-in-the-interauricular-septum-is-connected-with-the-mus-image370181106.html
. A text-book of physiology : for medical students and physicians . as repre-sented in Fig. 226, to form a system of strands that can be traced * See Retzer, Archiv f. Anatomie, 1904, p. 1, and Anatomical Record,2, 149, 1908; Braeunig, Archiv f. Physiologie, 1904, suppl. volume, p. 1;Tawara, Das Reizleitungssystem des Saugethierherzens, Jena, 1906. t DeWitt, Anatomical Record, 3, 475, 1909. THE HEART BEAT. 539 over the inner surface of the ventricles, constituting what wereformerly designated as Purkinje fibers. The auriculoventricularnode in the interauricular septum is connected with the mus Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-text-book-of-physiology-for-medical-students-and-physicians-as-repre-sented-in-fig-226-to-form-a-system-of-strands-that-can-be-traced-see-retzer-archiv-f-anatomie-1904-p-1-and-anatomical-record2-149-1908-braeunig-archiv-f-physiologie-1904-suppl-volume-p-1tawara-das-reizleitungssystem-des-saugethierherzens-jena-1906-t-dewitt-anatomical-record-3-475-1909-the-heart-beat-539-over-the-inner-surface-of-the-ventricles-constituting-what-wereformerly-designated-as-purkinje-fibers-the-auriculoventricularnode-in-the-interauricular-septum-is-connected-with-the-mus-image370181106.htmlRM2CE75NP–. A text-book of physiology : for medical students and physicians . as repre-sented in Fig. 226, to form a system of strands that can be traced * See Retzer, Archiv f. Anatomie, 1904, p. 1, and Anatomical Record,2, 149, 1908; Braeunig, Archiv f. Physiologie, 1904, suppl. volume, p. 1;Tawara, Das Reizleitungssystem des Saugethierherzens, Jena, 1906. t DeWitt, Anatomical Record, 3, 475, 1909. THE HEART BEAT. 539 over the inner surface of the ventricles, constituting what wereformerly designated as Purkinje fibers. The auriculoventricularnode in the interauricular septum is connected with the mus
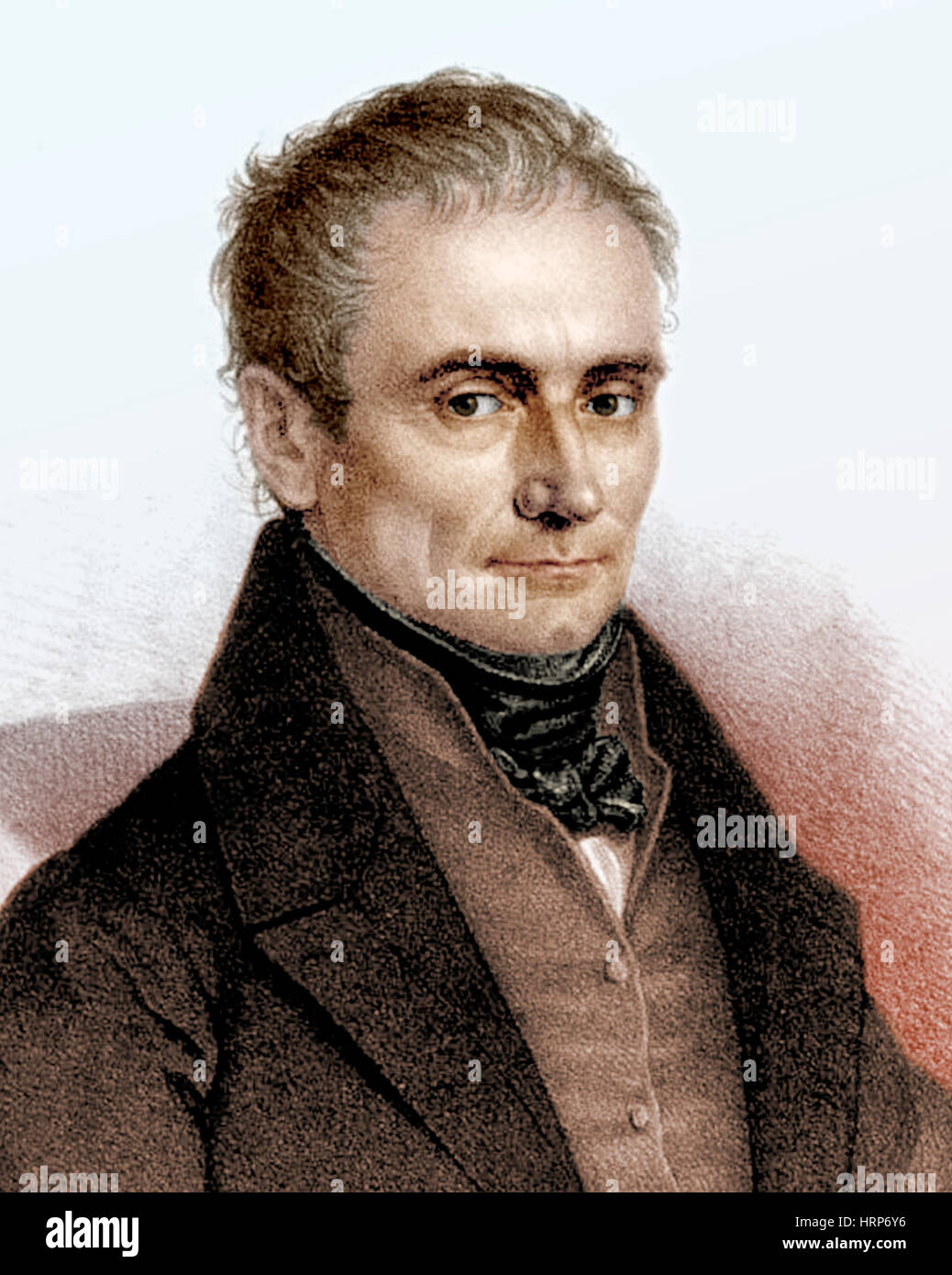 Johannes Purkinje, Czech Physiologist Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-johannes-purkinje-czech-physiologist-135098074.html
Johannes Purkinje, Czech Physiologist Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-johannes-purkinje-czech-physiologist-135098074.htmlRMHRP6Y6–Johannes Purkinje, Czech Physiologist
 Heart rate, illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/heart-rate-illustration-image69118414.html
Heart rate, illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/heart-rate-illustration-image69118414.htmlRME0CH6P–Heart rate, illustration
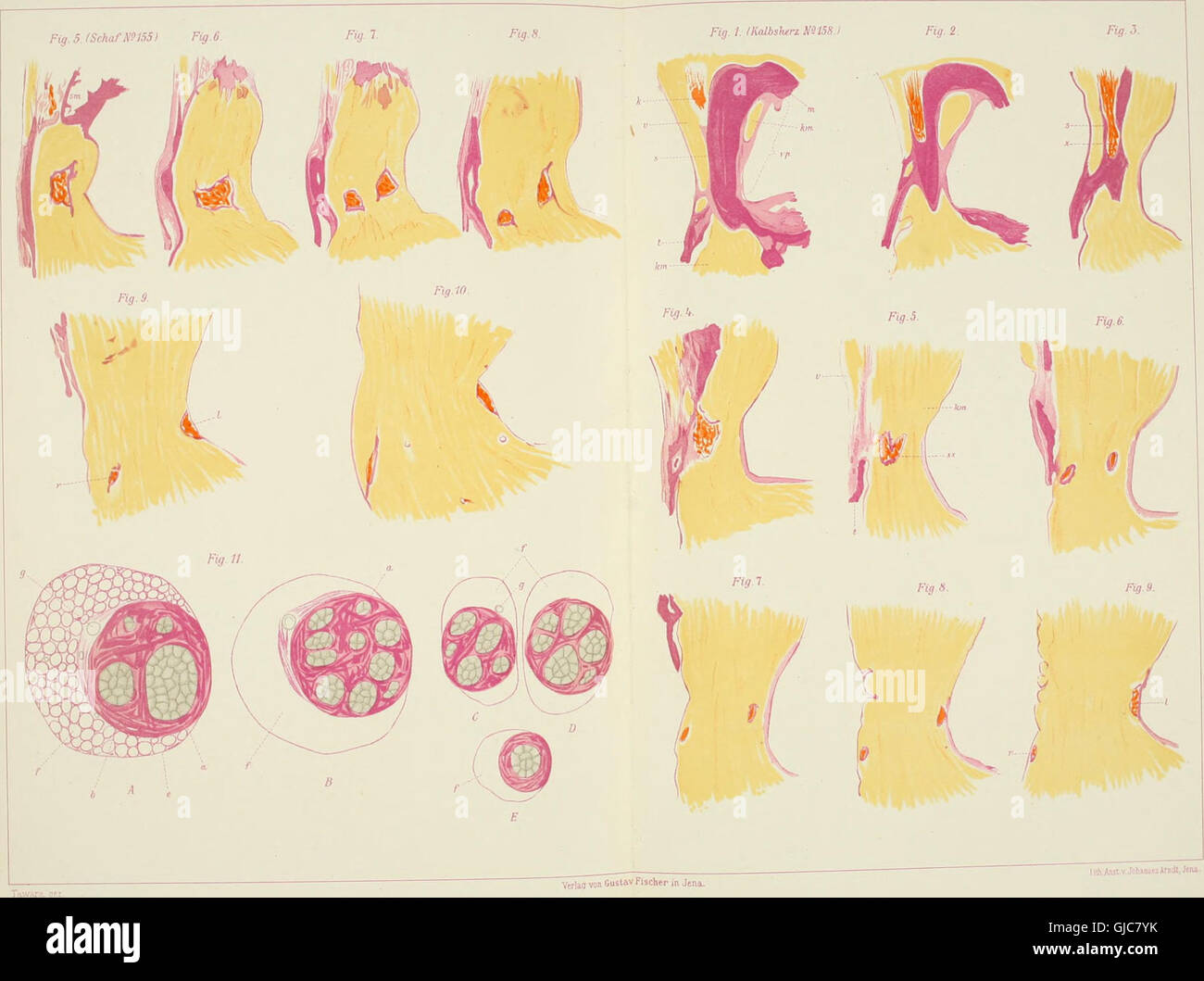 *Das Reizleitungenssystem des Säugetierherzens* (1906) is an anatomical and histological study of the mammalian heart’s conduction system, focusing on the atrioventricular bundle and Purkinje fibers, essential for understanding heart function and electrical signaling in mammals. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-das-reizleitungenssystem-des-sugetierherzens-1906-is-an-anatomical-114595703.html
*Das Reizleitungenssystem des Säugetierherzens* (1906) is an anatomical and histological study of the mammalian heart’s conduction system, focusing on the atrioventricular bundle and Purkinje fibers, essential for understanding heart function and electrical signaling in mammals. Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-das-reizleitungenssystem-des-sugetierherzens-1906-is-an-anatomical-114595703.htmlRMGJC7YK–*Das Reizleitungenssystem des Säugetierherzens* (1906) is an anatomical and histological study of the mammalian heart’s conduction system, focusing on the atrioventricular bundle and Purkinje fibers, essential for understanding heart function and electrical signaling in mammals.
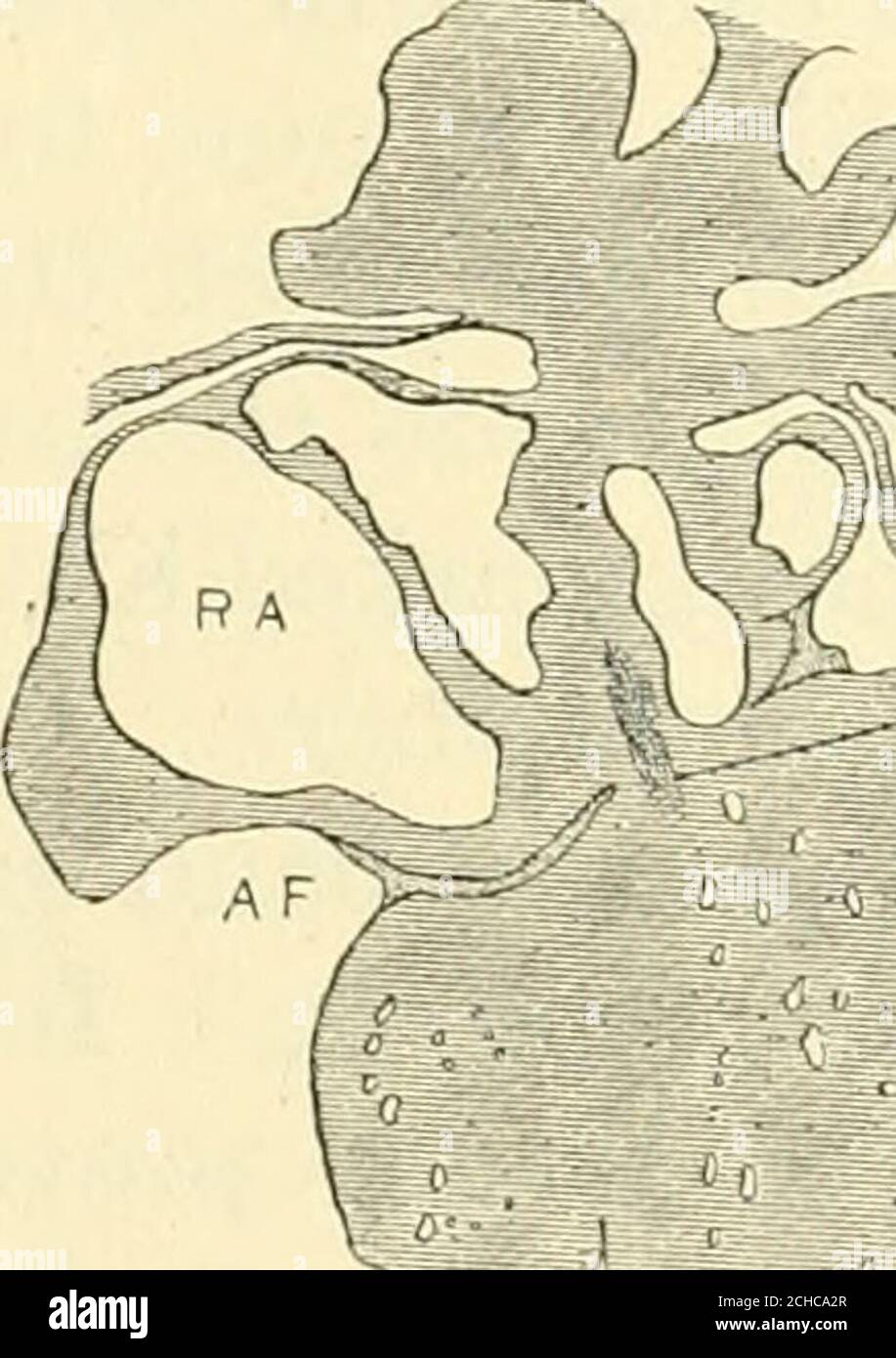 . The American journal of anatomy . 30 Fig. 29 Coronal section to show the position of the atrio-ventricular muscle.Embryo 16 mm. long (No. 409). X 18. Fig. 30 Coronal section, well dorsalwards, to show the extension of the atrio-ventricular muscle to the coronary sinus. Embryo 15.2 mm. long (No. 423).X 15. The spaces around the bundle in embryos from 10 to 20 mm.long appear to continue in the adult; possibly they form the bursaof the bundle described by Curran38 and the spaces which encirclethe Purkinje fibers. Brilliant injections of these have been madeby Lhamon.36 In an embryo 34 mm. long, Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-american-journal-of-anatomy-30-fig-29-coronal-section-to-show-the-position-of-the-atrio-ventricular-muscleembryo-16-mm-long-no-409-x-18-fig-30-coronal-section-well-dorsalwards-to-show-the-extension-of-the-atrio-ventricular-muscle-to-the-coronary-sinus-embryo-152-mm-long-no-423x-15-the-spaces-around-the-bundle-in-embryos-from-10-to-20-mmlong-appear-to-continue-in-the-adult-possibly-they-form-the-bursaof-the-bundle-described-by-curran38-and-the-spaces-which-encirclethe-purkinje-fibers-brilliant-injections-of-these-have-been-madeby-lhamon36-in-an-embryo-34-mm-long-image372138223.html
