Quick filters:
Page 1 of 6
Leaf adaxial side Stock Photos and Images

RF2T73J7H–Oak tree autumn dry brown leaf and branch isolated on white background. Adaxial surface or upper side of fall foliage.

RM2BMXA6B–Citrus rust mite (Phyllocoptruta oleivora) blister damage visible on the upper side of lemon leaves, Sicily, Italy

RF2HC061X–Alchemilla vulgaris, the common lady mantle, is an herbaceous perennial plant in Europe and Greenland
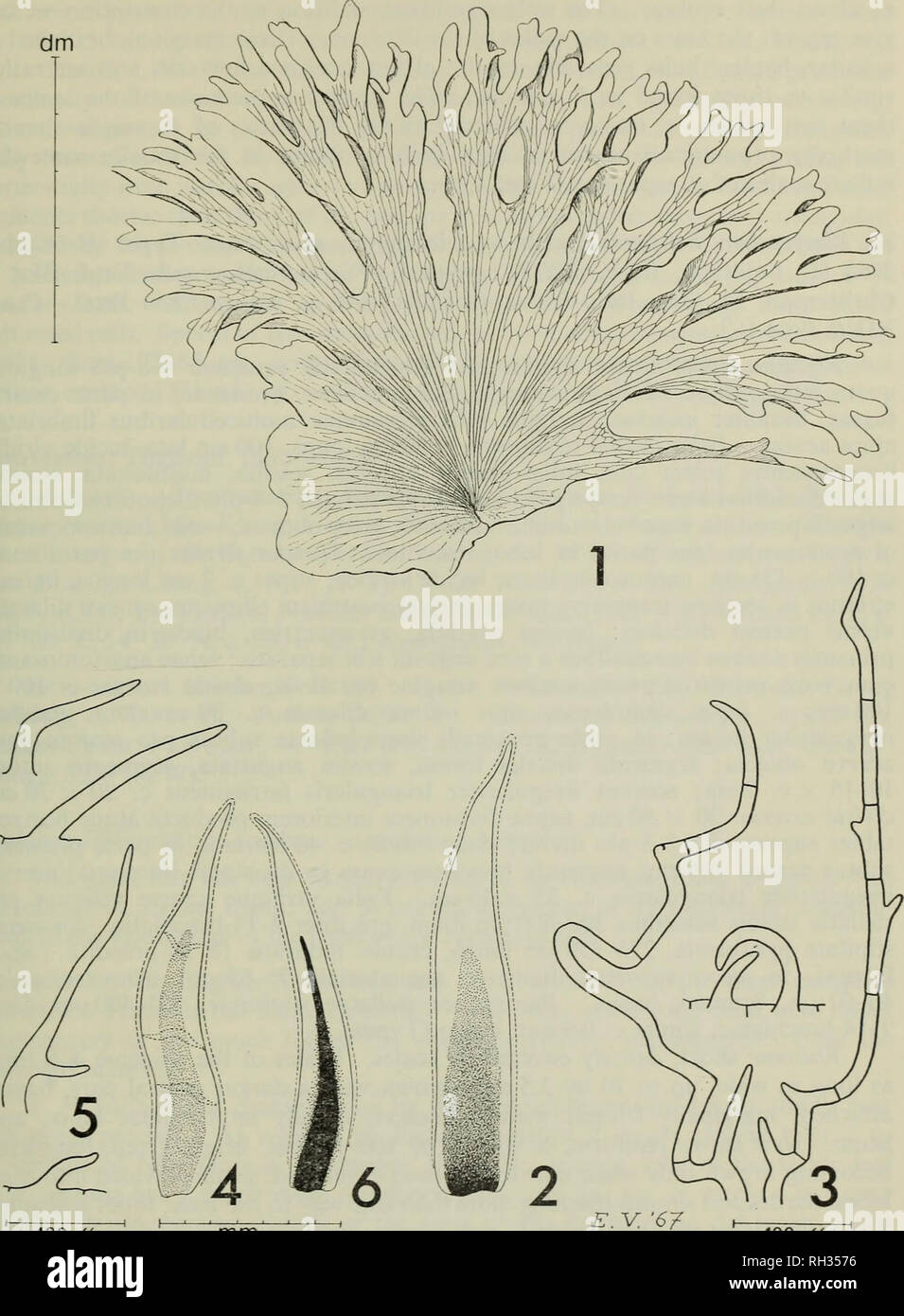
RMRH3576–. The British fern gazette. Ferns. NEW SPECIES OF PLATYCERIUM: DE JONCHEERE &HENNIPMAN 115. 100^ mm 100^ FIGURES 1 -6: 1 Platycerium holttumii (Hennipman 3520) sterile leaf (adaxial side), 2 scale of the rhizome, 3 hairs of the marginal area of