. Text book of zoology. Zoology. Vertehrata. 353 Segmentation of the ovum ia total in some of the Vertebrata—AmphioxuSj Cyclostomi, Ganoidei, Amphibia (with the exception of Coeoilia and several others), and most Mammalia; in others, in which the egg is large, segmentation is partial (Selachii, Teleostei, Eeptilia, Aves, Monotrema). As in the lower animals a gastrula is formed, Amphioxus offering the simplest instance (see p. 43), the formation in others being more complicated (pp. 43-45) ; the mode of gastrula formation in Mammalia is not yet fully elucidated. Most Vertebrate embryos are for
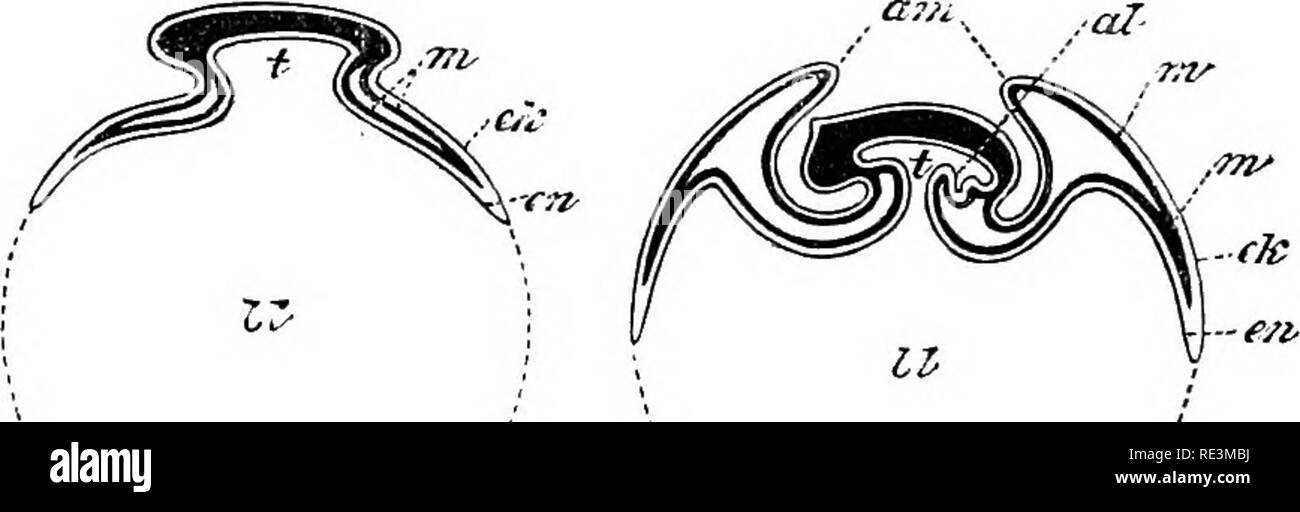
Image details
Contributor:
The Book Worm / Alamy Stock PhotoImage ID:
RE3MBJFile size:
7.1 MB (171.5 KB Compressed download)Releases:
Model - no | Property - noDo I need a release?Dimensions:
2773 x 901 px | 23.5 x 7.6 cm | 9.2 x 3 inches | 300dpiMore information:
This image is a public domain image, which means either that copyright has expired in the image or the copyright holder has waived their copyright. Alamy charges you a fee for access to the high resolution copy of the image.
This image could have imperfections as it’s either historical or reportage.
. Text book of zoology. Zoology. Vertehrata. 353 Segmentation of the ovum ia total in some of the Vertebrata—AmphioxuSj Cyclostomi, Ganoidei, Amphibia (with the exception of Coeoilia and several others), and most Mammalia; in others, in which the egg is large, segmentation is partial (Selachii, Teleostei, Eeptilia, Aves, Monotrema). As in the lower animals a gastrula is formed, Amphioxus offering the simplest instance (see p. 43), the formation in others being more complicated (pp. 43-45) ; the mode of gastrula formation in Mammalia is not yet fully elucidated. Most Vertebrate embryos are for a long time provided with a yolk-sac {see p. 49), which attains a huge size in some {e.g., the Selachians), but has usually vanished or is no longer visible when the animal is born {i.e., leaves the egg-shell or the body of the parent.) In Reptilia, Aves, and Mammalia (the amniote Vertebrata), certain peculiar conditions may be observed: the embryo is surrounded by several embryonic membranes, which develop as special outgrowths of the young animal. These are embryonic organs and are thrown off at birth. In the Hen's egg, at a very early stage of development, a fold, consisting of epiblast and the outer layer of mesoblast, is formed round that portion which will develop into the embiyo itself, as distinct from the yolk-sac portion. This fold gi-adually gi-ows round the whole embiyo, its walls meet and fuse, and thus a cavity is formed above, limited by the inner layer of the coalesced fold.. This inner layer is now called the amnion whilst the oiiter layer, which is. Please note that these images are extracted from scanned page images that may have been digitally enhanced for readability - coloration and appearance of these illustrations may not perfectly resemble the original work.. Boas, J. E. V. (Johan Erik Vesti), 1855-1935; Boas, J. E. V. (Johan Erik Vesti), 1855-1935. Lehrbuch der Zoologie. London, Sampson Low, Marston