. The American journal of anatomy . 30 Fig. 29 Coronal section to show the position of the atrio-ventricular muscle.Embryo 16 mm. long (No. 409). X 18. Fig. 30 Coronal section, well dorsalwards, to show the extension of the atrio-ventricular muscle to the coronary sinus. Embryo 15.2 mm. long (No. 423).X 15. The spaces around the bundle in embryos from 10 to 20 mm.long appear to continue in the adult; possibly they form the bursaof the bundle described by Curran38 and the spaces which encirclethe Purkinje fibers. Brilliant injections of these have been madeby Lhamon.36 In an embryo 34 mm. long, Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-american-journal-of-anatomy-30-fig-29-coronal-section-to-show-the-position-of-the-atrio-ventricular-muscleembryo-16-mm-long-no-409-x-18-fig-30-coronal-section-well-dorsalwards-to-show-the-extension-of-the-atrio-ventricular-muscle-to-the-coronary-sinus-embryo-152-mm-long-no-423x-15-the-spaces-around-the-bundle-in-embryos-from-10-to-20-mmlong-appear-to-continue-in-the-adult-possibly-they-form-the-bursaof-the-bundle-described-by-curran38-and-the-spaces-which-encirclethe-purkinje-fibers-brilliant-injections-of-these-have-been-madeby-lhamon36-in-an-embryo-34-mm-long-image372138223.htmlRM2CHCA2R–. The American journal of anatomy . 30 Fig. 29 Coronal section to show the position of the atrio-ventricular muscle.Embryo 16 mm. long (No. 409). X 18. Fig. 30 Coronal section, well dorsalwards, to show the extension of the atrio-ventricular muscle to the coronary sinus. Embryo 15.2 mm. long (No. 423).X 15. The spaces around the bundle in embryos from 10 to 20 mm.long appear to continue in the adult; possibly they form the bursaof the bundle described by Curran38 and the spaces which encirclethe Purkinje fibers. Brilliant injections of these have been madeby Lhamon.36 In an embryo 34 mm. long,
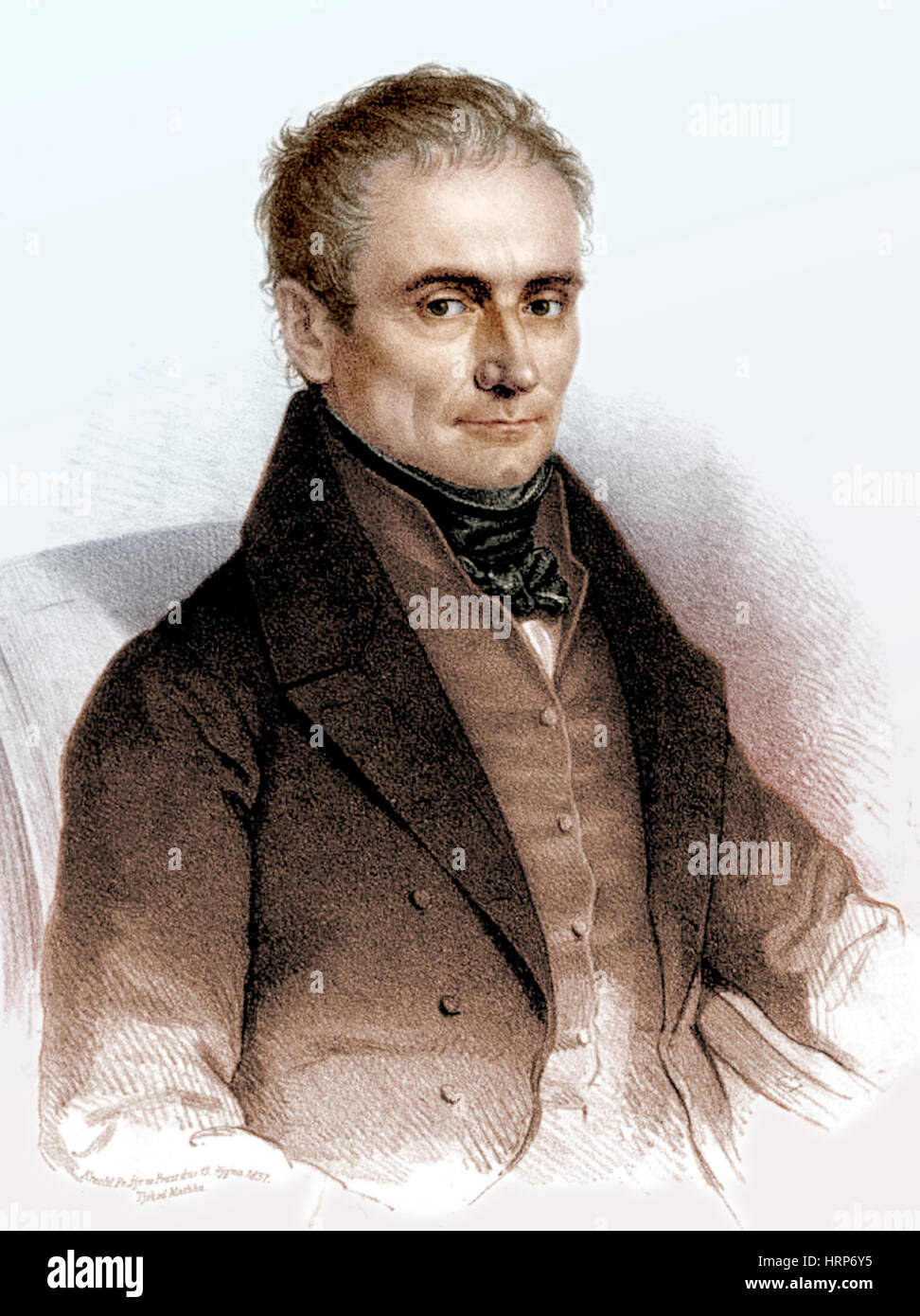 Johannes Purkinje, Czech Physiologist Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-johannes-purkinje-czech-physiologist-135098073.html
Johannes Purkinje, Czech Physiologist Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-johannes-purkinje-czech-physiologist-135098073.htmlRMHRP6Y5–Johannes Purkinje, Czech Physiologist
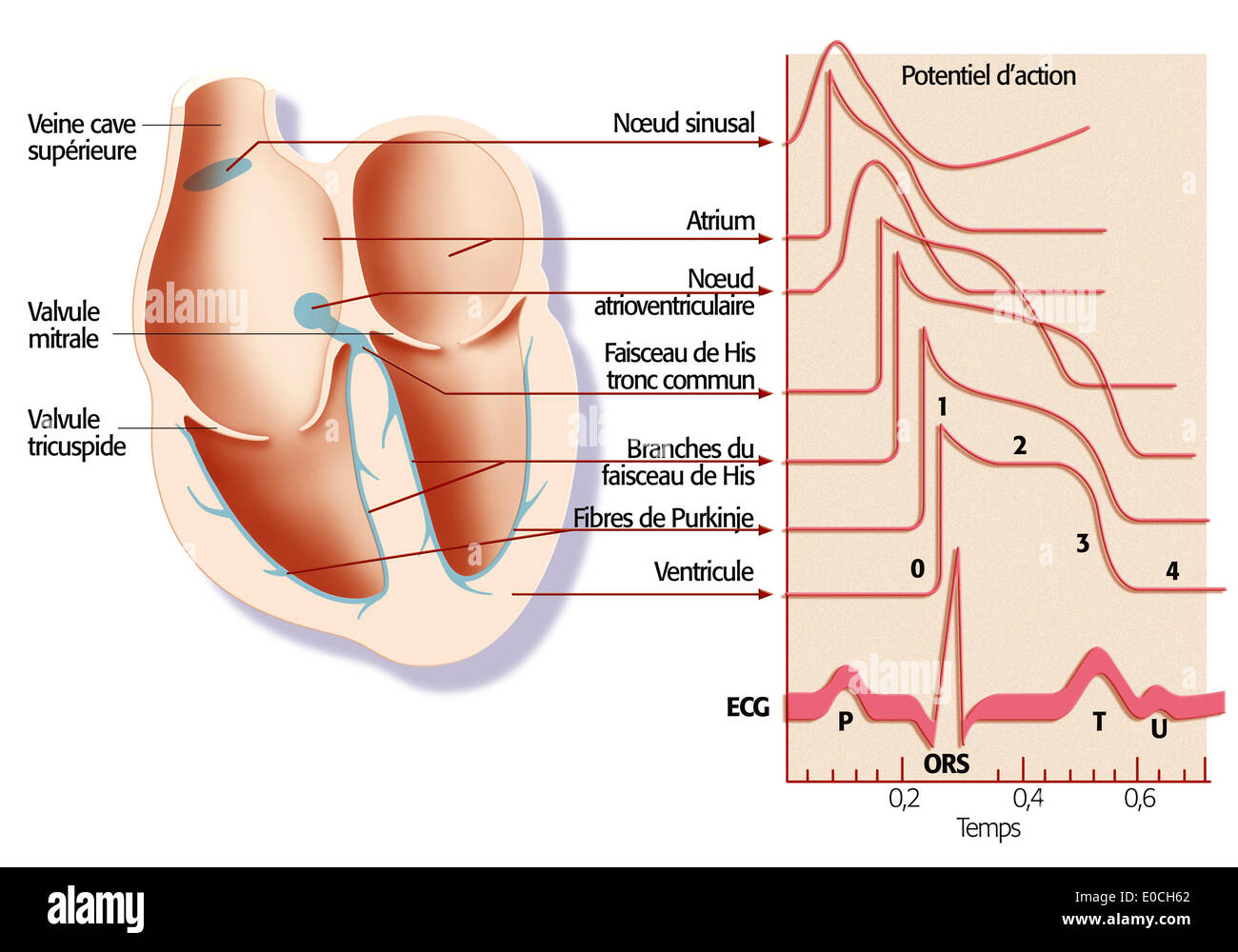 Heart rate, illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/heart-rate-illustration-image69118394.html
Heart rate, illustration Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/heart-rate-illustration-image69118394.htmlRME0CH62–Heart rate, illustration
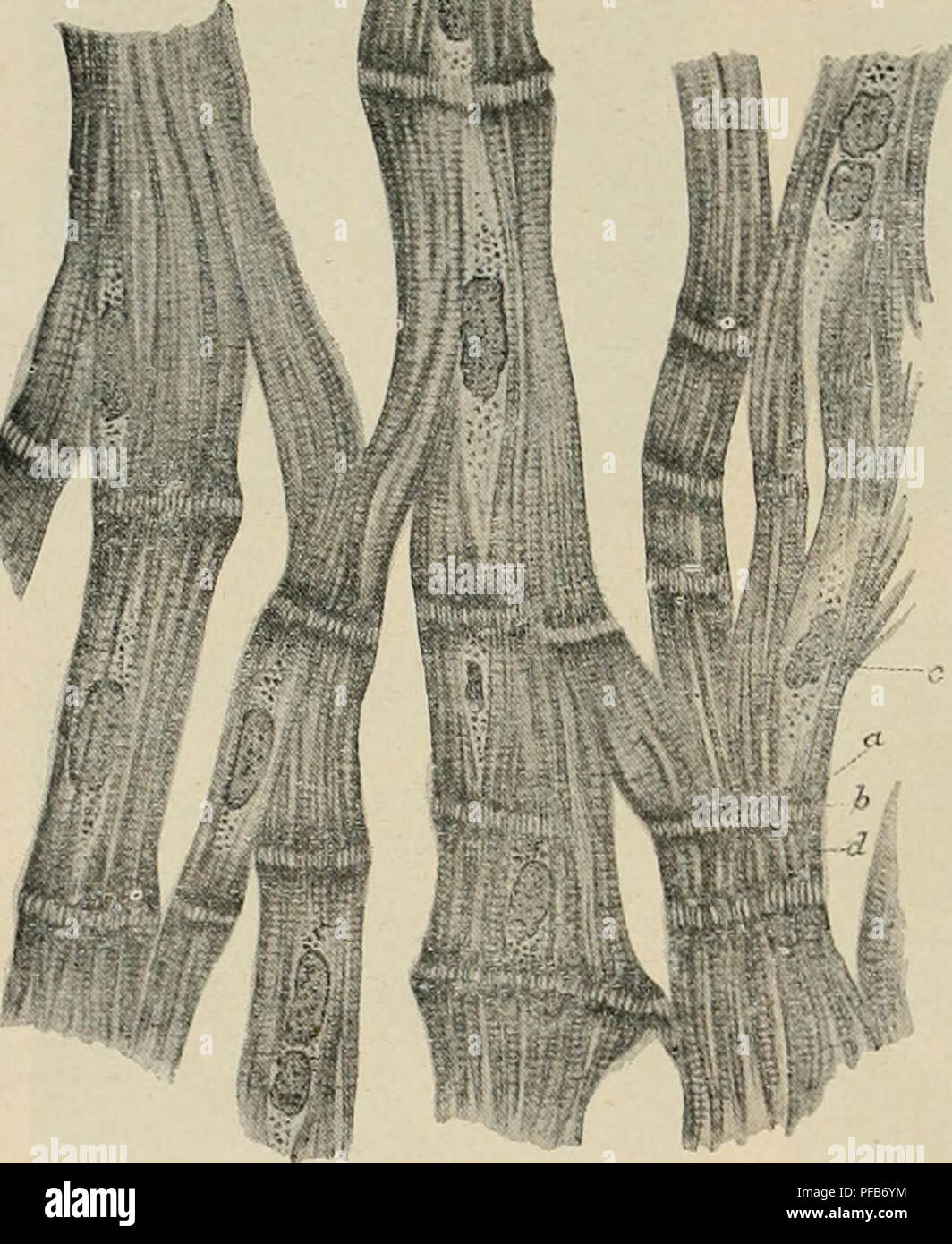 . Dictionnaire de physiologie. Physiology. 166 CÅUR. des sinus et des oreiHetles, ainsi tjue sur la région s'étendant des oreillettes aux ventri- cules, une structure qui se rapproche beaucoup de celle des cellules myocardiques embryonnaires. D'ailleurs, déjà en 1863, les fibres de Purkinje furent considérées par Aebv, et par tous les histologistes ensuite (Ranvier), comme composées de cellules myocardiques arrêtées dans leur développement. En général les éléments musculaires du cÅur doivent être rangés parmi les'plus l'iches en sarcoplasme (Ranvier, Knoll, Rollett). Il résulte Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/dictionnaire-de-physiologie-physiology-166-cur-des-sinus-et-des-oreihetles-ainsi-tjue-sur-la-rgion-stendant-des-oreillettes-aux-ventri-cules-une-structure-qui-se-rapproche-beaucoup-de-celle-des-cellules-myocardiques-embryonnaires-dailleurs-dj-en-1863-les-fibres-de-purkinje-furent-considres-par-aebv-et-par-tous-les-histologistes-ensuite-ranvier-comme-composes-de-cellules-myocardiques-arrtes-dans-leur-dveloppement-en-gnral-les-lments-musculaires-du-cur-doivent-tre-rangs-parmi-lesplus-liches-en-sarcoplasme-ranvier-knoll-rollett-il-rsulte-image215991208.html
. Dictionnaire de physiologie. Physiology. 166 CÅUR. des sinus et des oreiHetles, ainsi tjue sur la région s'étendant des oreillettes aux ventri- cules, une structure qui se rapproche beaucoup de celle des cellules myocardiques embryonnaires. D'ailleurs, déjà en 1863, les fibres de Purkinje furent considérées par Aebv, et par tous les histologistes ensuite (Ranvier), comme composées de cellules myocardiques arrêtées dans leur développement. En général les éléments musculaires du cÅur doivent être rangés parmi les'plus l'iches en sarcoplasme (Ranvier, Knoll, Rollett). Il résulte Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/dictionnaire-de-physiologie-physiology-166-cur-des-sinus-et-des-oreihetles-ainsi-tjue-sur-la-rgion-stendant-des-oreillettes-aux-ventri-cules-une-structure-qui-se-rapproche-beaucoup-de-celle-des-cellules-myocardiques-embryonnaires-dailleurs-dj-en-1863-les-fibres-de-purkinje-furent-considres-par-aebv-et-par-tous-les-histologistes-ensuite-ranvier-comme-composes-de-cellules-myocardiques-arrtes-dans-leur-dveloppement-en-gnral-les-lments-musculaires-du-cur-doivent-tre-rangs-parmi-lesplus-liches-en-sarcoplasme-ranvier-knoll-rollett-il-rsulte-image215991208.htmlRMPFB6YM–. Dictionnaire de physiologie. Physiology. 166 CÅUR. des sinus et des oreiHetles, ainsi tjue sur la région s'étendant des oreillettes aux ventri- cules, une structure qui se rapproche beaucoup de celle des cellules myocardiques embryonnaires. D'ailleurs, déjà en 1863, les fibres de Purkinje furent considérées par Aebv, et par tous les histologistes ensuite (Ranvier), comme composées de cellules myocardiques arrêtées dans leur développement. En général les éléments musculaires du cÅur doivent être rangés parmi les'plus l'iches en sarcoplasme (Ranvier, Knoll, Rollett). Il résulte
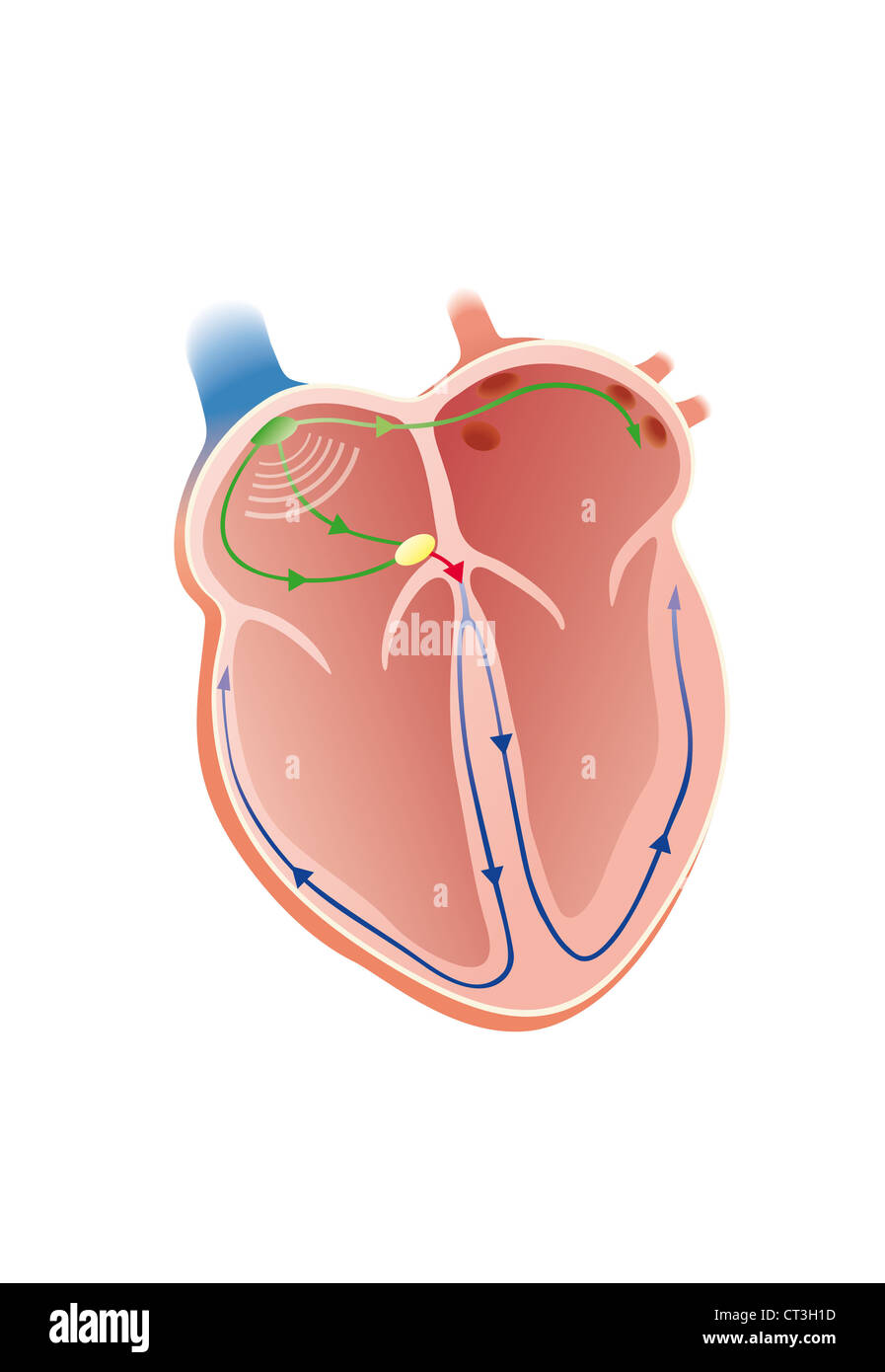 HEART RATE, ILLUSTRATION Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-heart-rate-illustration-49251705.html
HEART RATE, ILLUSTRATION Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-heart-rate-illustration-49251705.htmlRMCT3H1D–HEART RATE, ILLUSTRATION
 Physiology and biochemistry in modern medicine . This can be done by local warming of the apex, or by applyingthe ventricular electrode at varying parts of the ventricle in an excisedheart beating in Ringers solution of relatively high H-ion concentra-tion. Mines showed that under these conditions a typical T-wave ap-pears in the electrocardiogram, as shoAvn in Fig. 84.* The existence of the small Q-wave, indicating that the contractiondoes not really start from the base, conforms with the observation thatthe Purkinje system of fibers ends about the papillary muscles, whichtherefore would be t Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/physiology-and-biochemistry-in-modern-medicine-this-can-be-done-by-local-warming-of-the-apex-or-by-applyingthe-ventricular-electrode-at-varying-parts-of-the-ventricle-in-an-excisedheart-beating-in-ringers-solution-of-relatively-high-h-ion-concentra-tion-mines-showed-that-under-these-conditions-a-typical-t-wave-ap-pears-in-the-electrocardiogram-as-shoavn-in-fig-84-the-existence-of-the-small-q-wave-indicating-that-the-contractiondoes-not-really-start-from-the-base-conforms-with-the-observation-thatthe-purkinje-system-of-fibers-ends-about-the-papillary-muscles-whichtherefore-would-be-t-image340082011.html