the scale; 4 P. superbum (Gilbert NSW P-5789, NSW) scale of the rhizome, 5 hairs of the marginal area of the scale, 6 P. wandae (Docters van Leeuwen 10181, L) scale of the rhizome.. Please note that these images are extracted from scanned page images that may have been digitally enhanced for readability - coloration and appearance of these illustrat

RMRGJGR3–. Bulletin of the British Museum (Natural History) Botany. ALAN EDDY. Fig. 10 Sphagnum fimbriatwn Wilson. A, branch leaves; B, stem leaves; C, transverse section of branch leaf; D, adaxial surface of branch leaf; E, abaxial surface of branch leaf; F, lower lateral region of branch leaf, adaxial side; G, stem leaf tissue, upper mid-leaf; H, stem leaf tissue, lower mid-leaf; I, transverse section of stem (all drawn from Wager 1057). layers of thin-walled leucocysts, the majority of outer cells each having a large pore; internal cylinder yellowish to yellow-brown. Branch cortex strongly dimorphic
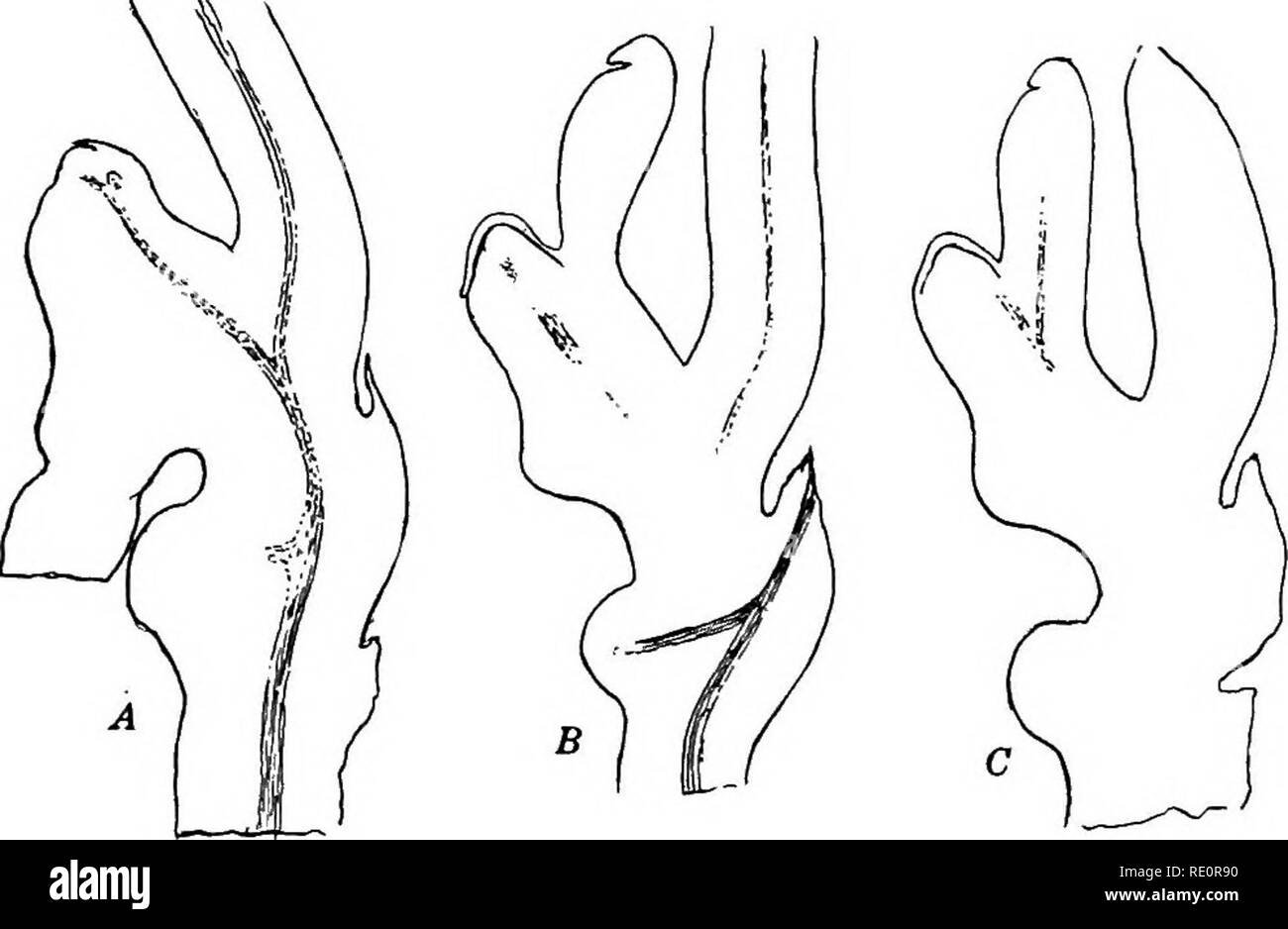
RMRE0R90–. The Eusporangiatae; the comparative morphology of the Ophioglossaceae and Marattiaceae. Ophioglossaceae; Marattiaceae. 80 THE OPHIOGLOSSALES The trace for the second leaf, the first functional one, is usually provided with a single undivided bundle passing through the petiole, but sometimes this divides into two, as it does in the cotyledon of Botrychium virginianum. Where a single bundle occurs in the petiole it occupies a nearly median position