. The structure and classification of birds . s fuse4anteriorly with the walls of the.skull. The nostrils are continuedforward by a groove precisely likethat of Scopus and Gancroma. Inthe palatine bones the fusion of theinternal laminae to form a mediankeel behind the interparietal spaceis precisely like Scopus; so, too, isthe lateral angle of these bones (see p. 422). There is a firmsynostosis between the furcula and the carina sterni. Cervical vertebrae 7-13 have, as in most other Herodiones(excluding, however, the supposed ally of BalcBniceps, Scopus),a ventral catapophysial canal. The fami
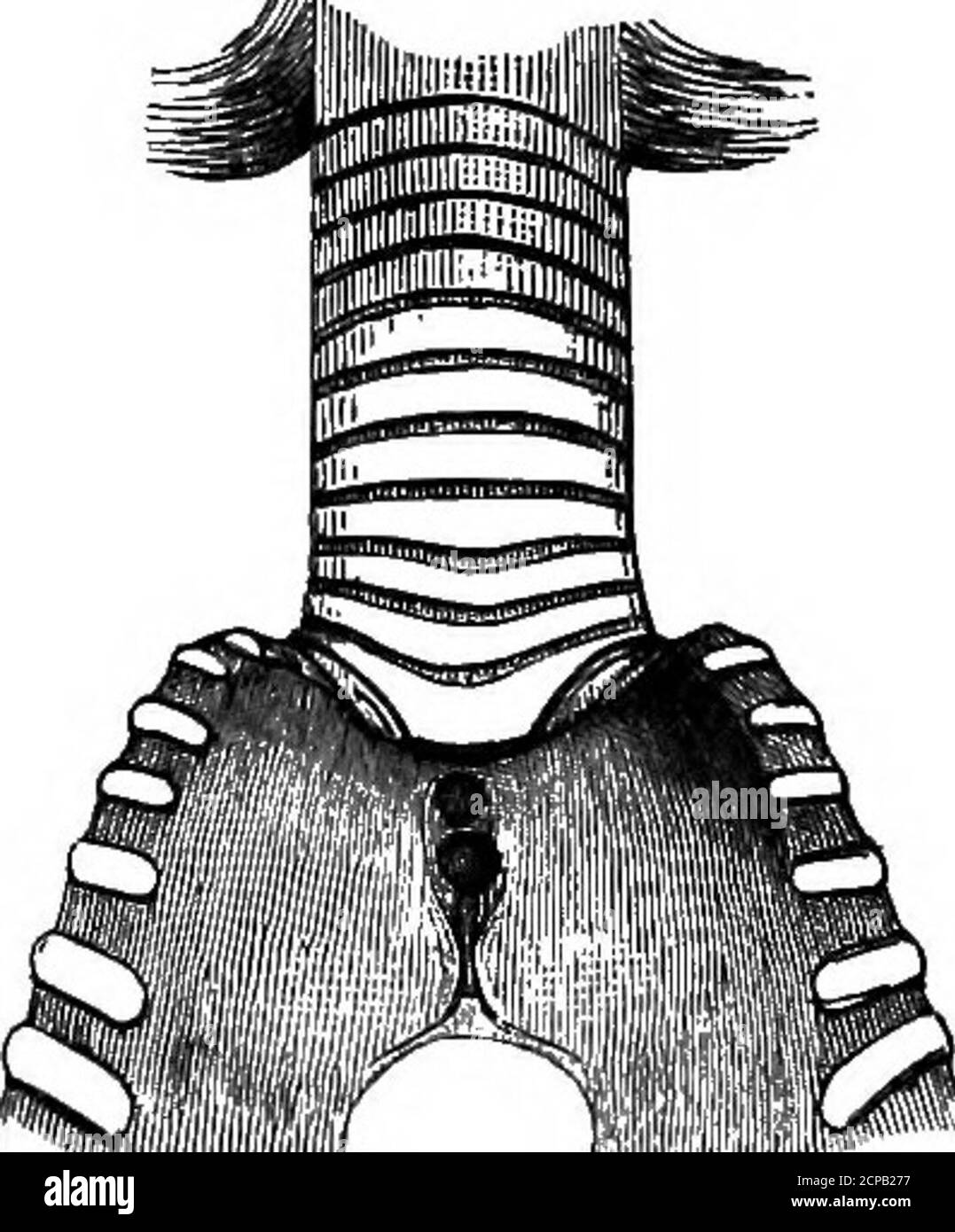
Image details
Contributor:
Reading Room 2020 / Alamy Stock PhotoImage ID:
2CPB277File size:
7.1 MB (311 KB Compressed download)Releases:
Model - no | Property - noDo I need a release?Dimensions:
1439 x 1736 px | 24.4 x 29.4 cm | 9.6 x 11.6 inches | 150dpiMore information:
This image could have imperfections as it’s either historical or reportage.
. The structure and classification of birds . s fuse4anteriorly with the walls of the.skull. The nostrils are continuedforward by a groove precisely likethat of Scopus and Gancroma. Inthe palatine bones the fusion of theinternal laminae to form a mediankeel behind the interparietal spaceis precisely like Scopus; so, too, isthe lateral angle of these bones (see p. 422). There is a firmsynostosis between the furcula and the carina sterni. Cervical vertebrae 7-13 have, as in most other Herodiones(excluding, however, the supposed ally of BalcBniceps, Scopus), a ventral catapophysial canal. The family Plataleidse includes not only the spoonbillsbut the ibises. The name Hemiglottides was applied byNiTZSCH to the group on account of the surprising small-ness of their tongues. The pterylosis is exactly as in the storks.^ The rectrices • According to Nitzsoh It appeared to me (in Platalea rosea) to be morelike that of Tantalus loculator, in that the hinder part of the spinal tract wasnot bifid, but continuously though sparsely feathered.. Fig. 205.—Stkinx of Balm-niceps, aeransed to displayPessulus and MembeanaTympanifohmis (afteb Bed-daed). HERODIONES 435 ;are twelve. The oil gland of Plaialea leucorodia has three■distinct orifices on each half, that of Ibis only one. Thelong downwardly bent bill of the ibises distinguishes themfrom the storks and suggests Nuvienius. Nitzsch, indeed, regarded the birds as intermediate between the two groupsrepresented by these types. The tensores patagii have always a biceps slip running tothe tendon of the longus, and there is a patagial fan. In Ibis cethiopica the tendon of the tensor brevis issimple and rather diffuse. In Eudocimus ruber and G. mela-nopis the tendon gives off a distinct wristward slip, while thepatagial fan is formed of two rather separate strands, withthe posterior of which, rather high up, the wristward slipfuses in Geronticiis melanopis. In Platalea the muscle and its tendons are much thesame, but the brevis is ve