Physiology and biochemistry in modern medicine . This can be done by local warming of the apex, or by applyingthe ventricular electrode at varying parts of the ventricle in an excisedheart beating in Ringers solution of relatively high H-ion concentra-tion. Mines showed that under these conditions a typical T-wave ap-pears in the electrocardiogram, as shoAvn in Fig. 84.* The existence of the small Q-wave, indicating that the contractiondoes not really start from the base, conforms with the observation thatthe Purkinje system of fibers ends about the papillary muscles, whichtherefore would be t Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/physiology-and-biochemistry-in-modern-medicine-this-can-be-done-by-local-warming-of-the-apex-or-by-applyingthe-ventricular-electrode-at-varying-parts-of-the-ventricle-in-an-excisedheart-beating-in-ringers-solution-of-relatively-high-h-ion-concentra-tion-mines-showed-that-under-these-conditions-a-typical-t-wave-ap-pears-in-the-electrocardiogram-as-shoavn-in-fig-84-the-existence-of-the-small-q-wave-indicating-that-the-contractiondoes-not-really-start-from-the-base-conforms-with-the-observation-thatthe-purkinje-system-of-fibers-ends-about-the-papillary-muscles-whichtherefore-would-be-t-image340082011.htmlRM2AN8223–Physiology and biochemistry in modern medicine . This can be done by local warming of the apex, or by applyingthe ventricular electrode at varying parts of the ventricle in an excisedheart beating in Ringers solution of relatively high H-ion concentra-tion. Mines showed that under these conditions a typical T-wave ap-pears in the electrocardiogram, as shoAvn in Fig. 84.* The existence of the small Q-wave, indicating that the contractiondoes not really start from the base, conforms with the observation thatthe Purkinje system of fibers ends about the papillary muscles, whichtherefore would be t
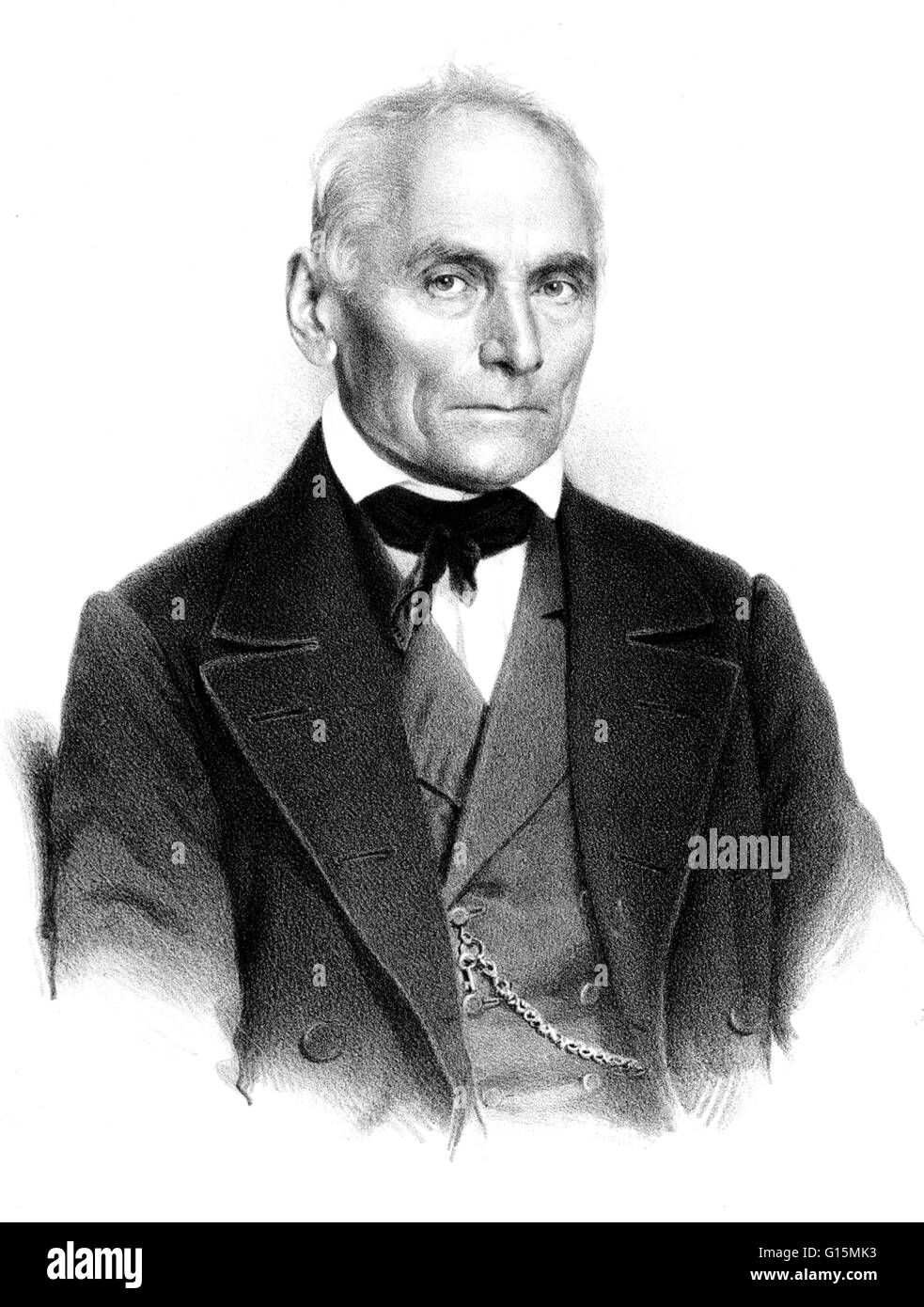 Johannes Evangelist Purkinje (December 17, 1787 - July 28, 1869) was a Czech anatomist and physiologist. He was one of the best known scientists of his time. He discovered the Purkinje effect whereby as light intensity decreases, red objects seems to fade Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-johannes-evangelist-purkinje-december-17-1787-july-28-1869-was-a-czech-104002839.html
Johannes Evangelist Purkinje (December 17, 1787 - July 28, 1869) was a Czech anatomist and physiologist. He was one of the best known scientists of his time. He discovered the Purkinje effect whereby as light intensity decreases, red objects seems to fade Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-johannes-evangelist-purkinje-december-17-1787-july-28-1869-was-a-czech-104002839.htmlRMG15MK3–Johannes Evangelist Purkinje (December 17, 1787 - July 28, 1869) was a Czech anatomist and physiologist. He was one of the best known scientists of his time. He discovered the Purkinje effect whereby as light intensity decreases, red objects seems to fade
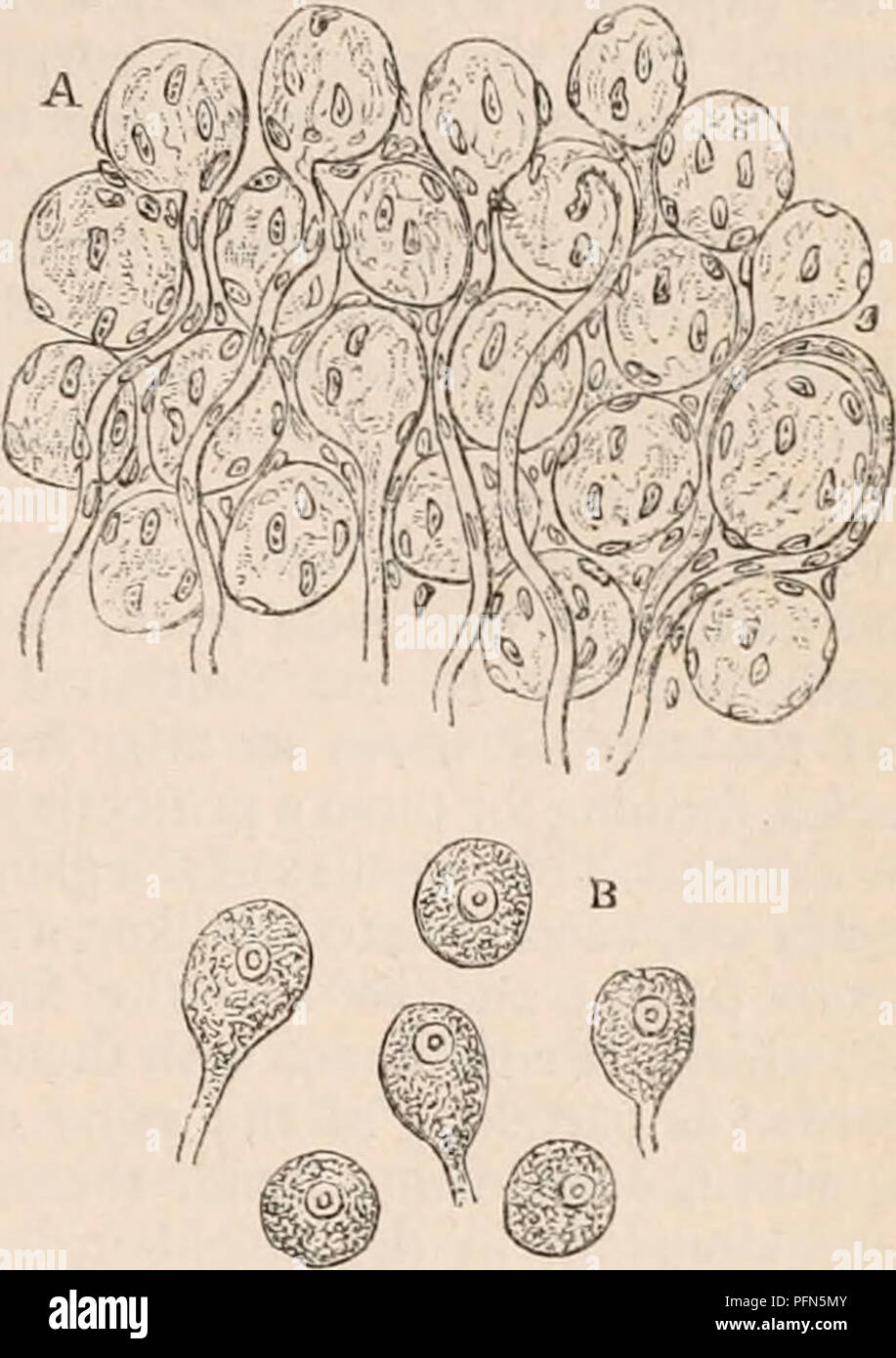 . The cyclopædia of anatomy and physiology. Anatomy; Physiology; Zoology. SYMPATHETIC NERVE. 433 organic nerve fibres. According to Purkinje *, the ganglionic nerve-fibres are much finer than those belonging to the cerebro-spinal system or animal fibres. He describes the latter as containing two substances,—an outer, which runs in the form of a tube through the elementary fibre immediately within its sheath, and an inner, which occupies the hollow in- terior of the former. The tubular sheaths of the elementary fibres of the ganglionic system contain, on the other hand, no double substance ; th Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-cyclopdia-of-anatomy-and-physiology-anatomy-physiology-zoology-sympathetic-nerve-433-organic-nerve-fibres-according-to-purkinje-the-ganglionic-nerve-fibres-are-much-finer-than-those-belonging-to-the-cerebro-spinal-system-or-animal-fibres-he-describes-the-latter-as-containing-two-substancesan-outer-which-runs-in-the-form-of-a-tube-through-the-elementary-fibre-immediately-within-its-sheath-and-an-inner-which-occupies-the-hollow-in-terior-of-the-former-the-tubular-sheaths-of-the-elementary-fibres-of-the-ganglionic-system-contain-on-the-other-hand-no-double-substance-th-image216209755.html
. The cyclopædia of anatomy and physiology. Anatomy; Physiology; Zoology. SYMPATHETIC NERVE. 433 organic nerve fibres. According to Purkinje *, the ganglionic nerve-fibres are much finer than those belonging to the cerebro-spinal system or animal fibres. He describes the latter as containing two substances,—an outer, which runs in the form of a tube through the elementary fibre immediately within its sheath, and an inner, which occupies the hollow in- terior of the former. The tubular sheaths of the elementary fibres of the ganglionic system contain, on the other hand, no double substance ; th Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-cyclopdia-of-anatomy-and-physiology-anatomy-physiology-zoology-sympathetic-nerve-433-organic-nerve-fibres-according-to-purkinje-the-ganglionic-nerve-fibres-are-much-finer-than-those-belonging-to-the-cerebro-spinal-system-or-animal-fibres-he-describes-the-latter-as-containing-two-substancesan-outer-which-runs-in-the-form-of-a-tube-through-the-elementary-fibre-immediately-within-its-sheath-and-an-inner-which-occupies-the-hollow-in-terior-of-the-former-the-tubular-sheaths-of-the-elementary-fibres-of-the-ganglionic-system-contain-on-the-other-hand-no-double-substance-th-image216209755.htmlRMPFN5MY–. The cyclopædia of anatomy and physiology. Anatomy; Physiology; Zoology. SYMPATHETIC NERVE. 433 organic nerve fibres. According to Purkinje *, the ganglionic nerve-fibres are much finer than those belonging to the cerebro-spinal system or animal fibres. He describes the latter as containing two substances,—an outer, which runs in the form of a tube through the elementary fibre immediately within its sheath, and an inner, which occupies the hollow in- terior of the former. The tubular sheaths of the elementary fibres of the ganglionic system contain, on the other hand, no double substance ; th