and is concentric in structure, although the phloem is somewhat less developed upon the adaxial side. The xylem consists of a large mass of trachei
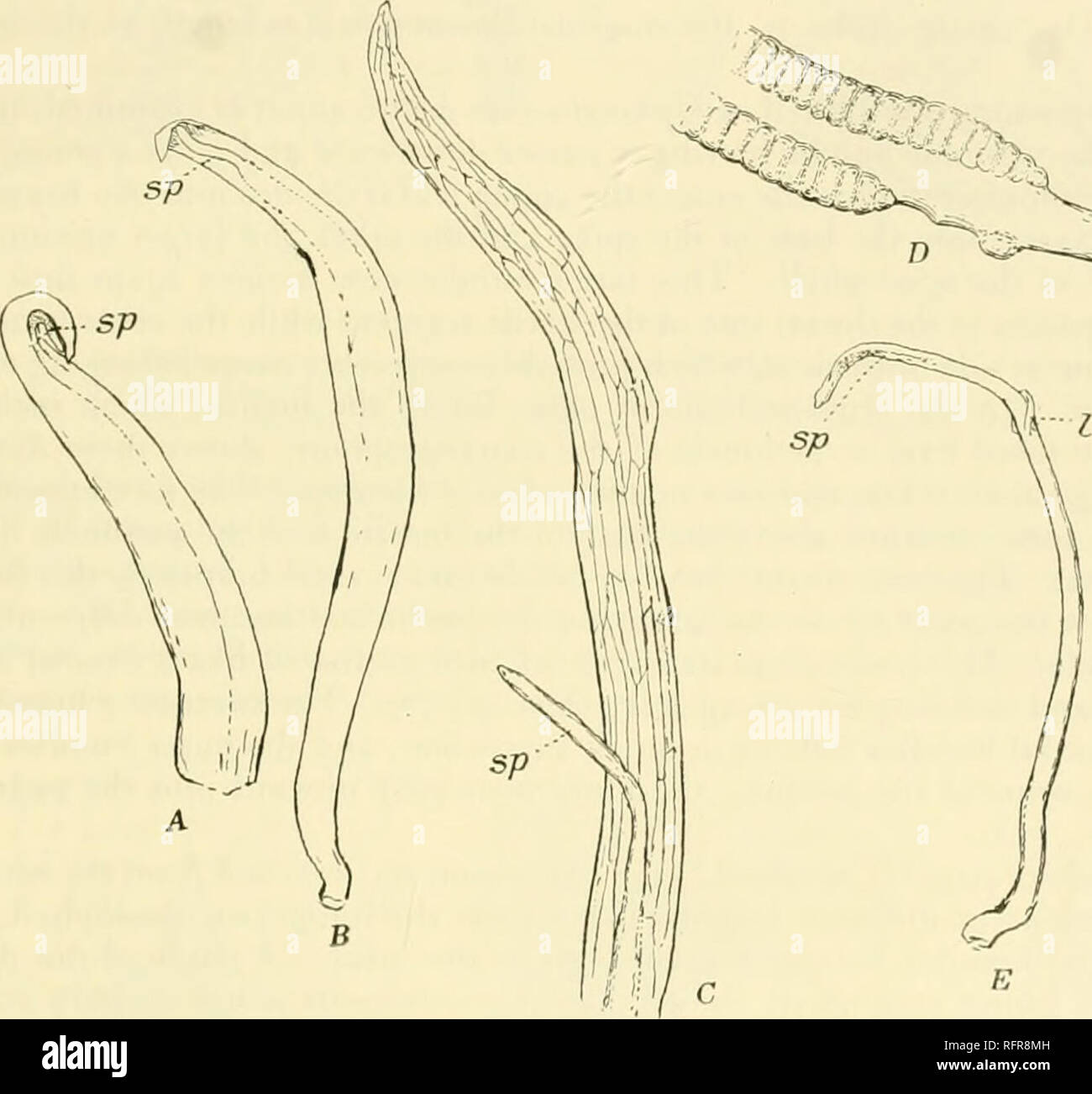
RMRFR8MH–. Carnegie Institution of Washington publication. THE ADULT SPOROPHYTE 111 0. moluccanum and 0. pendulum, and the conclusion that the young sporangiophore is an outgrowth of the sterile part of the leaf is the result of the subsequent rapid growth of the upper sterile portion of the leaf, which thus carries its apex far beyond the apex of the young spike. The young sporophyll in (). pendulum (fig. 64, E) resembles that of 0. moluc- canum, except that all the parts are much larger. The apex of the young sporangio- phore appears upon the adaxial side of the very broadly conical young sporophyll.