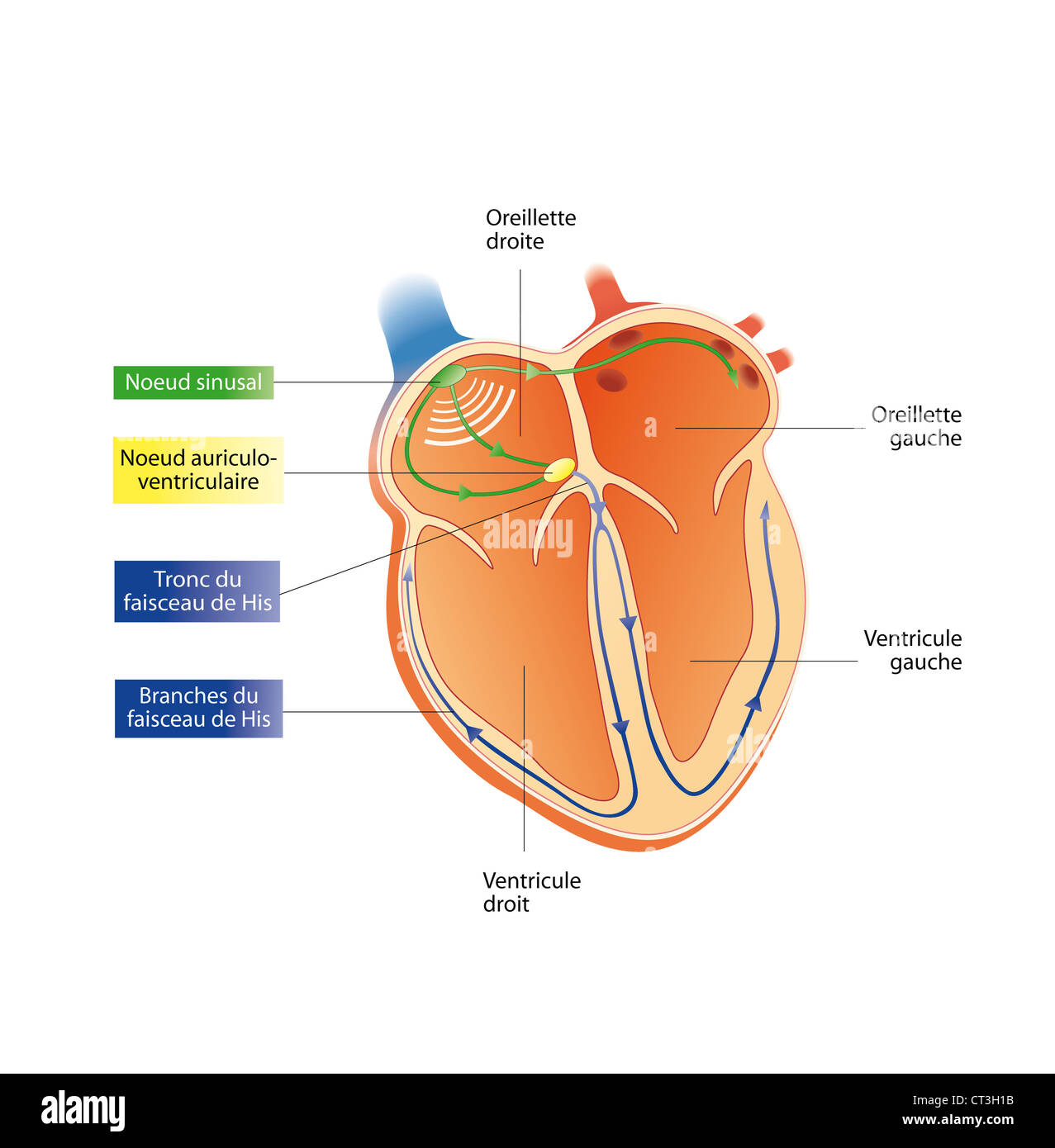 HEART RATE, ILLUSTRATION Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-heart-rate-illustration-49251703.html
HEART RATE, ILLUSTRATION Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-heart-rate-illustration-49251703.htmlRMCT3H1B–HEART RATE, ILLUSTRATION
 A text-book of physiology for medical students and physicians . m as climbing fibers. The granular layer (B) containsnumerous granules (g) or small nerve cells. These cells are spherical,and have a relatively large nucleus and a small amount of cyto-plasm. Their dendrites are few and short; their axons run intothe molecular layer, divide in T, and the two branches then run 231 232 PHYSIOLOGY OF CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM. parallel to the surface and doubtless make connections with the den-drites of the Purkinje cells as well as with the cells of the molecularlayer. A few larger nerve cells of Golg Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-text-book-of-physiology-for-medical-students-and-physicians-m-as-climbing-fibers-the-granular-layer-b-containsnumerous-granules-g-or-small-nerve-cells-these-cells-are-sphericaland-have-a-relatively-large-nucleus-and-a-small-amount-of-cyto-plasm-their-dendrites-are-few-and-short-their-axons-run-intothe-molecular-layer-divide-in-t-and-the-two-branches-then-run-231-232-physiology-of-central-nervous-system-parallel-to-the-surface-and-doubtless-make-connections-with-the-den-drites-of-the-purkinje-cells-as-well-as-with-the-cells-of-the-molecularlayer-a-few-larger-nerve-cells-of-golg-image342793212.html
A text-book of physiology for medical students and physicians . m as climbing fibers. The granular layer (B) containsnumerous granules (g) or small nerve cells. These cells are spherical,and have a relatively large nucleus and a small amount of cyto-plasm. Their dendrites are few and short; their axons run intothe molecular layer, divide in T, and the two branches then run 231 232 PHYSIOLOGY OF CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM. parallel to the surface and doubtless make connections with the den-drites of the Purkinje cells as well as with the cells of the molecularlayer. A few larger nerve cells of Golg Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-text-book-of-physiology-for-medical-students-and-physicians-m-as-climbing-fibers-the-granular-layer-b-containsnumerous-granules-g-or-small-nerve-cells-these-cells-are-sphericaland-have-a-relatively-large-nucleus-and-a-small-amount-of-cyto-plasm-their-dendrites-are-few-and-short-their-axons-run-intothe-molecular-layer-divide-in-t-and-the-two-branches-then-run-231-232-physiology-of-central-nervous-system-parallel-to-the-surface-and-doubtless-make-connections-with-the-den-drites-of-the-purkinje-cells-as-well-as-with-the-cells-of-the-molecularlayer-a-few-larger-nerve-cells-of-golg-image342793212.htmlRM2AWKG6M–A text-book of physiology for medical students and physicians . m as climbing fibers. The granular layer (B) containsnumerous granules (g) or small nerve cells. These cells are spherical,and have a relatively large nucleus and a small amount of cyto-plasm. Their dendrites are few and short; their axons run intothe molecular layer, divide in T, and the two branches then run 231 232 PHYSIOLOGY OF CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM. parallel to the surface and doubtless make connections with the den-drites of the Purkinje cells as well as with the cells of the molecularlayer. A few larger nerve cells of Golg
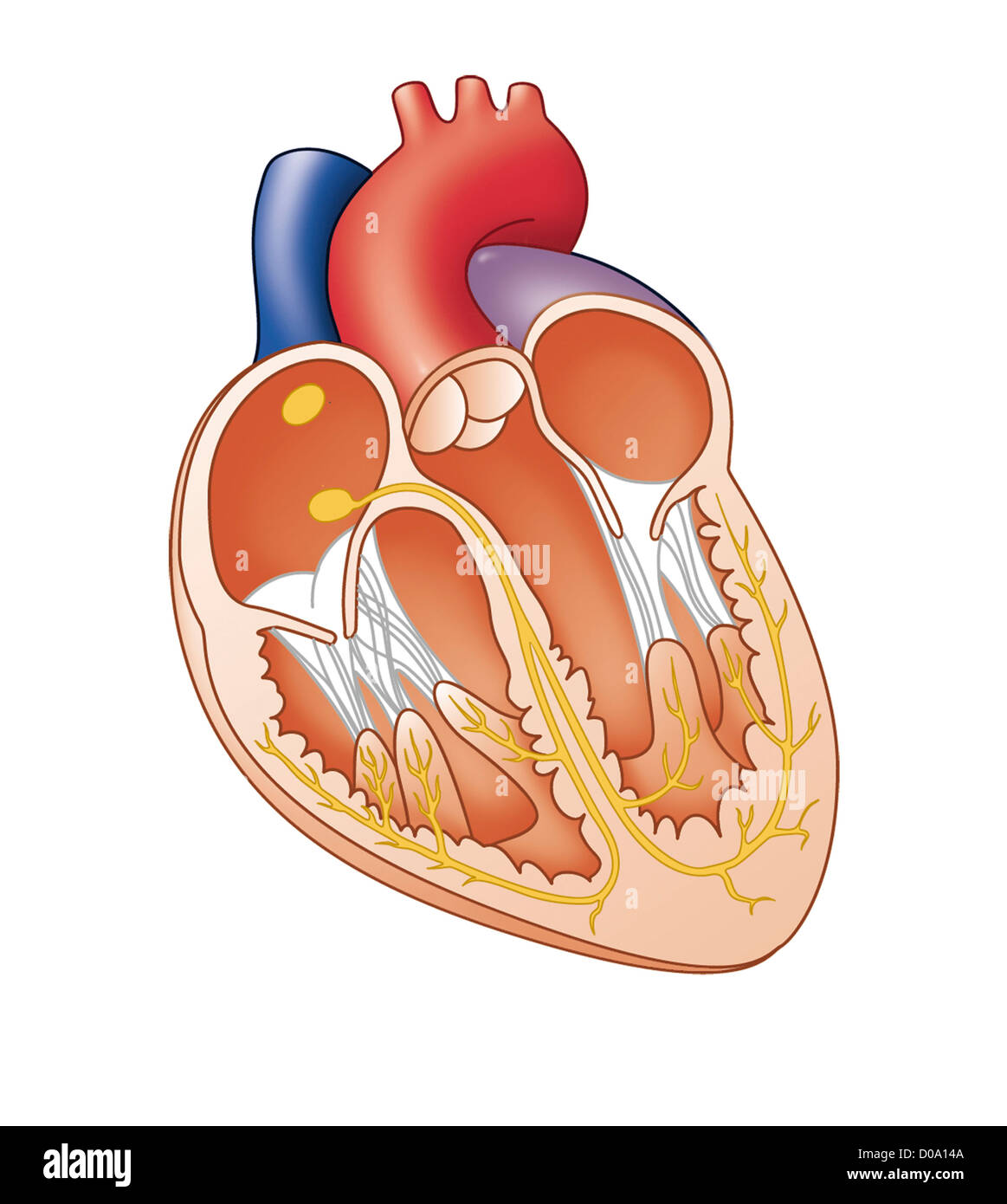 HEART, ILLUSTRATION Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-heart-illustration-51851530.html
HEART, ILLUSTRATION Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-heart-illustration-51851530.htmlRMD0A14A–HEART, ILLUSTRATION
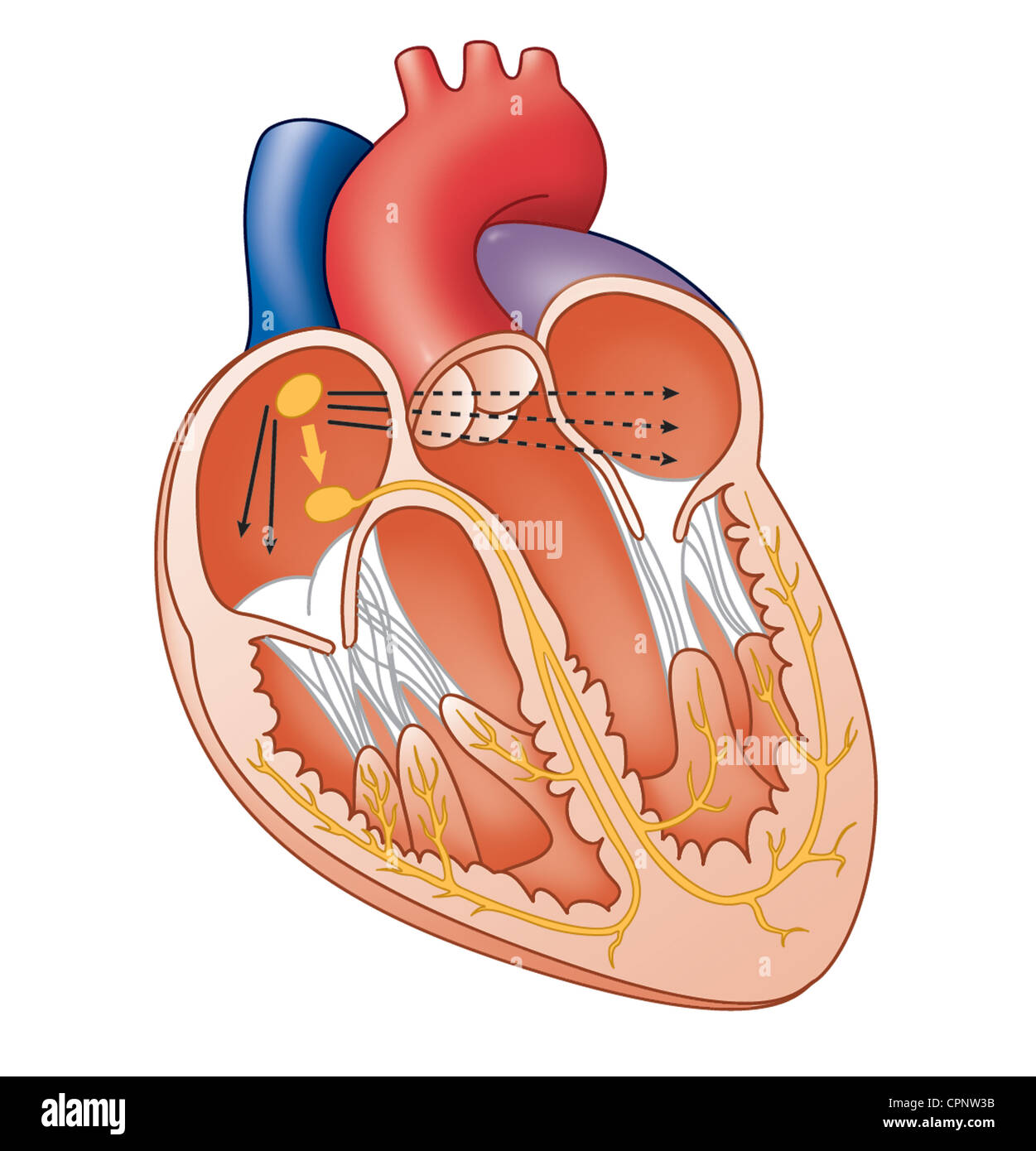 HEART, ILLUSTRATION Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-heart-illustration-48423855.html
HEART, ILLUSTRATION Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-heart-illustration-48423855.htmlRMCPNW3B–HEART, ILLUSTRATION
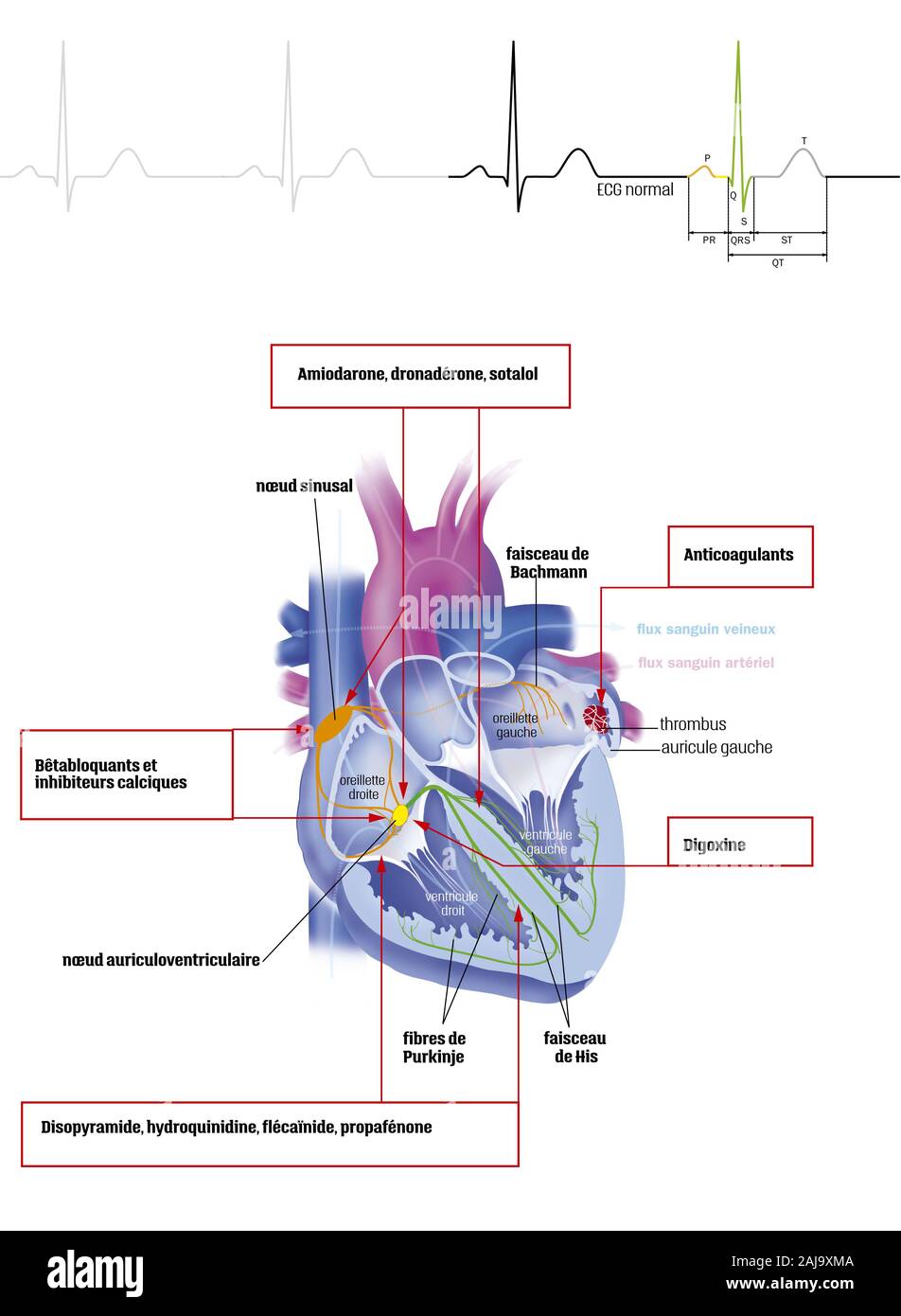 Atrial fibrillation and treatments Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/atrial-fibrillation-and-treatments-image338279322.html
Atrial fibrillation and treatments Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/atrial-fibrillation-and-treatments-image338279322.htmlRM2AJ9XMA–Atrial fibrillation and treatments