RF2R1996D–3d illustration of set rorippa palustris plant isolated on black background human's eye view
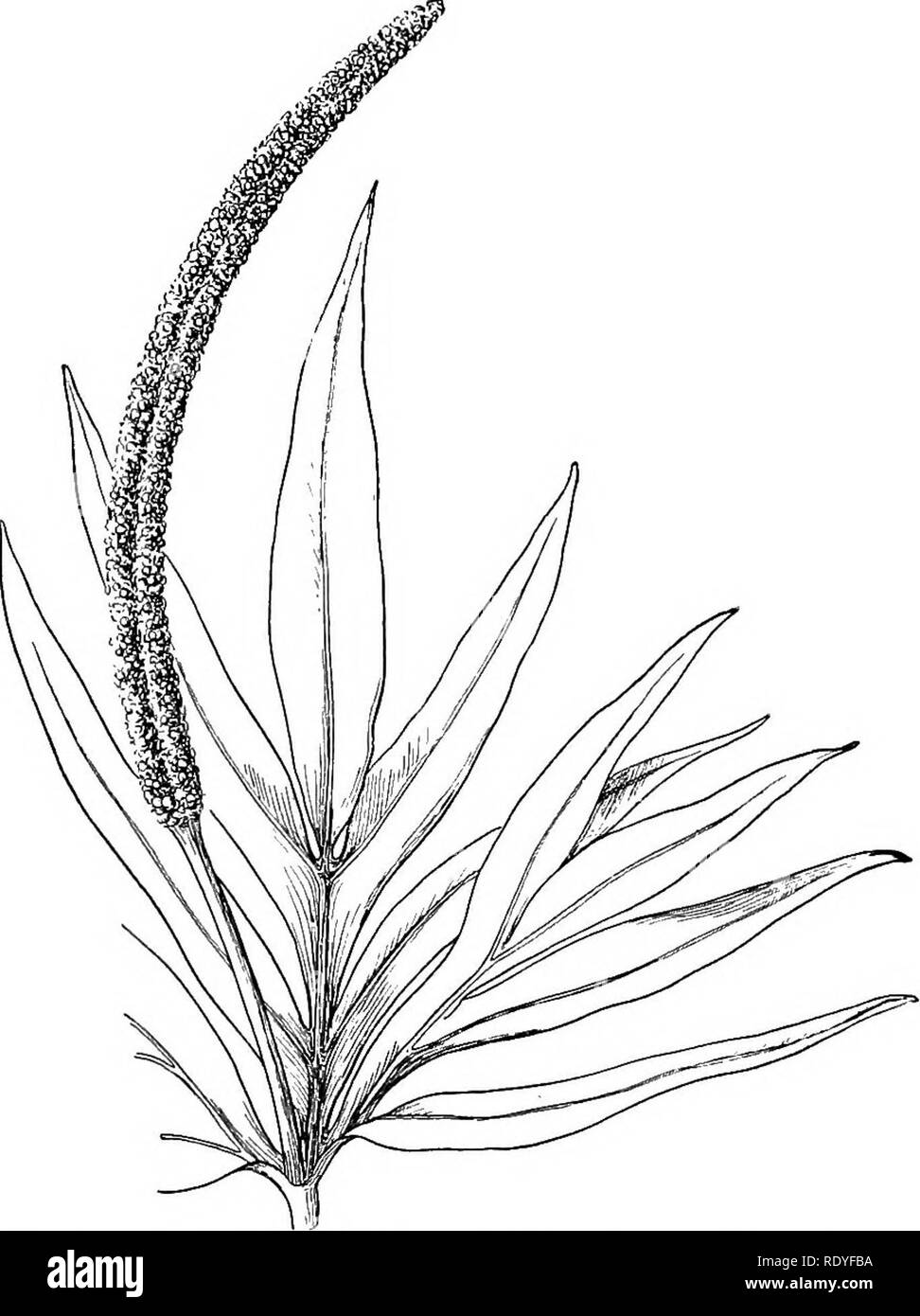
RMRDYFBA–. A textbook of botany for colleges and universities ... Botany. PTERIDOPHYTES 151 bordered pits, elements characteristic of gymnosperms (fig. 547), but not of pteridophytes. Fertile spike. — In Ophioglossum the fertile spike begins to appear very early in the history of the leaf. As it begins to project from the adaxial face of the young leaf, a superficial band of cells becomes differ-. FiG, 354. — General habit of Helminthostachys. — After Hooker. entiated on each side, from near the apex downwards. As the spike elongates, these two bands elongate and deepen, eventually giving rise to two c
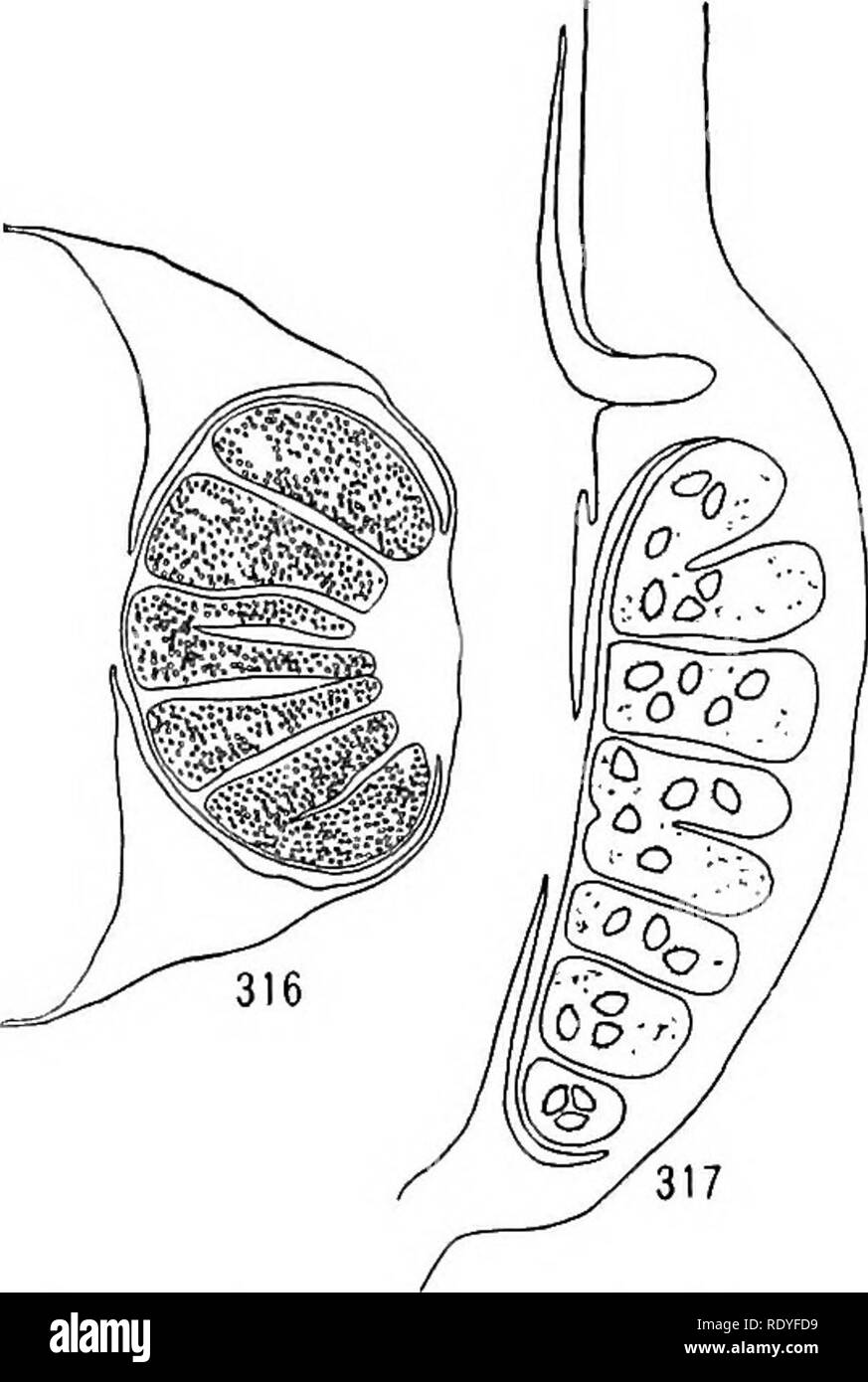
RMRDYFD9–. A textbook of botany for colleges and universities ... Botany. PTERIDOPHYTES 139 spiral, and every leaf is a sporophyll, either bearing a sporangium or traces of one. In this sense the whole sporophyte body is a strobilus. Each leaf is distincdy differentiated into sporangium and foliage regions (fig- 317)- The foliage portion of the leaf resembles a narrow grass blade, and contains four longitudinal series of air chambers. At the base of this blade, on the adaxial side, the ligule appears, socketed in a small pitiike depression. Below the ligule the sporangium region occurs, the sporangium