 A text-book of physiology, for medical students and physicians . m as climbing fibers. The granular layer (B) containsnumerous granules (g) or small nerve cells. These cells are spherical,and have a relatively large nucleus and a small amount of cyto-plasm. Their dendrites are few and short; their axons run intothe molecular layer, divide in T, and the two branches then run 229 230 PHYSIOUKiY OF CENTRAL XKRYOUS SYSTEM. parallel to the surface and doubtless make connections with the den-drites of the Purkinje cells as well as with the cells of the molecularlayer. A few larger nerve cells of Gol Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-text-book-of-physiology-for-medical-students-and-physicians-m-as-climbing-fibers-the-granular-layer-b-containsnumerous-granules-g-or-small-nerve-cells-these-cells-are-sphericaland-have-a-relatively-large-nucleus-and-a-small-amount-of-cyto-plasm-their-dendrites-are-few-and-short-their-axons-run-intothe-molecular-layer-divide-in-t-and-the-two-branches-then-run-229-230-physioukiy-of-central-xkryous-system-parallel-to-the-surface-and-doubtless-make-connections-with-the-den-drites-of-the-purkinje-cells-as-well-as-with-the-cells-of-the-molecularlayer-a-few-larger-nerve-cells-of-gol-image342970879.html
A text-book of physiology, for medical students and physicians . m as climbing fibers. The granular layer (B) containsnumerous granules (g) or small nerve cells. These cells are spherical,and have a relatively large nucleus and a small amount of cyto-plasm. Their dendrites are few and short; their axons run intothe molecular layer, divide in T, and the two branches then run 229 230 PHYSIOUKiY OF CENTRAL XKRYOUS SYSTEM. parallel to the surface and doubtless make connections with the den-drites of the Purkinje cells as well as with the cells of the molecularlayer. A few larger nerve cells of Gol Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-text-book-of-physiology-for-medical-students-and-physicians-m-as-climbing-fibers-the-granular-layer-b-containsnumerous-granules-g-or-small-nerve-cells-these-cells-are-sphericaland-have-a-relatively-large-nucleus-and-a-small-amount-of-cyto-plasm-their-dendrites-are-few-and-short-their-axons-run-intothe-molecular-layer-divide-in-t-and-the-two-branches-then-run-229-230-physioukiy-of-central-xkryous-system-parallel-to-the-surface-and-doubtless-make-connections-with-the-den-drites-of-the-purkinje-cells-as-well-as-with-the-cells-of-the-molecularlayer-a-few-larger-nerve-cells-of-gol-image342970879.htmlRM2AWYJRY–A text-book of physiology, for medical students and physicians . m as climbing fibers. The granular layer (B) containsnumerous granules (g) or small nerve cells. These cells are spherical,and have a relatively large nucleus and a small amount of cyto-plasm. Their dendrites are few and short; their axons run intothe molecular layer, divide in T, and the two branches then run 229 230 PHYSIOUKiY OF CENTRAL XKRYOUS SYSTEM. parallel to the surface and doubtless make connections with the den-drites of the Purkinje cells as well as with the cells of the molecularlayer. A few larger nerve cells of Gol
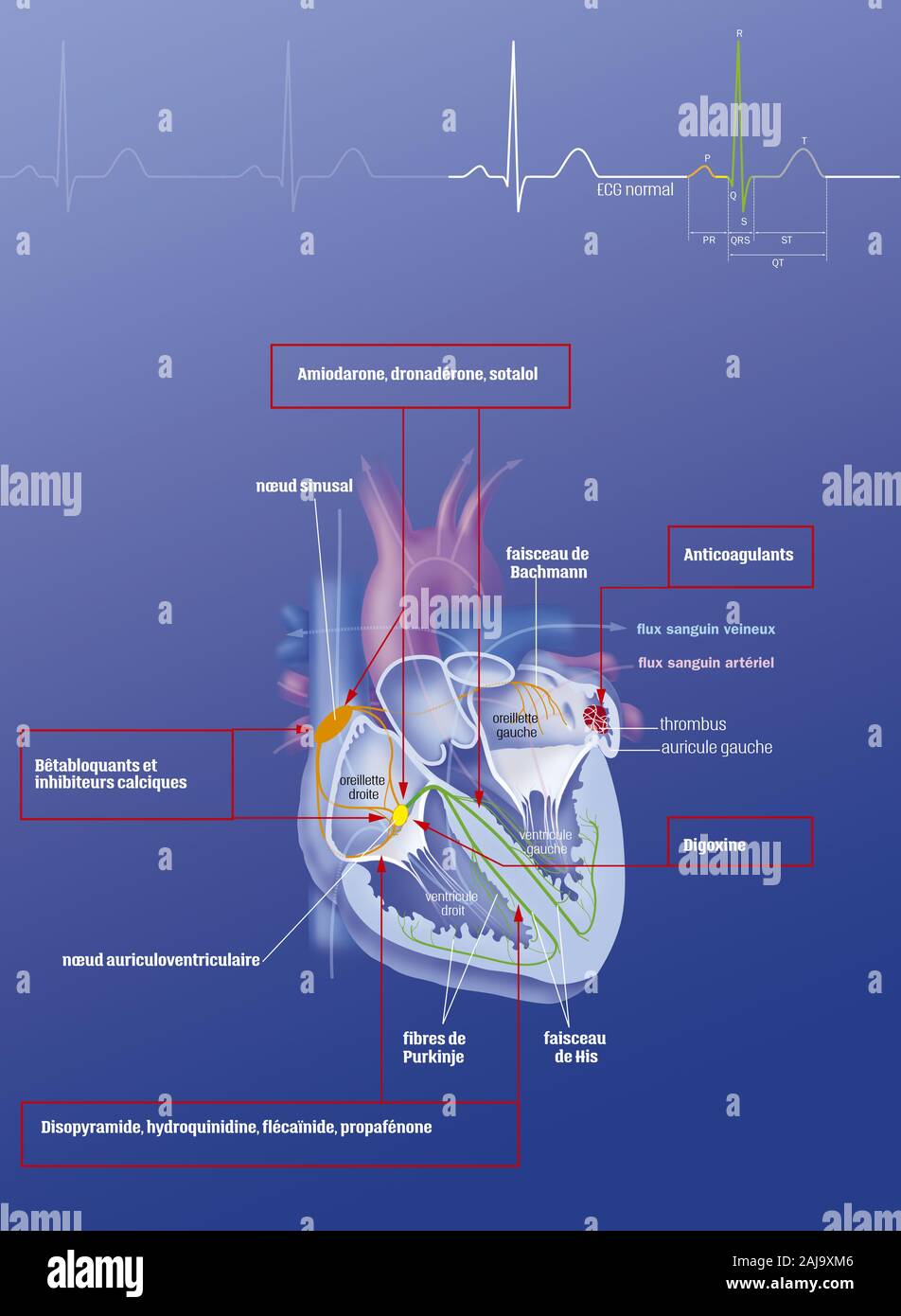 Atrial fibrillation and treatments Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/atrial-fibrillation-and-treatments-image338279318.html
Atrial fibrillation and treatments Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/atrial-fibrillation-and-treatments-image338279318.htmlRM2AJ9XM6–Atrial fibrillation and treatments
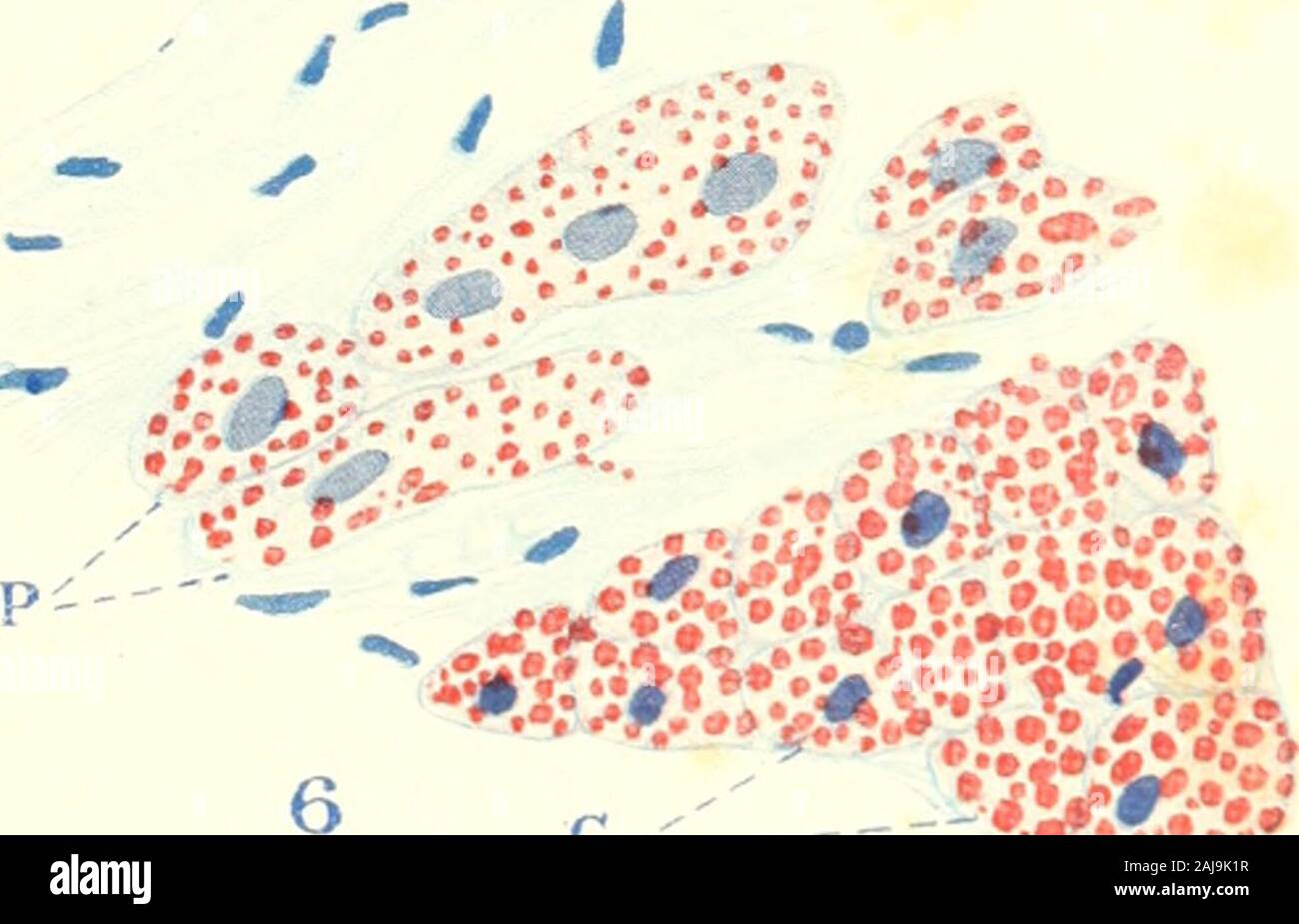 The American journal of anatomy . > —. C- 33 THK AMEKICAN JOURNAL OF ANATOMY, VOI,. 19, NO. 1 PLATE 2 TOXPLANATION OF FIGURES 9 From tlu moderator hand of a fattened hog (animal 104, table?). Fibersof right limb of bundle of His, P, and light cardiac fibers, L, contain a vcru sukiUamount of fat, dark cardiac fibers, D, a large amount. X 300. 10 From the interventricular septum and left limb of the bundle of His ofa well nourished dog (figs. 10 to 16 inclusive from same animal, no. 90, table6). Dark cardiac fibers, D, and light cardiac fibers, L, contain a muderdteamount of fat; Purkinje fib Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-american-journal-of-anatomy-gt-c-33-thk-amekican-journal-of-anatomy-voi-19-no-1-plate-2-toxplanation-of-figures-9-from-tlu-moderator-hand-of-a-fattened-hog-animal-104-table-fibersof-right-limb-of-bundle-of-his-p-and-light-cardiac-fibers-l-contain-a-vcru-sukiuamount-of-fat-dark-cardiac-fibers-d-a-large-amount-x-300-10-from-the-interventricular-septum-and-left-limb-of-the-bundle-of-his-ofa-well-nourished-dog-figs-10-to-16-inclusive-from-same-animal-no-90-table6-dark-cardiac-fibers-d-and-light-cardiac-fibers-l-contain-a-muderdteamount-of-fat-purkinje-fib-image338273315.html
The American journal of anatomy . > —. C- 33 THK AMEKICAN JOURNAL OF ANATOMY, VOI,. 19, NO. 1 PLATE 2 TOXPLANATION OF FIGURES 9 From tlu moderator hand of a fattened hog (animal 104, table?). Fibersof right limb of bundle of His, P, and light cardiac fibers, L, contain a vcru sukiUamount of fat, dark cardiac fibers, D, a large amount. X 300. 10 From the interventricular septum and left limb of the bundle of His ofa well nourished dog (figs. 10 to 16 inclusive from same animal, no. 90, table6). Dark cardiac fibers, D, and light cardiac fibers, L, contain a muderdteamount of fat; Purkinje fib Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-american-journal-of-anatomy-gt-c-33-thk-amekican-journal-of-anatomy-voi-19-no-1-plate-2-toxplanation-of-figures-9-from-tlu-moderator-hand-of-a-fattened-hog-animal-104-table-fibersof-right-limb-of-bundle-of-his-p-and-light-cardiac-fibers-l-contain-a-vcru-sukiuamount-of-fat-dark-cardiac-fibers-d-a-large-amount-x-300-10-from-the-interventricular-septum-and-left-limb-of-the-bundle-of-his-ofa-well-nourished-dog-figs-10-to-16-inclusive-from-same-animal-no-90-table6-dark-cardiac-fibers-d-and-light-cardiac-fibers-l-contain-a-muderdteamount-of-fat-purkinje-fib-image338273315.htmlRM2AJ9K1R–The American journal of anatomy . > —. C- 33 THK AMEKICAN JOURNAL OF ANATOMY, VOI,. 19, NO. 1 PLATE 2 TOXPLANATION OF FIGURES 9 From tlu moderator hand of a fattened hog (animal 104, table?). Fibersof right limb of bundle of His, P, and light cardiac fibers, L, contain a vcru sukiUamount of fat, dark cardiac fibers, D, a large amount. X 300. 10 From the interventricular septum and left limb of the bundle of His ofa well nourished dog (figs. 10 to 16 inclusive from same animal, no. 90, table6). Dark cardiac fibers, D, and light cardiac fibers, L, contain a muderdteamount of fat; Purkinje fib
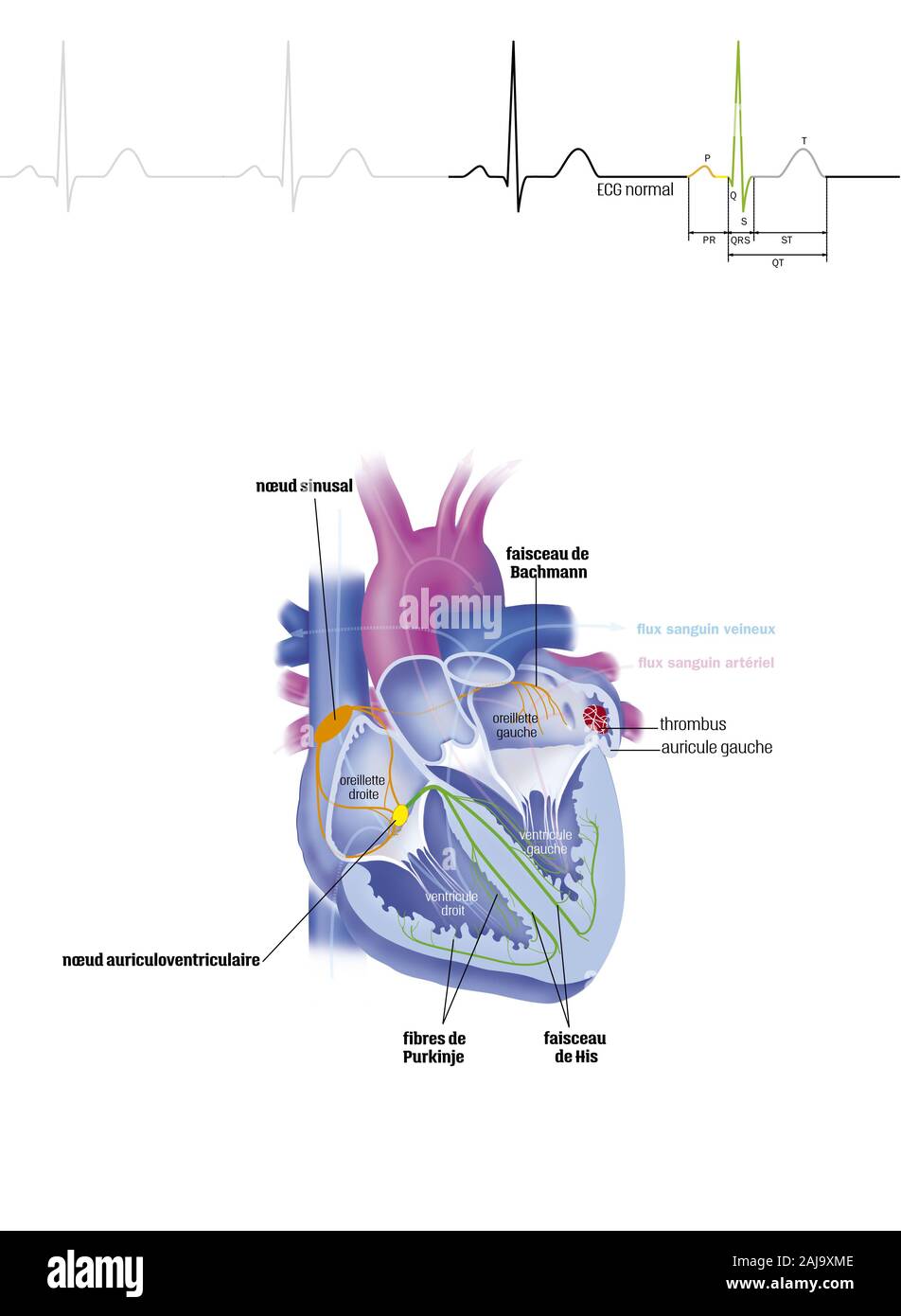 Atrial fibrillation Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/atrial-fibrillation-image338279326.html
Atrial fibrillation Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/atrial-fibrillation-image338279326.htmlRM2AJ9XME–Atrial fibrillation
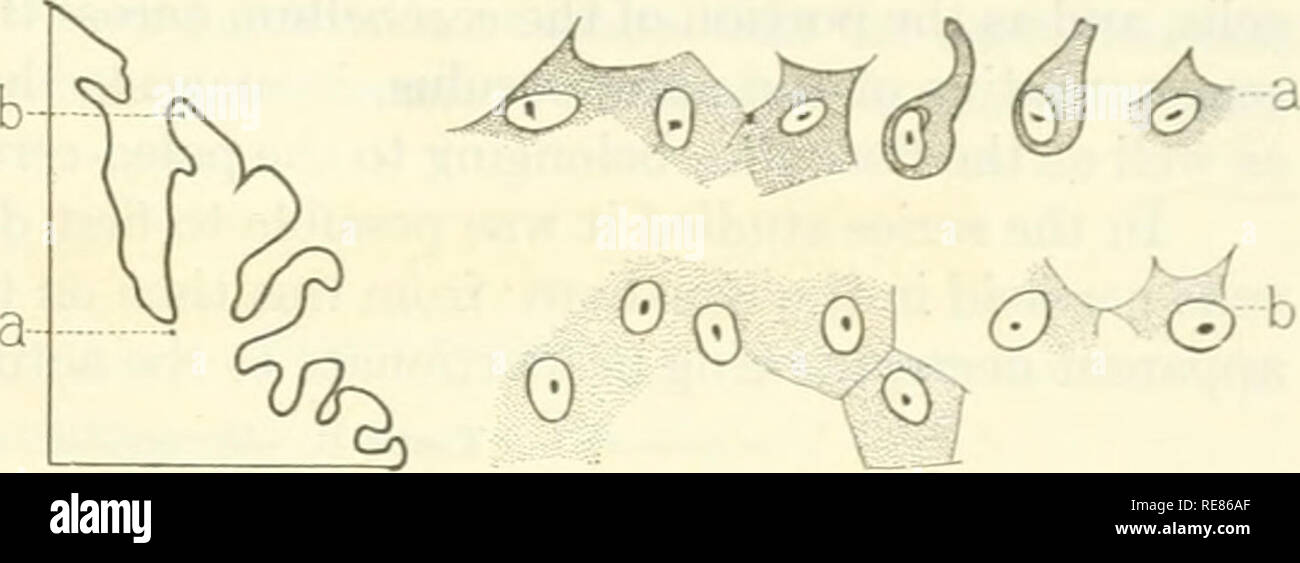 . Contributions to embryology. Embryology. THE DEVELOPMENT OF CERTAIN FEATURES OF THE CEREBELLUM. 369 in the former than in the latter. An average field in the vermis shows 36 cells, in the flocculus 22, and in the hemisphere 45. In the infant 16 days old the Purkinje cells in these three structures have maintained their relative number and size, being largest and lea.st numerous in the flocculus, smallest and most numerous in the hemispheres, and in the vermis occupy- ing an intermediate position as to size and number be- tween the two extremes. An average field in the flocculus shows 19.6 ce Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/contributions-to-embryology-embryology-the-development-of-certain-features-of-the-cerebellum-369-in-the-former-than-in-the-latter-an-average-field-in-the-vermis-shows-36-cells-in-the-flocculus-22-and-in-the-hemisphere-45-in-the-infant-16-days-old-the-purkinje-cells-in-these-three-structures-have-maintained-their-relative-number-and-size-being-largest-and-least-numerous-in-the-flocculus-smallest-and-most-numerous-in-the-hemispheres-and-in-the-vermis-occupy-ing-an-intermediate-position-as-to-size-and-number-be-tween-the-two-extremes-an-average-field-in-the-flocculus-shows-196-ce-image232520583.html
. Contributions to embryology. Embryology. THE DEVELOPMENT OF CERTAIN FEATURES OF THE CEREBELLUM. 369 in the former than in the latter. An average field in the vermis shows 36 cells, in the flocculus 22, and in the hemisphere 45. In the infant 16 days old the Purkinje cells in these three structures have maintained their relative number and size, being largest and lea.st numerous in the flocculus, smallest and most numerous in the hemispheres, and in the vermis occupy- ing an intermediate position as to size and number be- tween the two extremes. An average field in the flocculus shows 19.6 ce Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/contributions-to-embryology-embryology-the-development-of-certain-features-of-the-cerebellum-369-in-the-former-than-in-the-latter-an-average-field-in-the-vermis-shows-36-cells-in-the-flocculus-22-and-in-the-hemisphere-45-in-the-infant-16-days-old-the-purkinje-cells-in-these-three-structures-have-maintained-their-relative-number-and-size-being-largest-and-least-numerous-in-the-flocculus-smallest-and-most-numerous-in-the-hemispheres-and-in-the-vermis-occupy-ing-an-intermediate-position-as-to-size-and-number-be-tween-the-two-extremes-an-average-field-in-the-flocculus-shows-196-ce-image232520583.htmlRMRE86AF–. Contributions to embryology. Embryology. THE DEVELOPMENT OF CERTAIN FEATURES OF THE CEREBELLUM. 369 in the former than in the latter. An average field in the vermis shows 36 cells, in the flocculus 22, and in the hemisphere 45. In the infant 16 days old the Purkinje cells in these three structures have maintained their relative number and size, being largest and lea.st numerous in the flocculus, smallest and most numerous in the hemispheres, and in the vermis occupy- ing an intermediate position as to size and number be- tween the two extremes. An average field in the flocculus shows 19.6 ce
 Atrial fibrillation Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/atrial-fibrillation-image338279314.html
Atrial fibrillation Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/atrial-fibrillation-image338279314.htmlRM2AJ9XM2–Atrial fibrillation
 . A text-book of physiology : for medical students and physicians . em as climbing fibers. The granular layer (B) containsnumerous granules (g) or small nerve cells. These cells are spherical,and have a relatively large nucleus and a small amount of cyto-plasm. Their dendrites are few and short; their axons run intothe molecular layer, divide in T, and the two branches then nmparallel to the surface and doubtless make connections with the den- 233 234 PHYSIOLOGY OF CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM. drites of the Purkinje cells as well as with the cells of the molecularlayer. A few larger nerve cells of Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-text-book-of-physiology-for-medical-students-and-physicians-em-as-climbing-fibers-the-granular-layer-b-containsnumerous-granules-g-or-small-nerve-cells-these-cells-are-sphericaland-have-a-relatively-large-nucleus-and-a-small-amount-of-cyto-plasm-their-dendrites-are-few-and-short-their-axons-run-intothe-molecular-layer-divide-in-t-and-the-two-branches-then-nmparallel-to-the-surface-and-doubtless-make-connections-with-the-den-233-234-physiology-of-central-nervous-system-drites-of-the-purkinje-cells-as-well-as-with-the-cells-of-the-molecularlayer-a-few-larger-nerve-cells-of-image370188094.html