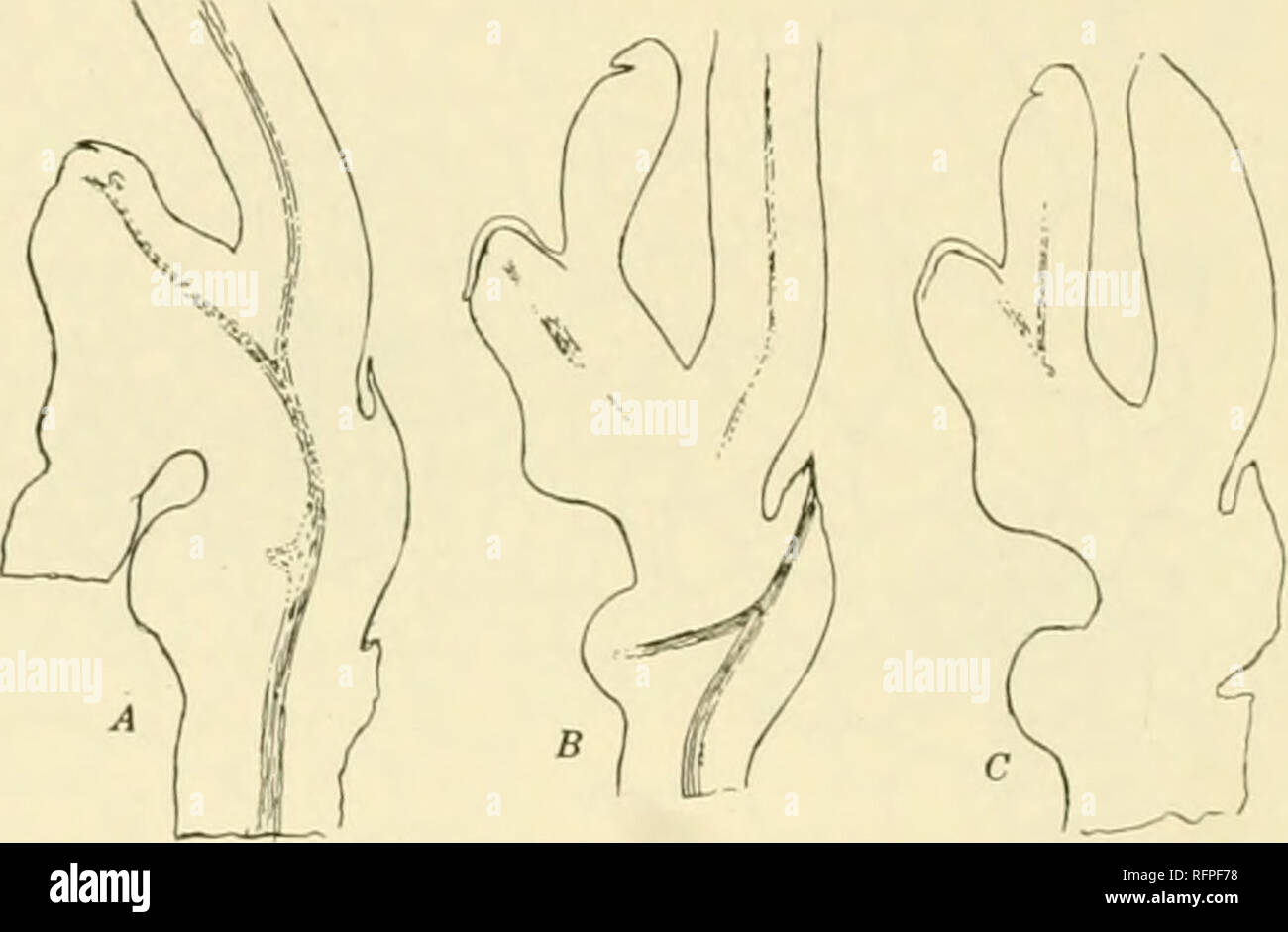
RMRFPF78–. Carnegie Institution of Washington publication. 80 THE OPHIOGLOSSALES rhe trace foi the second leaf, the Inst functional one, is usually provided with .1 single undivided bundle passing through rlu- petiole, hut sometimes this divides into two, as it does in the cotyledon of Botrychium virginianum. Where a single hunille occurs in the petiole it occupies a nearly nu-dian position and is concentric in structure, although the phloem is somewhat less developed upon the- adaxial side. I he xylem consists of a huge mass oftracheids surrounded by the phloem, which is reduced to about two rows of c
Search Results for Leaf adaxial side Stock Photos and Images (568)
Page 1 of 6