. A text-book of physiology : for medical students and physicians . em as climbing fibers. The granular layer (B) containsnumerous granules (g) or small nerve cells. These cells are spherical,and have a relatively large nucleus and a small amount of cyto-plasm. Their dendrites are few and short; their axons run intothe molecular layer, divide in T, and the two branches then nmparallel to the surface and doubtless make connections with the den- 233 234 PHYSIOLOGY OF CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM. drites of the Purkinje cells as well as with the cells of the molecularlayer. A few larger nerve cells of Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/a-text-book-of-physiology-for-medical-students-and-physicians-em-as-climbing-fibers-the-granular-layer-b-containsnumerous-granules-g-or-small-nerve-cells-these-cells-are-sphericaland-have-a-relatively-large-nucleus-and-a-small-amount-of-cyto-plasm-their-dendrites-are-few-and-short-their-axons-run-intothe-molecular-layer-divide-in-t-and-the-two-branches-then-nmparallel-to-the-surface-and-doubtless-make-connections-with-the-den-233-234-physiology-of-central-nervous-system-drites-of-the-purkinje-cells-as-well-as-with-the-cells-of-the-molecularlayer-a-few-larger-nerve-cells-of-image370188094.htmlRM2CE7EKA–. A text-book of physiology : for medical students and physicians . em as climbing fibers. The granular layer (B) containsnumerous granules (g) or small nerve cells. These cells are spherical,and have a relatively large nucleus and a small amount of cyto-plasm. Their dendrites are few and short; their axons run intothe molecular layer, divide in T, and the two branches then nmparallel to the surface and doubtless make connections with the den- 233 234 PHYSIOLOGY OF CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM. drites of the Purkinje cells as well as with the cells of the molecularlayer. A few larger nerve cells of
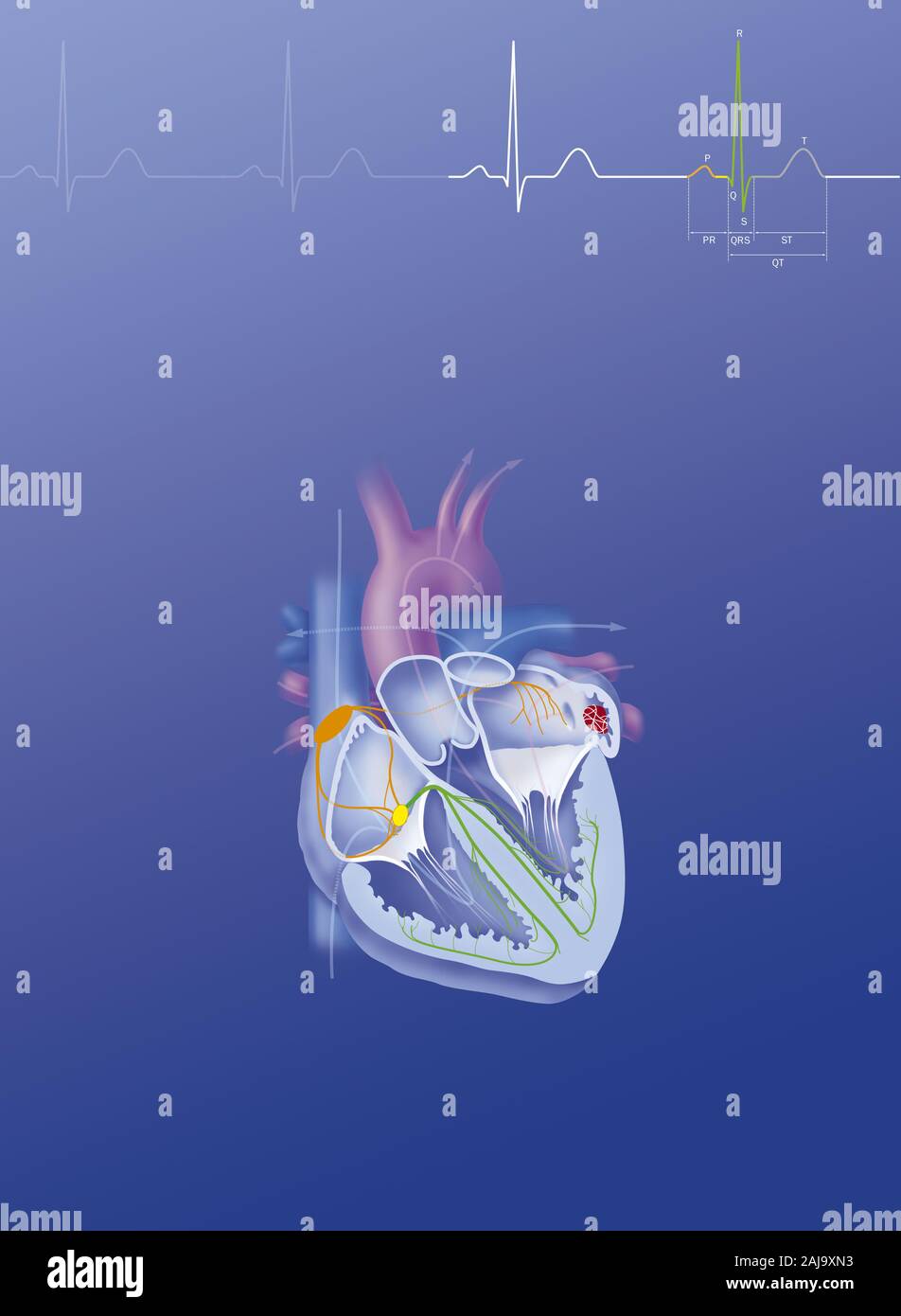 Atrial fibrillation Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/atrial-fibrillation-image338279343.html
Atrial fibrillation Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/atrial-fibrillation-image338279343.htmlRM2AJ9XN3–Atrial fibrillation
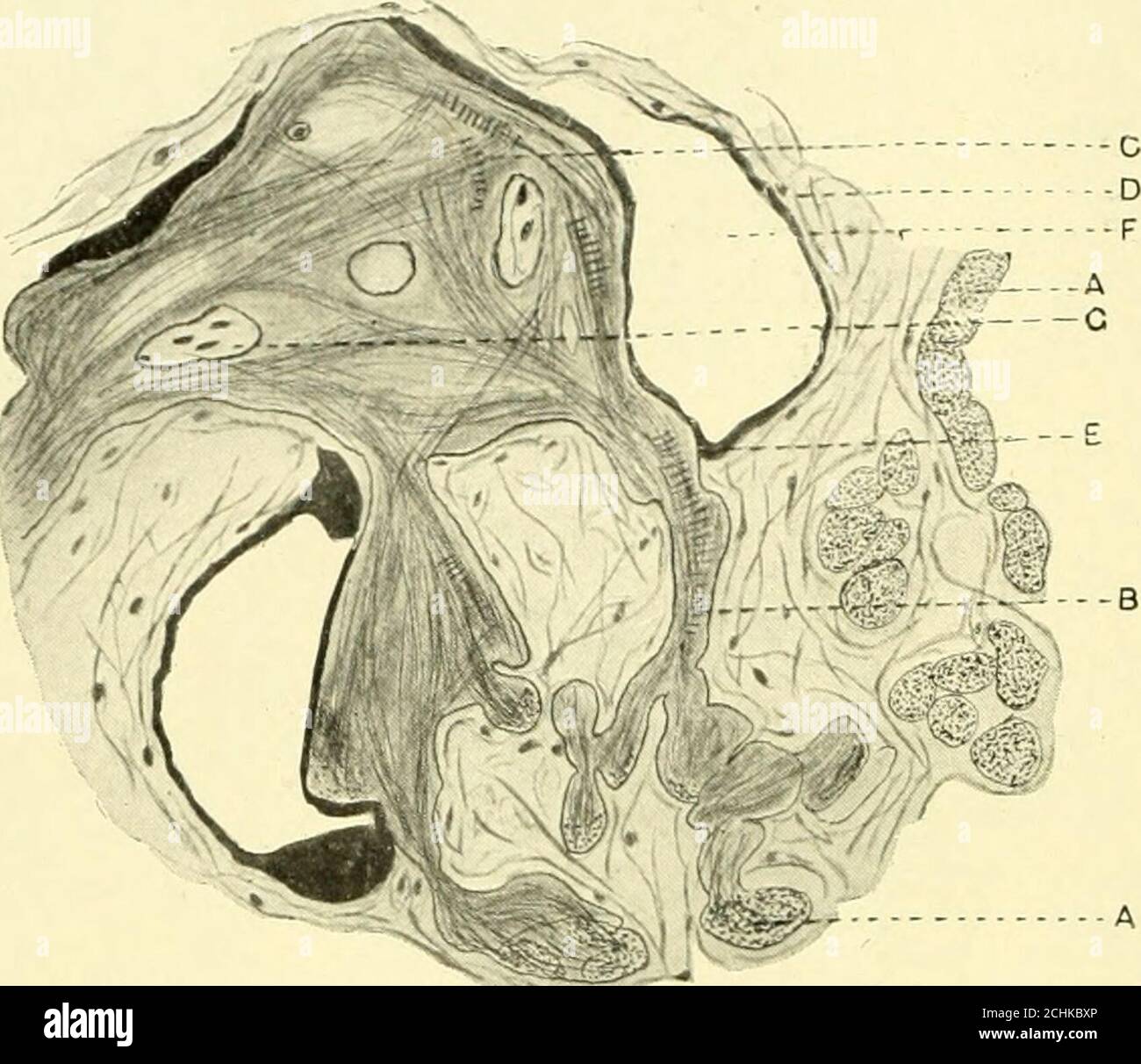 . The American journal of anatomy . Fig. 4 Camera lucida drawing; section of ventricular myocardium, beef heart.A and B, Purkinje fasciculi; C, injection material within connective tissue sheath;D, cardiac muscle fibers; E, fasciculus of heart muscle fibers in which fiber A ter-minates. X 275. Point A shows the auricular muscle fibers cut in cross section.From these, bundles of fibrillae pass off to enter a point of unionfor many such fibril fasciculi, which place Tawara has called anode. In this nodal point the fibrils are seen as confused strandscoursing in many different directions. The cle Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-american-journal-of-anatomy-fig-4-camera-lucida-drawing-section-of-ventricular-myocardium-beef-hearta-and-b-purkinje-fasciculi-c-injection-material-within-connective-tissue-sheathd-cardiac-muscle-fibers-e-fasciculus-of-heart-muscle-fibers-in-which-fiber-a-ter-minates-x-275-point-a-shows-the-auricular-muscle-fibers-cut-in-cross-sectionfrom-these-bundles-of-fibrillae-pass-off-to-enter-a-point-of-unionfor-many-such-fibril-fasciculi-which-place-tawara-has-called-anode-in-this-nodal-point-the-fibrils-are-seen-as-confused-strandscoursing-in-many-different-directions-the-cle-image372293342.html
. The American journal of anatomy . Fig. 4 Camera lucida drawing; section of ventricular myocardium, beef heart.A and B, Purkinje fasciculi; C, injection material within connective tissue sheath;D, cardiac muscle fibers; E, fasciculus of heart muscle fibers in which fiber A ter-minates. X 275. Point A shows the auricular muscle fibers cut in cross section.From these, bundles of fibrillae pass off to enter a point of unionfor many such fibril fasciculi, which place Tawara has called anode. In this nodal point the fibrils are seen as confused strandscoursing in many different directions. The cle Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-american-journal-of-anatomy-fig-4-camera-lucida-drawing-section-of-ventricular-myocardium-beef-hearta-and-b-purkinje-fasciculi-c-injection-material-within-connective-tissue-sheathd-cardiac-muscle-fibers-e-fasciculus-of-heart-muscle-fibers-in-which-fiber-a-ter-minates-x-275-point-a-shows-the-auricular-muscle-fibers-cut-in-cross-sectionfrom-these-bundles-of-fibrillae-pass-off-to-enter-a-point-of-unionfor-many-such-fibril-fasciculi-which-place-tawara-has-called-anode-in-this-nodal-point-the-fibrils-are-seen-as-confused-strandscoursing-in-many-different-directions-the-cle-image372293342.htmlRM2CHKBXP–. The American journal of anatomy . Fig. 4 Camera lucida drawing; section of ventricular myocardium, beef heart.A and B, Purkinje fasciculi; C, injection material within connective tissue sheath;D, cardiac muscle fibers; E, fasciculus of heart muscle fibers in which fiber A ter-minates. X 275. Point A shows the auricular muscle fibers cut in cross section.From these, bundles of fibrillae pass off to enter a point of unionfor many such fibril fasciculi, which place Tawara has called anode. In this nodal point the fibrils are seen as confused strandscoursing in many different directions. The cle
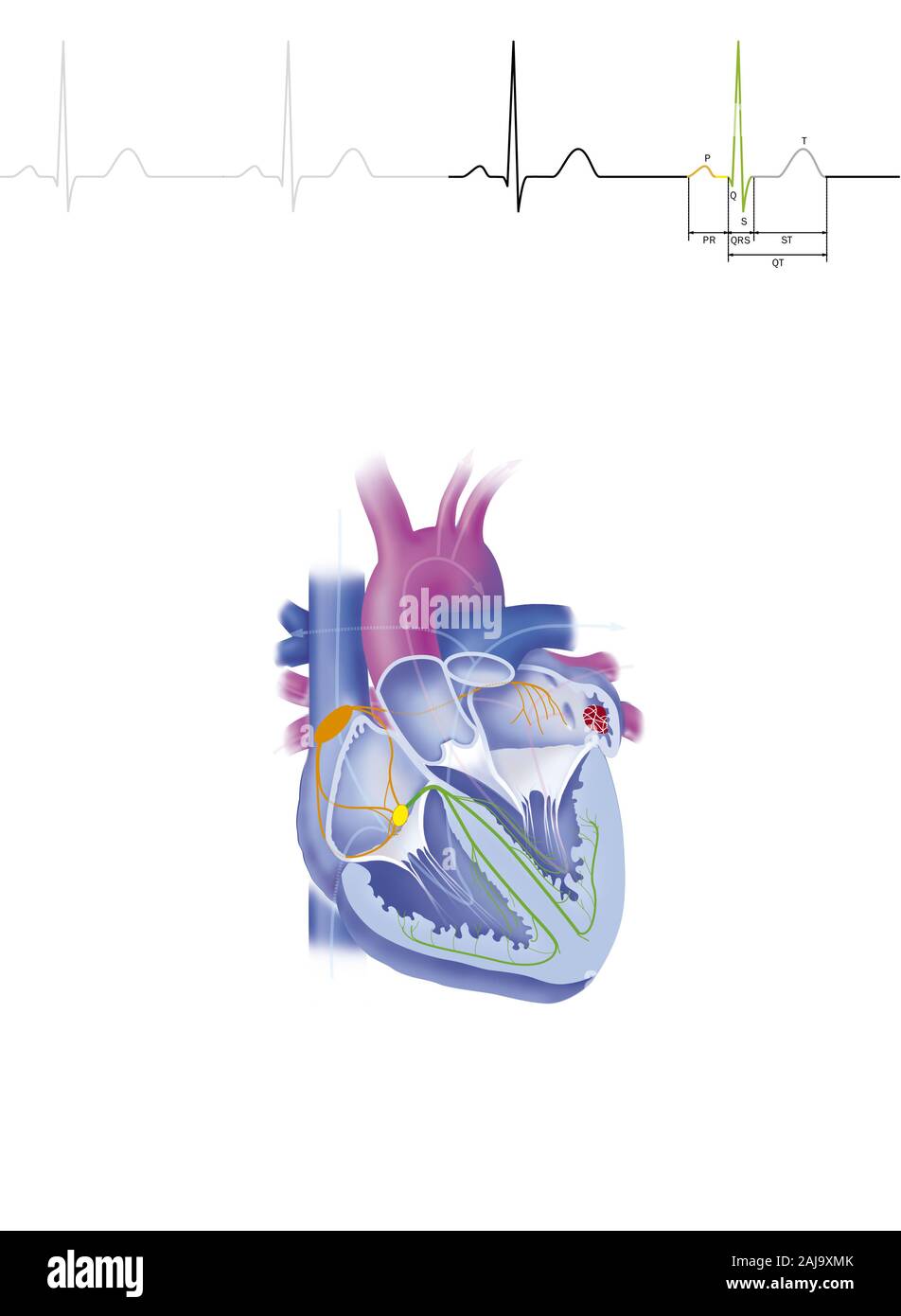 Atrial fibrillation Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/atrial-fibrillation-image338279331.html
Atrial fibrillation Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/atrial-fibrillation-image338279331.htmlRM2AJ9XMK–Atrial fibrillation
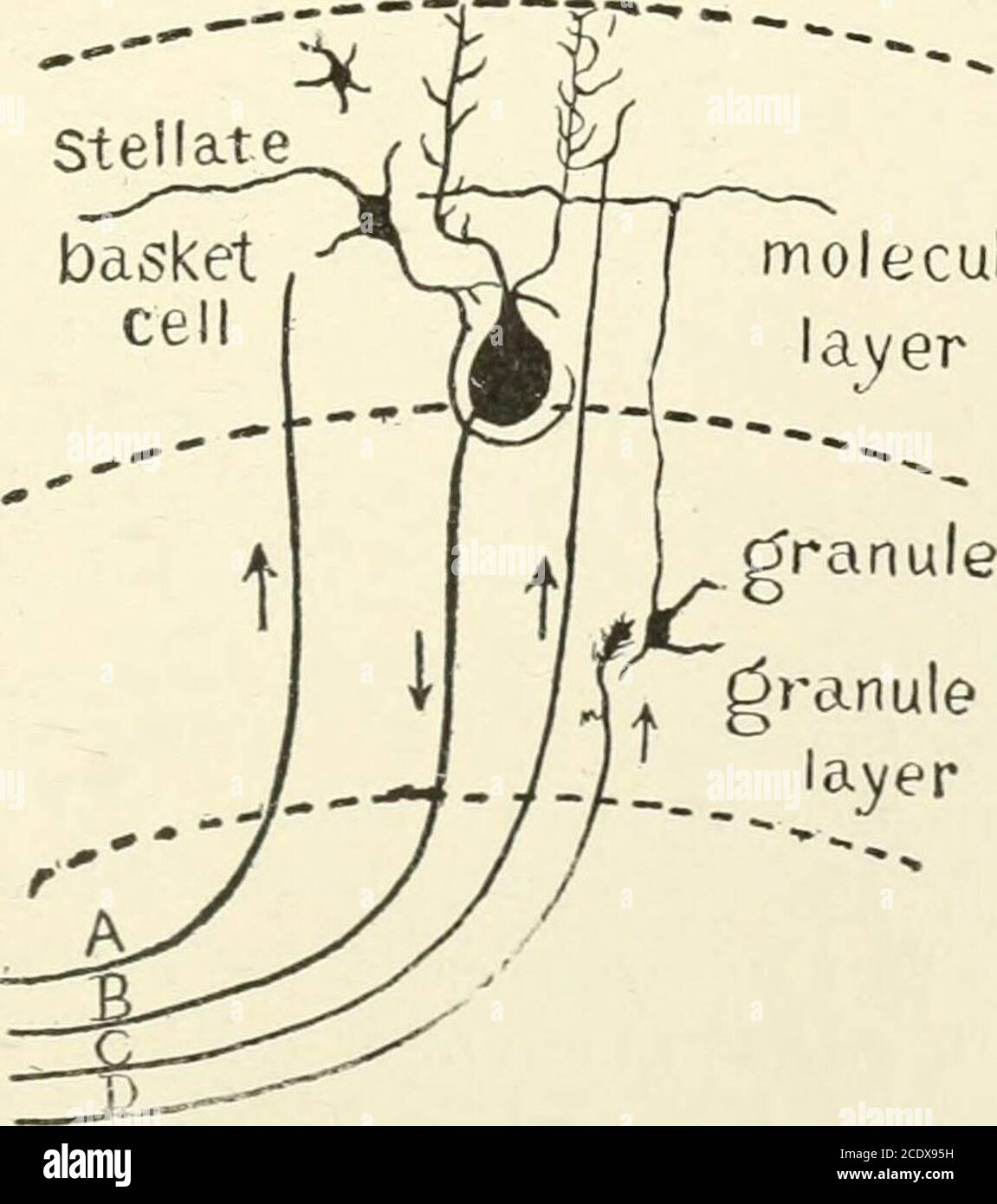 . Kirkes' handbook of physiology . Fig. 394.—Transverse Section Through a Cerebellar Folium (after Kolliker). Treated by theGolgi method. P, Axone of cell of Purkinje; F, moss fibers; K and K, fibers from white core offolium ending in molecular layer in conection with the dendrites of the cells of Purkinje; M,simple cell of the molecular layer; GR, granule cell; GR1, axones of granule cells in molecular layercut transversely; M, basket cells; ZK, basket work around the cells of Purkinje; GL, neurogliacell; N, axone of an association cell. Stellate molecularlayer. Fig. 395.—A, Afferent fiber to Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/kirkes-handbook-of-physiology-fig-394transverse-section-through-a-cerebellar-folium-after-kolliker-treated-by-thegolgi-method-p-axone-of-cell-of-purkinje-f-moss-fibers-k-and-k-fibers-from-white-core-offolium-ending-in-molecular-layer-in-conection-with-the-dendrites-of-the-cells-of-purkinje-msimple-cell-of-the-molecular-layer-gr-granule-cell-gr1-axones-of-granule-cells-in-molecular-layercut-transversely-m-basket-cells-zk-basket-work-around-the-cells-of-purkinje-gl-neurogliacell-n-axone-of-an-association-cell-stellate-molecularlayer-fig-395a-afferent-fiber-to-image369986221.html
. Kirkes' handbook of physiology . Fig. 394.—Transverse Section Through a Cerebellar Folium (after Kolliker). Treated by theGolgi method. P, Axone of cell of Purkinje; F, moss fibers; K and K, fibers from white core offolium ending in molecular layer in conection with the dendrites of the cells of Purkinje; M,simple cell of the molecular layer; GR, granule cell; GR1, axones of granule cells in molecular layercut transversely; M, basket cells; ZK, basket work around the cells of Purkinje; GL, neurogliacell; N, axone of an association cell. Stellate molecularlayer. Fig. 395.—A, Afferent fiber to Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/kirkes-handbook-of-physiology-fig-394transverse-section-through-a-cerebellar-folium-after-kolliker-treated-by-thegolgi-method-p-axone-of-cell-of-purkinje-f-moss-fibers-k-and-k-fibers-from-white-core-offolium-ending-in-molecular-layer-in-conection-with-the-dendrites-of-the-cells-of-purkinje-msimple-cell-of-the-molecular-layer-gr-granule-cell-gr1-axones-of-granule-cells-in-molecular-layercut-transversely-m-basket-cells-zk-basket-work-around-the-cells-of-purkinje-gl-neurogliacell-n-axone-of-an-association-cell-stellate-molecularlayer-fig-395a-afferent-fiber-to-image369986221.htmlRM2CDX95H–. Kirkes' handbook of physiology . Fig. 394.—Transverse Section Through a Cerebellar Folium (after Kolliker). Treated by theGolgi method. P, Axone of cell of Purkinje; F, moss fibers; K and K, fibers from white core offolium ending in molecular layer in conection with the dendrites of the cells of Purkinje; M,simple cell of the molecular layer; GR, granule cell; GR1, axones of granule cells in molecular layercut transversely; M, basket cells; ZK, basket work around the cells of Purkinje; GL, neurogliacell; N, axone of an association cell. Stellate molecularlayer. Fig. 395.—A, Afferent fiber to
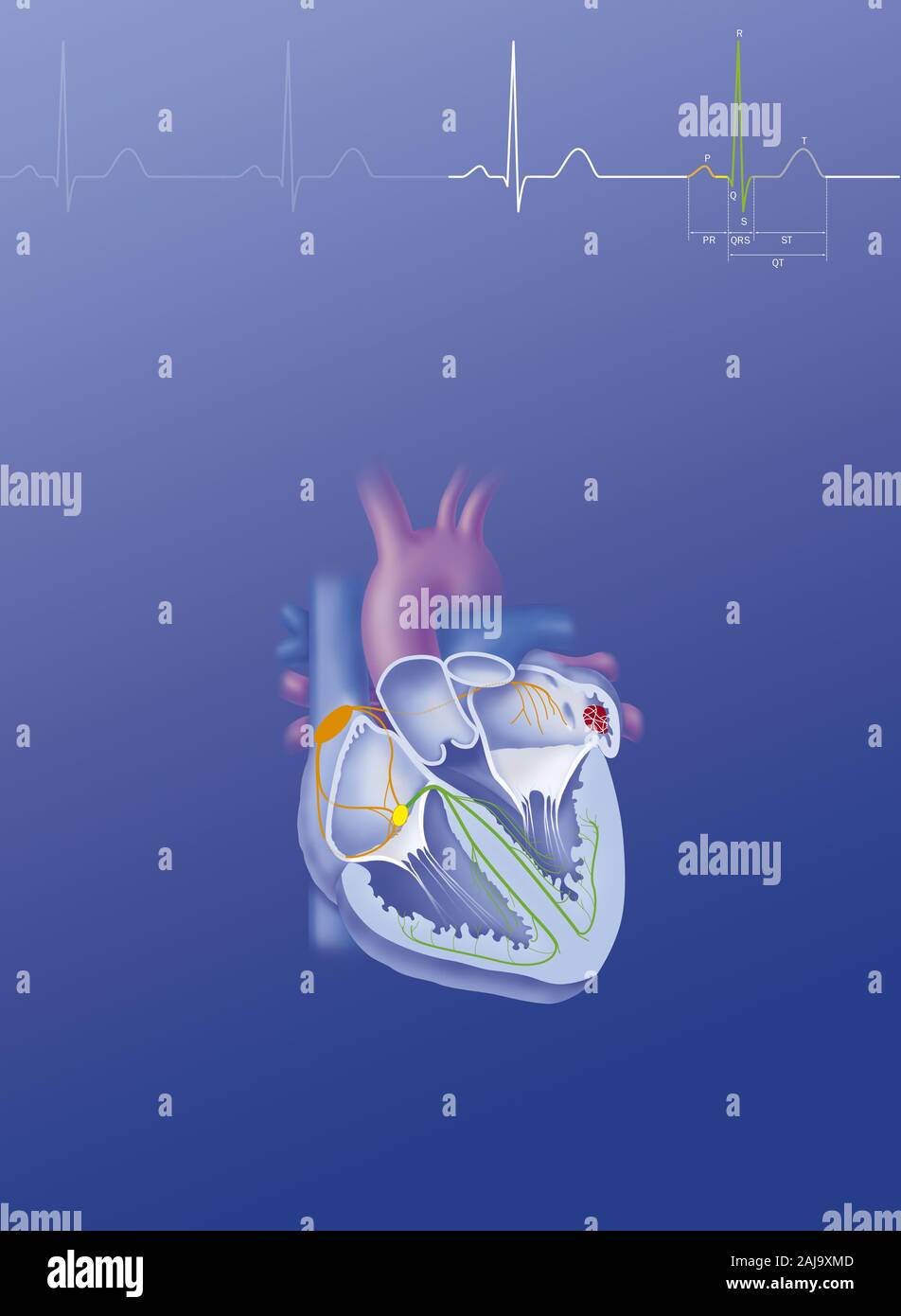 Atrial fibrillation Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/atrial-fibrillation-image338279325.html
Atrial fibrillation Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/atrial-fibrillation-image338279325.htmlRM2AJ9XMD–Atrial fibrillation
 . The cyclopædia of anatomy and physiology. Anatomy; Physiology; Zoology. SYMPATHETIC NERVE. 433 organic nerve fibres. According to Purkinje *, the ganglionic nerve-fibres are much finer than those belonging to the cerebro-spinal system or animal fibres. He describes the latter as containing two substances,—an outer, which runs in the form of a tube through the elementary fibre immediately within its sheath, and an inner, which occupies the hollow in- terior of the former. The tubular sheaths of the elementary fibres of the ganglionic system contain, on the other hand, no double substance ; th Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-cyclopdia-of-anatomy-and-physiology-anatomy-physiology-zoology-sympathetic-nerve-433-organic-nerve-fibres-according-to-purkinje-the-ganglionic-nerve-fibres-are-much-finer-than-those-belonging-to-the-cerebro-spinal-system-or-animal-fibres-he-describes-the-latter-as-containing-two-substancesan-outer-which-runs-in-the-form-of-a-tube-through-the-elementary-fibre-immediately-within-its-sheath-and-an-inner-which-occupies-the-hollow-in-terior-of-the-former-the-tubular-sheaths-of-the-elementary-fibres-of-the-ganglionic-system-contain-on-the-other-hand-no-double-substance-th-image231840067.html
. The cyclopædia of anatomy and physiology. Anatomy; Physiology; Zoology. SYMPATHETIC NERVE. 433 organic nerve fibres. According to Purkinje *, the ganglionic nerve-fibres are much finer than those belonging to the cerebro-spinal system or animal fibres. He describes the latter as containing two substances,—an outer, which runs in the form of a tube through the elementary fibre immediately within its sheath, and an inner, which occupies the hollow in- terior of the former. The tubular sheaths of the elementary fibres of the ganglionic system contain, on the other hand, no double substance ; th Stock Photohttps://www.alamy.com/image-license-details/?v=1https://www.alamy.com/the-cyclopdia-of-anatomy-and-physiology-anatomy-physiology-zoology-sympathetic-nerve-433-organic-nerve-fibres-according-to-purkinje-the-ganglionic-nerve-fibres-are-much-finer-than-those-belonging-to-the-cerebro-spinal-system-or-animal-fibres-he-describes-the-latter-as-containing-two-substancesan-outer-which-runs-in-the-form-of-a-tube-through-the-elementary-fibre-immediately-within-its-sheath-and-an-inner-which-occupies-the-hollow-in-terior-of-the-former-the-tubular-sheaths-of-the-elementary-fibres-of-the-ganglionic-system-contain-on-the-other-hand-no-double-substance-th-image231840067.htmlRMRD56AB–. The cyclopædia of anatomy and physiology. Anatomy; Physiology; Zoology. SYMPATHETIC NERVE. 433 organic nerve fibres. According to Purkinje *, the ganglionic nerve-fibres are much finer than those belonging to the cerebro-spinal system or animal fibres. He describes the latter as containing two substances,—an outer, which runs in the form of a tube through the elementary fibre immediately within its sheath, and an inner, which occupies the hollow in- terior of the former. The tubular sheaths of the elementary fibres of the ganglionic system contain, on the other hand, no double substance ; th